* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Parts and their Functions
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
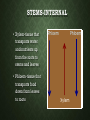
PLANT PHYSIOLOGY Essential Standard 3.00: Summarize Plant Anatomy OBJECTIVE 3.01 • Discuss biological terms used to describe plants. PLANT SCIENCES • Biology-the branch of science that deals with both plant and animal organisms and life processes • Zoology-the part of biology that deals with animals • Botany the part of biology that deals with plants PLANT SCIENCES • Applied plant sciences are based on the purposes for which the plants are grown • Agronomy-The science and practice of growing field crops such as cotton, wheat, tobacco, corn and soybeans. • Forestry-The science and practice of growing, managing and harvesting trees for building materials and other products. • Horticulture-The science and practice of growing, processing and marketing fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants LIFE CYCLES OF PLANTS • Annual-a plant that completes its life cycle in one year • Biennial-a plant that completes its life cycle in two years • Perennial-a plant that lives more than two years LEAF RETENTION • Deciduous-loses leaves during the dormant season • Evergreen-keeps leaves and remains green yearround MOISTURE IN PLANTS • Turgid-plant is swollen or filled with moisture • Wilted-plant is limp because it does not have enough moisture PLANT GROWTH • Dormant • A plant rest or grows very little • Response to an adverse condition SEASON CROP TYPE • Cool Season • Plants relish cool weather • Pansies grow best in spring or fall • Warm Season • Grow best in summer and early fall • Zinnia • Marigold • Vinca • Poinsettia OBJECTIVE 3.02 • Discuss the anatomy and functions of plants. LEAVES-EXTERNAL • Petiole-leaf stalk or part that connects the leaf to the stem • Blade-the large, flat part of the leaf • Midrib-the large center vein • Veins-the structural framework of the leaf • Margin-the edge of the leaf • Apex – Leaf Tip LEAVES-EXTERNAL LEAVES-INTERNAL • Upper and lower epidermis-skin of the leaf that prevents the loss of too much moisture • Stomates-small openings under the leaf for breathing or transpiration • Guard Cells-open and close stomates LEAVES-INTERNAL • Chloroplasts-small green particles that contain chlorophyll • gives leaves their green color • necessary for photosynthesis LEAVES-INTERNAL LEAVES-INTERNAL LEAVE-ADDITIONS • Sessile describes leaves without a petiole • Example zinnia • Bracts are modified leaves • Example poinsettia • Needles and scales are modified leaves • Example pine tree LEAVE-ADDITIONS • Glabrous leaves or stems have a smooth non-hairy feel • Example southern magnolia • Pubescent leaves or stems have a hairy feel • Example African violet LEAVE-FUNCTIONS • Respiration • converts sugars and starches into energy • Transpiration • release of water vapor from the leaves of plants • It also cools the plant FUNCTIONS OF LEAVES • Photosynthesis-manufactures food in green plants which is the beginning of the food chain for all living things • Photosynthesis is the process by which carbon dioxide and water in the presence of light are converted to sugar and oxygen • Video STEMS-EXTERNAL • Lenticels-breathing pores • Bud scale scars-show where terminal buds have been located • Leaf Scars-show where leaves were attached • Terminal bud-bud on the end of a stem • Axillary or lateral bud-bud on side of stem STEMS-INTERNAL • Xylem-tissue that transports water and nutrients up from the roots to stems and leaves • Phloem-tissue that transports food down from leaves to roots Phloem Phloem Xylem STEMS-INTERNAL • Cambium-thin, green, actively growing tissue located between bark and wood and produces all new stem cells • Bark-old inactive phloem • Heartwood-old inactive xylem • Sapwood-new active xylem STEMS-INTERNAL Bark Cambium Sapwood Heartwood STEMS-INTERNAL • Monocots-plant stems have vascular bundles that contain both xylem and phloem in each bundle • Produce one seed leaf (cotyledons) • examples: corn, grasses • Dicots-plant stems have the phloem layer and xylem layer separated by cambium • Produce two seed leaves (cotyledons) • example: trees STEMS-INTERNAL Monocot Dicot FUNCTIONS OF STEMS • Translocation-moves water and minerals from roots up to the leaves and move food from the leaves down to the roots • Supports branches, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds • Video ROOTS-EXTERNAL • Root cap- indicates growth of new cells • Root Hairs - absorb moisture (water) and minerals Root images from a rice plant ROOTS-INTERNAL • Much like stems in that they have a phloem, cambium, and xylem layer • Phloem-the outer layer that carries food down the root • Xylem-the inner layer that carries water and minerals up to the stem LAYERS OF ROOTS • Fibrous-many branched shallow roots • are easier to transplant • Tap-long root with few branched ones • more difficult to transplant FUNCTIONS OF ROOTS • Absorption-take water and nutrients from the soil and conduct them to the stem • Anchor the plant and hold it upright • Store food for plant use • Asexual reproduction in some plants • Video FLOWERS • Sepals-Green parts that cover and protect flower bud before it opens • Petals-are really leaves that are modified to attract insects for flower pollination, the pretty part that we call flowers • Stamen-male part of the flower • Pistil-female part of the flower FLOWERS PARTS OF THE STAMEN • Filament-short stalk that holds up the anther • Anther-a sac-like structure that contains pollen, the male sex cells PARTS OF THE PISTIL • Ovules-the eggs or female sex cells that become seeds if fertilized • Ovary-if fertilized becomes a fruit or seed coat • Style-holds up the stigma and connects it to the ovary • Stigma-sticky part on top of style where insects leave pollen PARTS OF THE PISTIL Stigma Style Ovary COMPLETE-VS-INCOMPLETE • Complete flowers have both male and female parts • Incomplete flowers have only male or female parts FUNCTIONS OF FLOWERS • Produce seeds used for sexual reproduction • Attract insects for pollination (Pollination is the transfer of pollen from anther to stigma.) • Produce fruit to protect, nourish and carry seeds • Helps with seed dispersal • Video OBJECTIVE 3.03 • Discuss floriculture and landscape plants TAXONOMY • The science of classifying and identifying plants • Scientific names are used because the same common name is used for different plants in different areas of the world. KARL VON LINNE • Swedish botanist that developed the binomial system of naming plants using two Latin words to indicate the genus and species. • Linne changed his name to the Latin name Carolus Linneaus. SCIENTIFIC NAMES • Latin is the language used for scientific classification. • The first word is the genus and the second word is the species. If there are additional words, they indicate a variety or cultivar. GENUS VS. SPECIES • Plants in the same genus have similar characteristics. • Plants in the same species consistently produce plants of the same type. SCIENTIFIC CLASSIFICATION • The broadest category of scientific classification is the Kingdom--either plant or animal. • The broadest category in the plant kingdom is division or phylum. DIVISIONS • The four most important divisions of the plant kingdom are: • Thallophites • Bryophytes • Pteriophytes • Spermatophytes SPERMATOPHYTES • Contains flowering or seed-bearing plants • Two subdivisions are: • Gymnosperms and Angiosperms COMMON PLANT GENUS • Pinus-Pine • Acer-Maple • Cornus-dogwood • Rhododendronrhododendron • Ilex-Holly • Quercus-oak • Ficus-fig