* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3: Elements and the Periodic Table
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
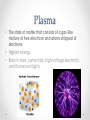
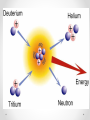
Chapter 3: Elements and the Periodic Table Section 5: Elements from Stardust Conditions in Stars • The sun, and many other stars, is made mostly of hydrogen. • Extremely high pressure and temperatures (15 million degrees Celsius) Plasma • The state of matter that consists of a gas-like mixture of free electrons and atoms stripped of electrons. • Highest energy • Exists in stars, comet tails, high-voltage electricity, and fluorescent lights. Checkpoint 1 • What is plasma? Checkpoint 1 • What is plasma? • The state of matter that consists of a gas-like mixture of free electrons and atoms stripped of electrons. Elements Form in Stars: Nuclear Fusion • Process in which two atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus, releasing huge amounts of energy. • Usually nuclei would repel each other (both positively charged), but are forced together in the high pressure environment of stars. • Creates heavier elements than it started with. o Different isotopes of hydrogen fuse, producing nuclei of helium, producing huge amounts of energy Fusion in the Sun • Hydrogen is the fuel that powers the sun o Scientists estimate that the sun has enough hydrogen to last another 5 billion years • As more helium builds up in the core, the sun’s temperature and volume change. • New fusion reactions occur o Two helium = beryllium o Helium + beryllium = carbon o Helium + carbon = oxygen • Stars the size of the sun don’t contain enough energy to produce elements heavier than oxygen • Eventually, shrinks and its elements blow away o Forms a nebula – cloudlike region of gases. Elements From Large Stars • Larger stars become hotter than the sun and have enough energy to produce heavier elements, like magnesium and silicon • In more massive stars, fusion continues until the core is almost all iron • In the final hours of the most massive stars, a supernova (huge explosion that breaks apart a massive star, producing temperatures up to 1 billion degrees Celsius) occurs o Creates the heaviest elements Everything is Stardust • Most astronomers agree that the matter in our solar system originally came from a gigantic supernova that occurred billions of years ago. Checkpoint 2 • What element does the fusion of a helium nucleus and a beryllium nucleus produce? Checkpoint 2 • What element does the fusion of a helium nucleus and a beryllium nucleus produce? • Carbon Post-lesson Quiz 1. Which state of matter has the highest energy of all? a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma Post-lesson Quiz 2. What do scientists call a huge explosion that breaks apart a massive star, producing temperatures up to 1 billion degrees Celsius? a. nebula b. supernova c. plasma d. fusion Post-lesson Quiz 3. What is it called when two nuclei are force together, creating a heavier element and producing large amounts of energy? a. nebula b. supernova c. plasma d. fusion Post-lesson Quiz 4. What do scientists call a cloud-like region of gases that can form at the end of a medium-sized star’s life? a. nebula b. supernova c. plasma d. fusion Post-lesson Quiz 5. Which of the following is not a place that you can find plasma? a. comet tails b. stars c. flashlights d. high-voltage electricity