* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
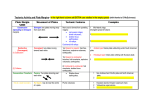
Plate Tectonics Aims: To understand the four different types of plate boundaries and the natural hazards associated with them. The Location of volcanoes and earthquakes around the world Volcanoes occur: •In narrow bands •Most often at destructive plate margins •Along constructive plate margins e.g. Mid Atlantic Ridge •They do not occur at collision margins and conservative margins. There is a concentration of volcanoes around the Pacific Ring of Fire Ext: Suggest a reason why there are no active volcanoes in Britain. Earthquakes occur: •In long narrow bands •In a dense ring around Pacific ocean •Down the entire length of the Mid-Atlantic ocean •Along all types of plate margin •Close to volcanoes •On land or underwater Earthquakes and volcanoes have a similar but not identical global distribution. Ext: What do you think continental drift is about Plate Tectonics Millions of years ago it is believed that the world was once one huge ‘super continent’ named Pangea Through the process of continental drift, the world became what we know today. Plate Boundaries The black indicates the position of the continents today. Each of the coloured parts are the ‘plates’. The plates move at different speeds and in different directions. This is because of the convection currents that operate underneath the earth. Around the pacific plate (green) is the ‘pacific ring of fire’ – many volcanoes and earthquakes are located here. Plate movement The diagram shows the different convection currents at work within the earth. Convection currents flow in different directions according to where the plate is. Constructive plate boundaries Constructive plate boundaries are caused when two plates move away from each other (diverge). When they move apart from each other a ‘gap’ is created. The gap is filled with hot, molten lava that solidifies when it reaches the surface (meeting either the sea or air). Land is therefore formed. Earthquakes and volcanoes are associated with constructive plate margins. Destructive Plate Margins At a destructive plate margin, the heavier oceanic crust slides under the lighter, less dense continental crust. This results in both volcanoes and earthquakes, due to land being lost (destroyed). Collision Plate Margins Collision plate margins occur where two continental crust plates meet. As they are the same density neither is able to slide under the other one. Therefore, fold mountains are created. Earthquakes are common at collision plate boundaries. Conservative Plate Margins Earthquakes are associated with conservative plate margins. They are caused by the friction as the plates rub next to each other. Copy and complete the table Plate Margin Example of Earthquake/ Plates volcano? Constructive Destructive Collision Conservative Ext: Why do only weak earthquakes occur at constructive margins? GCSE questions (contd) 1. What is the ‘Pacific Ring of Fire’? (2) 2. Briefly explain how volcanoes are created at a) Constructive and b) destructive plate margins (6) 3. Name one volcano from: North America, South America, Europe and Asia 4. What are plates? What causes them to move? 5. Give three differences between continental and oceanic crust Ext. Pages 210-211 will help you Answers Plate Margin Example of Earthquake/ Plates volcano? Eurasian plate/North Volcanoes and weak Constructive American earthquakes Destructive South American/Pacific Violent volcanoes and strong earthquakes Collision IndoAutralian/Eurasian Strong earthquakes Conservative North American/Pacific Strong earthquakes Homework Explain what the following words mean: plate, plate boundary/margin, mantle, oceanic crust, continental crust, collision zones, constructive margin, destructive margin, conservative margin, Pacific Ring of Fire, continental drift. Ext - Research a volcano or earthquake Useful website: www.bbc.co.uk/gcsebitesize