* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spread of the Cold War
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Germany wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
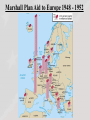
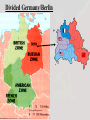
Topic: The Cold War (1945-1991) The United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) emerged as the two strongest powers in international affairs. Ideologically opposed, they challenged one another in a series of confrontations known as the Cold War. The costs of this prolonged contest weakened the USSR so that it collapsed due to internal upheavals as well as American pressure. The Cold War had social and political implications in the United States. Content Statement: The United States followed a policy of containment during the Cold War in response to the spread of communism. Expectations for Learning: Analyze the policy of containment the United States followed during the Cold War in response to the spread of communism. Truman Doctrine: Background • Greek Government vs Greek Communists • Truman requested that Congress provide $400,000,000 worth of aid to both the Greek and Turks to stave off communism in the region • Truman argued that a Communist victory in the Greek Civil War would endanger the political stability of Turkey, which would undermine the political stability of the Middle East Truman Doctrine: Background • This could not be allowed in light of the region’s immense strategic importance to U.S. national security Truman Doctrine – 1947 • The U.S. was compelled to assist “free peoples” in their struggles against “totalitarian regimes” because the spread of authoritarianism would “undermine the foundations of international peace and hence the security of the United States.” Truman Doctrine – 1947 • The Truman Doctrine committed the U.S. to actively offering assistance to preserve the political integrity of democratic nations when such an offer was deemed to be in the best interest of the U.S. Truman Doctrine: Legacy • The Truman Doctrine effectively reoriented U.S. foreign policy, away from withdrawal and isolation to one of possible intervention in faraway conflicts • It became the U.S. policy for decades Containment and the Truman Doctrine • The policy for the U.S. to provide military and economic aid to Greece and Turkey because they were threatened by Communism • Policy of Containment – Adopted by U.S. in 1947 – Keep communism within its existing boundaries and prevent further Soviet aggressive moves Marshall Plan 1948: Rebuild War-torn Europe “The U.S. should provide aid to all European nations that need it. This move is not against any country or doctrine, but against hunger, poverty, desperation, and chaos.” ~ George Marshall Secretary of State under President Truman Marshall Plan: Legacy • A great humanitarian effort • Secretary of State Marshall became the only military general ever to receive a Nobel Prize for peace • The Marshall Plan also institutionalized and legitimized the concept of U.S. foreign aid programs, which have become a integral part of U.S. foreign policy Marshall Plan Aid to Europe 1948 - 1952 The Problem of Germany • Split into 4 zones –U.S., Great Britain, France, and Soviet Union • Berlin also split into 4 zones –Surrounded by the Soviet Union zone of Germany Divided Germany/Berlin The Problem of Germany • Soviet Union –Eventually, they took control of East Germany and East Berlin –Forced their regime and communism on their new territories, even though Stalin promised free and democratic elections in these places Eastern European nations East Germany The Spread of Communism • Following WWII, the Soviets stayed in Eastern European countries after chasing Hitler back to Germany • The Soviets set up Communist governments in: –Poland –Hungary –Latvia –Bulgaria –Lithuania –Romania –Estonia The Spread of Communism • Stalin wanted a communist buffer • Communism threatened all of Europe Iron Curtain Berlin Blockade: June 24, 1948 – May 12, 1949 • The three western sections of Germany and Berlin and created a West German government and announced a new currency • Stalin responded by attempting to force the western allies out of Berlin altogether − He cut off rail and road access to the western side of the city and turned off electricity Berlin Airlift Begins: June 25, 1948 • The U.S. and Great Britain mounted a massive airlift to keep the western sectors supplied with the 5000 tons of food per day and fuel that the city needed…and chocolate for children Lt. Halvorsen dropping candy. He became known as the “candy bomber”. Berlin Airlift 277,264 flights and 1.5 million tons of aid Video Berlin Blockade Ends • Lasted 324 days • May 1949, Stalin cancels blockade • Germany divided after blockade cancelled – September, 1949 The Federal Republic of Germany, or West Germany was formally created – October 7, 1949 The German Democratic Republic, East Germany was set up by the Soviets Alliances Soon Formed • NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization –A military alliance of 28 North American and European countries An attack on one = An attack on all –The role of the organization is to safeguard the freedom and security of its member countries by political and military means Alliances Soon Formed • Warsaw Pact –An organization formed in 1955 comprising Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and the U.S.S.R., for collective defense under a joint military command Warsaw Pact • Alliance formed by the Soviet Union • Countered NATO • This increased fears during the Cold War Spread of the Communism: China • Communist Mao Zedong was victorious over Chiang Kai-shek, who was supported by the U.S. • Establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC) • The “fall” of mainland China to communism in 1949 led the U.S. to suspend diplomatic ties with the PRC for decades Mutually Assured Destruction Whoever shoots first, dies second. Spread of the Cold War: Proxy Wars • The policy of containment was the basis for U.S. involvement in the Korean and Vietnam wars • Mindful that a full-scale nuclear exchange would be a disaster for both sides, the superpowers fought each other through a variety of proxy wars in other places