* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
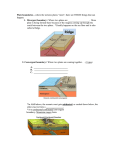
Name_________________________________________________Date_______________ Period____ (B) Modeling Plate Boundaries Background Information: The Earth’s crust is divided into a set of large moving plates. The place where these plates meet is called a plate boundary. There are three different types of plate boundaries. The first type is called a divergent boundary and this is where plates separate from each other. The second type is called a convergent boundary and this is where plates collide with each other. Lastly, the third type of plate boundary is called a transform boundary and this is where plates slide past each other. This lab will focus on each of these boundaries and the geological features created at these boundaries. Materials: Clay Wax paper Permanent marker Part I: Divergent Boundary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The first type of plate movement you will model is a divergent plate boundary. One partner should take a small handful of clay and set the rest of the clay to the side. Next, separate the handful of clay that you just took into 2 separate pieces. Now create a DIVERGENT boundary with the clay. Take the permanent marker and below the model you just created as “divergent boundary” on the wax paper. Answer the questions below BEFORE moving on to Part II: 1. What happens at a divergent boundary? _At a divergent boundary…___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What geological feature (CIRCLE ONE: volcanoes, earthquakes, valleys, or mountains) are created at divergent boundaries? Why? (CIRCLE ONE: volcanoes, earthquakes, valleys, or mountains) are created at divergent boundaries because…__________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Name_________________________________________________Date_______________ Period____ (B) Part II: Convergent Boundary (oceanic and continental crust) 1. The second type of plate movement that you will explore is when oceanic crust converges (meets) with continental crust. 2. Pick up the clay that you just set to the side. 3. Take a small handful of that clay and put the rest to the side. 4. Next, separate the clay that you just took a handful of into 2 pieces. 5. Now create a CONVERGENT boundary with the clay. 6. Place your convergent boundary on the wax paper. 7. Take the permanent marker and below the model you just created write “convergent boundary” on the wax paper. 8. Now take another handful of the clay that you set to the side and create a SUBDUCTION ZONE between oceanic and continental crust. 9. Place the subduction zone that you created on the wax paper. 10. Take the permanent marker and below the model you just created write “subduction zone” on the wax paper. Answer the questions below BEFORE moving on to Part III: 1. What happens at a convergent boundary? _At a convergent boundary…__________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What geological feature is formed at a convergent boundary? (CIRCLE ONE: mountains, valleys, earthquakes, or volcanoes) are created at convergent boundaries_ because…__________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What happens at a subduction zone? Why? _At a subduction zone, _______________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Name_________________________________________________Date_______________ Period____ (B) Part III: Convergent Boundary (continental and continental crust) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Now you will explore when continental crust converges (meets) with continental crust. Remove the graham cracker and the hard chocolate chip cookie from the icing. Smooth out the icing using the spoon. Place 2 SOFT chocolate chip cookies onto the icing. Slowly, push the cookies toward each other. Notice how the edges crumble and push up! Draw and label your model below. Use these labels: continental plates, mountains. Use arrows to show the direction the plates are moving. Convergent boundary What geological features (mountains, valleys, hills, volcanoes, or earthquakes) are formed at convergent boundaries? Why? How do plate tectonics affect life on Earth? Name_________________________________________________Date_______________ Period____ (B) Why do you think there is more destruction (damage) produced when certain types of crust collide? (continental to continental, continental to oceanic, or oceanic to oceanic) Part IV: Transform Boundary 1. The last type of plate movement you will explore is when continental plates slide past each other (transform plate boundaries). 2. Remove the 2 soft chocolate chip cookies and place them to the side. 3. Place the 2 hard chocolate chip cookies onto the icing. 4. Push the 2 cookies together. 5. Apply pressure so that the 2 cookies begin to slide past each other. 6. This is the same type of movement taking place at the San Andreas Fault in California! 7. Notice that small bits of cookies are pressing together. This models that the land is under stress where plates pass beside each other. 8. Draw and label your model below. Include these labels: stress (where earthquakes would be taking place) and continental plates. Use arrows to show the direction the plates are moving. Transform Boundary Explain why crust is neither created nor destroyed along transform boundaries? Name_________________________________________________Date_______________ Period____ (B) In California, there is a fault that separates it from other states. What do you think will eventually happen in this area? Summarize what you learned from this lab (3-4 sentences):