* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit A: Biological Diversity
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
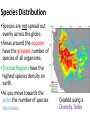
Unit A: Biological Diversity 1.1 Examining Diversity Pg. 8,9 Examining Diversity •Species – a group of organisms that have the same structure and can reproduce with one another •It is estimated that there are 30-100 million kinds of organisms today •Regardless of their uniqueness, all life forms share similar characteristics Understanding Biological Diversity •Biological diversity – refers to all the different types of organisms on Earth •Ecosystem – living (biotic) things interact with other living and nonliving (abiotic) things in a shared environment Diversity Within an Ecosystem •Population – members of a species that live in a specific area and share the same resources •Community – populations of different species living in the same area (the biotic components of an ecosystem) Diversity Within Species •Individuals within a species show variation Ex. The banded snail shows great genetic diversity •Some diversity is visible and some is not Ex. Blood type Species Distribution •Species are not spread out evenly across the globe. •Areas around the equator have the greatest number of species of all organisms. •Tropical Regions have the highest species density on earth. •As you move towards the poles the number of species decreases Created using a Diversity Index Classifying Biological Diversity • Carolus Linnaeus created a naming system based on the structure of organisms and they are named using Latin, their Genus and then species Ex. •Wolf = Canis lupus •Dog = Canis familiaris The Kingdoms •Scientists have been using the 5-Kingdom Classification system 1) Animalia 2) Plantae 3) Fungi (yeast, mould, mushrooms) 4) Protista (mostly single-celled organisms) 5) Monera (bacteria) Classification •Kingdom •Phylum •Class •Order •Family •Genus •Species Questions 1. Pg. 15 - Check & Reflect Questions #1 -3, 6 – 7, & 9 2. Diversity Index Worksheet 1.1 - Pg. 15 C&R Answers 1. Biological diversity describes the variety of species and ecosystems on Earth as well as the ecological processes of which they are part. 2.There are so many different kinds of organisms on Earth because the environment varies a great deal from place to place. This can cause evolutionary pressures. 3. Scientists use a five-kingdom classification system. Once an organism is placed into a kingdom, they are further divided into phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species. 6. A population describes the members of the same species that live in a specific area and share resources. A community describes the populations of different species that live in the same area and share resources. 7. Generally, there is greater diversity toward the equator because the climate (warmer, wetter, more stable) can support a greater variety of plants, which, in turn, support a greater variety of animals by providing food and shelter. 9. It is in our best interests to preserve biodiversity because no one is quite sure of what losing species or ecosystems may mean in the long term. May could food chain/web and ecosystem collapse. Section 1.2 – Interdependence 1. Read pages 16-19 2. Fill in the notes handout 3. Complete: •Pg. 19 C&R # 2, 3 (space on back of notes) Assignment - Pg. 19 C&R # 2, 3 2) A decreased population will mean that there are more resources available for those that are left. This will lead to less hunger/starvation in the population. If there are less hungry/starving animals around (a less dense population) there will also be a decreased spread of diseases and overall healthier population. 1.3 - Variation Within Species Stability of an ecosystem relies on the diversity of its species and interactions between species. The only reason these species survive is due to the complex relationships in which everything in the ecosystem supports everything else. This is known as____________________________ Healthy ecosystems have a great deal of biodiversity of species. But there is also a great deal of diversity within a species itself. Ex. Human Variations Variability - Variation of characteristics within a species. Variability and Survival Why is variation important? What advantage could it have for a species if its members have differing characteristics? Ex. See infoBIT pg. 20 - Coats of Many Colours As we have already seen not only is there a huge diversity in species but also in environments (differing environments create evolutionary pressures to create new species and variation). Species with greater variation among their members will have a greater chance of surviving in differing environments. Discovery Ed. Vid: Snakes – Variations and Characteristics Environmental variation and change does not always involve climate, it can also include: • Introduction of a new predator • Spread of a new disease • Introduction of a toxic substance • Loss of a food source In all cases variability within a species will help it to survive. How can the differences in coat colours for the foxes in the infoBIT example help them survive environmental changes? Discovery Ed. Vid: Insects Produce lots of Offspring Another aspect of species survival and variability is natural selection. Natural Selection - Gradual change (over generations) in a species' structure or behavior due to environmental stress and/or changes. Ex. Read pg.24 for further examples Read Section 1.3 in text (pg. 20-24) to fill in the remaining sections of your notes. Assignment 1. Read Section 1.3 2. Complete 1.3 Notes 3. Pg. 24 #3-5 Check & Reflect pg. 24 # 3-5 3. Changes related to climatic events, such as flooding or drought. Other examples may include: • the introduction of a new predator • the loss of a food supply • or the loss of a nesting or breeding site 4. Ex. Red foxes and banded snails are examples where colour variation in coats and shells would provide camouflage; Ex. variation in size and symmetry allowed individuals in the cliff swallow population to survive; Ex. variation in bacteria enables some to survive antibiotics and develop into “super bugs.” 5. If a population of sparrows were to inhabit a new island and the only food source were plants that produced large seeds, those birds with large beaks would be most likely to survive because they would be able to make use of the food source. Future generations of large-beaked sparrows on the island would likely be favored over smallbeaked birds.