* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RC circuit
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor plague wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
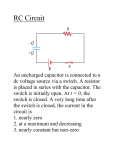
Chapter 21 Electric Current and DirectCurrent Circuits (Cont.) Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1161 1 Outline RC circuit Charging of an RC circuit Charge on a capacitor Current in an RC circuit Voltage across the resistor and capacitor Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1161 2 RC Circuits Dr. Jie Zou The simplest example of a RC circuit consists of a battery, a resistor, and a capacitor. The resistors limit the rate at which charge can flow, and an appreciable amount of time may be required before the capacitors become fully charged. PHY 1161 3 Charging of an RC Circuit Initially (t<0) the switch is open, and there is no current in the resistor or charge on the capacitor. At t=0, the switch is closed, and current begins to flow. The capacitor is being charged. As time goes on, the charge on the capacitor increases but the charging slows down. At t∞, the charge on the capacitor does not change with time and the current approaches zero. Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1161 4 Charge on the Capacitor The charge on the capacitor varies with time as follows: q(t) = C(1-e -t/), for t >= 0 Dr. Jie Zou = RC: the time constant of the RC circuit. At t = 0, q(0) = 0 At t, q(t) = C (charging complete). PHY 1161 5 Current in an RC Circuit The current in an RC circuit changes with time as follows: I(t) = (/R)e -t/, for t>= 0 Dr. Jie Zou At t = 0, I(0) = /R. The capacitor behaves like a short circuit. At t, I(t) = 0. The capacitor behaves like an open switch. PHY 1161 6 Voltage across the Resistor and the Capacitor Voltage across the resistor: VR = IR = e -t/. At t = 0, VR(0) = At t, VR(t) = 0 Voltage across the capacitor VC: VC = - VR = - e -t/ = (1- e At t = 0, VC (0) = 0 At t, VC (t) = Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1161 -t/) 7 Example 21-9 Charging a Capacitor A circuit consists of a 126- resistor, a 275- resistor, a 182F capacitor, a switch, and a 3.00V battery all connected in series. Initially, the capacitor is unchanged and the switch is open. At time t = 0 the switch is closed. (a) What charge will the capacitor have a long time after the switch is closed? (b) At what time will the charge on the capacitor be 80.0% of the value found in part (a)? Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1161 8 Homework #5 Chapter 21, P. 759, Problems: #79, 81 (Physics, Walker, 4th edition). Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1161 9











![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)