* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
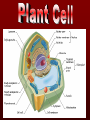
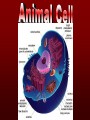
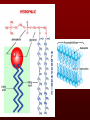
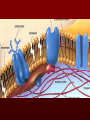
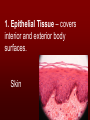
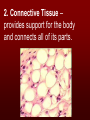
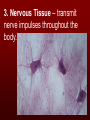
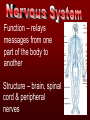
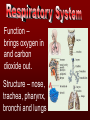
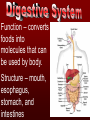
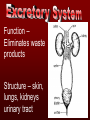
The basic unit of structure for all living things! Theory – well tested hypothesis. 1.All living things are made up of cells. 2.Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.New cells come from existing cells. Prokaryotic Cell – cells that lack a membrane bound nucleus. Example: Bacteria Eukaryotic Cell – a cell that contains a membrane bound nucleus and many specialized structures called organelles “tiny organs” Single Celled – organisms made up of 1 cell (ex. amoeba, paramecium, euglena) Multicellular – organisms made up of many independent cells working together (plants and animals) Plant & Animal Cells Function – protection & controls what enters and leaves cell. Structure – double layered Phospholipid membrane Function – holds all organelles and nutrients. Structure – semi-solid fluid (water, proteins, various nutrients) Function – Protects the DNA Structure – phospholipid membrane (nuclear envelop) & internal fluid called nucleoplasm. Function – constructs lipids and special proteins (enzymes) for detoxification Structure – folded phospholipid membrane Function – modifies proteins and packages them to be shipped out. Structure – phospholipid membrane found in stacks. Function – power house of cell – place where food is broken down and turned into energy. Structure – phospholipid membrane Plant Cells Only Function – makes food (sugars) Structure – phospholipid membrane Function – protection and support Structure – cellulose (carbs.) Groups of similar cells working together. 1. Epithelial Tissue – covers interior and exterior body surfaces. Skin 2. Connective Tissue – provides support for the body and connects all of its parts. 3. Nervous Tissue – transmit nerve impulses throughout the body. 4. Muscle Tissue – enable the body to move. Groups of similar tissues working together. Groups of similar organs working together. Function – relays messages from one part of the body to another Structure – brain, spinal cord & peripheral nerves Function – serves as a barrier against infection Structure – skin Function – brings oxygen in and carbon dioxide out. Structure – nose, trachea, pharynx, bronchi and lungs Function – converts foods into molecules that can be used by body. Structure – mouth, esophagus, stomach, and intestines Function – Eliminates waste products Structure – skin, lungs, kidneys urinary tract Function – supports body,allows movement and produces blood cells. Structure – Bones Function – allows body to move. Structure – smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & skeletal muscle. Function – brings oxygen, nutrients, and chemical messengers to cells. Structure – heart and blood Function – regulates & controls the bodies functions Structure – glands Function – produces sperm & egg cells. Structure – testes & penis; ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina. Function – protects the body from disease. Structure – white blood cells and lymph nodes