* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download More Exam Review SPH 4U1
Survey
Document related concepts
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Mechanics of planar particle motion wikipedia , lookup
Roche limit wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
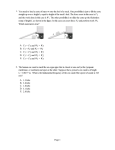
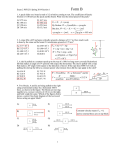
More Exam Review SPH 4U1 Redo all tests and quizzes Do Exam Review on website Then you may complete this Good Luck in your studying! Material covered: Chapter 1 – Kinematics all of it Chapter 2 – Dynamics all of it (plus we did extra on pulleys and static equilibrium) Chapter 3 – Circular Motion and Universal Gravitation..all Chapter 4 – Work Chapter 5Chapter 6Chapter 7 – Electricity focus on 7.2 to 7.6 (see your tests and quizzes for typical questions) Chapter 8 – Magnetism focus on 8.2, 8.5 (see your tests and quizzes for typical questions) Chapter 9 – Waves Chapter 10- Light Chapter 11 –Relativity 11.1, 11.2 (time and length) multiple choice Chapter 12 – Quantum 12..1, 12.4, 12.5 (see homework assigned to you for typical questions) NOTE: Chapters 11 and 12 will not be weighted much on the exam. More Exam Review Questions: 1. At the instant when the traffic light turns green, an automobile starts with a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s 2. At the same instant a truck travelling with a constant speed of 8.5 m/s overtakes and passes the automobile. (a) How far beyond the starting point will the automobile overtake the truck? (b) How fast will the car be travelling at that instant? 2. A hockey puck hits the boards with a velocity of 10 m/s at an angle of 20º to the boards. It is deflected with a velocity of 8.0 m/s at 24º to the boards. If the time of impact is 0.03 s, what is the average acceleration of the puck? 3. The navigator of an airplane plans a flight from one airport to another 1200 km away, in one direction 30° east of north. The weather office informs him of a prevailing wind from the west, of 80 km/h. The pilot wants to maintain an air speed of 300 km/h. (a) What heading should the navigator give the pilot? (b) How long will the flight take? (c) How much time did the wind save? 5. A canoeist paddles “north” across a river at 3.0 m/s. (The canoe is always kept pointed at right angles to the river.) The river is flowing east at 4.0 m/s and is 100 m wide. (a) What is the velocity of the canoe relative to the river bank? (b) Calculate the time required to cross the river. (c) How far downstream is the landing point from the starting point? 6. A 2.0 kg mass, placed on a smooth, level table, is attached by a light string passing over a frictionless pulley to a 5.0 kg mass hanging freely over the edge of the table, as illustrated. Calculate (a) the tension in the string (b) the acceleration of the 2.0 kg mass. 7. A cannonball shot horizontally from the top of a cliff with an initial velocity of 425 m/s is aimed towards a schooner on the ocean below. If the cliff is 78 m above the ocean surface, calculate the following: (a) the time for the cannonball to reach the water (b) the horizontal displacement of the cannonball (c) the velocity of the cannonball just before it strikes the water 8. A boy pulls a 50 kg crate across a level floor with a force of 200 N. If the force acts at an angle of 30° up from the horizontal, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30, determine the following. (a) the normal force exerted on the crate by the floor (b) the horizontal frictional force exerted on the crate by the floor (c) the acceleration of the crate 9. A skier skiing downhill reaches the bottom of a hollow with a velocity of 20 m/s, and then coasts up a hill with a 10° slope. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.10, how far up the slope will she travel before she stops? 10. A 0.50 kg block of cheese sits on a level table, as shown. The coefficient of static friction is 0.60. Three strings are tied together in a knot at K. Kc is horizontal and fastened to the cheese. Kw angles up to the wall at 30° to the horizontal. Km hangs vertically, supporting a mouse. What is the maximum mass of the mouse, if the cheese and the mouse remain in equilibrium? 11. The force of gravity on a spacecraft some distance from Earth is 900 N. What will be the force of gravity on a spacecraft with twice the mass, at a distance from Earth’s centre that is as far? 12. A 4.0 kg ball moving to the right at 5.0 m/s collides head-on with a 2.0 kg ball moving to the left at 4.0 m/s. If the collision is elastic, determine the direction and speed of each ball after the collision. Fixed frame of reference 13. A Hooke’s Law spring is compressed 10 cm by an applied force of 50 N. This compressed spring is then used to project a 20 g marble straight up into the air. To what maximum height does the marble rise? 14. A 500 kg satellite is in circular orbit 200 km above Earth’s surface. Calculate: (a) the gravitational potential energy of the satellite (b) the kinetic energy of the satellite (c) its binding energy 15. A student measuring the wavelength produced by a sodium vapour lamp directed the sodium light through two slits with a separation of 0.15 mm. An interference pattern was created on the screen, 3.0 m away. The student found that the distance between the first and the eighth consecutive dark lines was 8.0 cm. What was the wavelength of the light emitted by the sodium vapour lamp? 16. Two identical, small spheres of mass 2.0 g are fastened to the ends of a 0.60 m long light, flexible, insulating fishline. The fishline is suspended by a hook in the ceiling at its exact centre. The spheres are each given an identical electric charge. They are in static equilibrium, with an angle of 30° between the string halves, as shown. Calculate the magnitude of the charge on each sphere. 17. Three negatively charged spheres, each with a charge of 4.0 10–6 C, are fixed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle whose sides are 20 cm long. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the net electric force on each sphere. 18. Two small spheres, with charges 1.6 10–5 C and 6.4 10–5 C, are situated 2.0 m apart. They have the same sign. Where, relative to these two objects, should a third object be situated, of the opposite sign and whose charge is 3.0 10–6 C, so that it experiences no net electrical force? Do we really need to know the charge or sign of the third object? (on the line joining them, 0.67 m from the 1.6 10–5 C charge) Answers to More Exam Review Sheet (a) The automobile will be 80 m beyond the starting point when it will overtake the truck. (b) The car will be travelling at 17 m/s at that instant. 2. Using cosine law: Using the sine law: 3. (a) Using the sine law, The heading is [N17°E]. (b) The flight will take 3.6 h. (c) Without wind, The time saved by the wind is 0.4 h, or 24 min. 5. (a) (b) The canoe crosses the river at (c) The canoe “moves downstream” at 6. (a) Using Newton’s Law of Motion, (b) 7. (a) (b) (c) 8. (a) Taking vertical components: (since ) (b) (c) Taking horizontal components: 9. Taking components perpendicular to the slope (up positive) Taking components parallel to the slope (up positive) 10. Since the knot is in equilibrium, we know that Taking horizontal components, with right as positive, this vector equation gives us Taking vertical components, with up as positive, gives us Since Tm = Fg, the force of gravity on the mouse is 1.7 N, and its mass would be 11. The ratio of the masses is Therefore the ratio of the forces due to mass alone is The ratio of the distance is Therefore the ratio of the forces due to distance alone is Thus, the new force will be Alternate Solution: 12. Since both balls are moving before the collision, the specific equations developed earlier do not apply. However, if the collision is viewed from the frame of reference of the 2.0 kg ball before the collision, they do apply. In that frame of reference (i.e., a frame moving to the left at 4.0 m/s), . Moving frame of reference Therefore, However, both of these velocities are measured in a frame of reference moving to the left at 4.0 m/s. Therefore, in Earth’s frame of reference: That is, the 4.0 kg ball rebounds to the left at 1.0 m/s, while the 2.0 kg ball rebounds and moves to the right at 8.0 m/s. 13. After the spring is released, the total energy of the spring-marble-Earth system remains constant. Let the height of the marble, at release, be the zero level of gravitational potential energy. Just before release: Then, as the marble reaches its maximum height, Note that this distance, being positive, is above the starting point. The spring will have expanded 0.10 m to its normal length, so that the marble is 12.7 m above the top of the now-uncompressed spring. 14. (a) (b) In orbit: (c) Therefore, the binding energy is 15. . 16. For each sphere, a free body diagram shows Resolving forces in the x and y directions For d: Then, 17. For the magnitude of each repulsive force, For sphere 1: Using components in the x-y plane, The net forces on 2 and 3 have the same magnitude and act along in symmetrical outward directions. 18. The third charge must be situated on a line joining q1 and q2, a distance x from q1, as shown. For there to be no net force on q3: Omitting units for simplicity and multiplying both sides by 105 , Since x = –2.0 is an inadmissible solution, the third charge is located 0.67 m from the 1.6 10–5 C charge. Note: Q3 divides out of the original equation—we really do not need to know its value or even its sign.