* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System - Dayton Independent Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
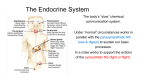
Endocrine System Endocrine System • Regulates overall metabolism, homeostasis, growth and reproduction • Glands – are organs that specialize in the secretion of substances needed by an organism • Hormones – are the secretions produced by the endocrine glands - released into the bloodstream Chemical Regulation: Effect on the body: • Hormones are specific to a target organ or tissue to stimulate or inhibit • Response of system is slower than nervous system because it must travel through the blood to reach target • Effect of hormone- last minutes to hours or even years Organs of the Endocrine System : GLAND HORMONE(S) FUNCTION IN THE BODY Pineal melatonin Daily sleep and wake cycles Pituitary (Master gland) TSH,ACTH, Growth Hormone, FSH, LH, Prolactin/ oxytocin, vasopressin Controls other glands Thyroid Thyroxine, calcitonin Overall body metabolism, blood calcium levels Organs of the Endocrine System: Parathyroid parathormone Thymus thymosin Pancreas Insulin, glucagon Calcium and phosphate metabolism Stimulate T-cells in immune system Blood sugar (glucose) Organs of the Endocrine System: Adrenal Epinephrine (adrenaline) & norepinephrine, cortisol, aldosterone Stimulate nervous system “fight or flight” mechanism, stress response, sodium balance Ovary/ testis Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone Sperm and egg production, secondary and primary sex characteristics Every cell in body Prostaglandin Secreted in response to injury and affect metabolic activities such as heart beat, blood pressure & immune response Feedback Mechanisms • Negative Feedback – is when an activity alters a condition in the body, and this triggers a series of events that reverses the altered condition Ex. Body temperature - When body temp. goes up, we sweat - When body temp. goes down, we shiver Ex. Blood sugar levels - When blood sugar goes up, insulin lowers blood sugar - When blood sugar goes down, glucagon raises blood sugar Feedback Mechanisms (continued) • Positive Feedback – is when a change initiates a response, and that response intensifies the original change Ex. Contractions of the uterus during childbirth Endocrine System Video Disorders • Diabetes – is a disease where a person cannot produce insulin - Inability of the body to store sugar as glycogen • Goiter – is enlargement of the thyroid gland caused by iodine deficiency