* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulation - Berkeley County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
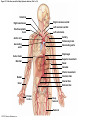
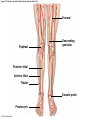
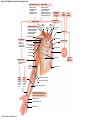
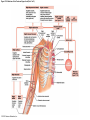
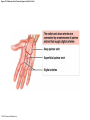
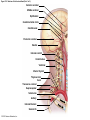
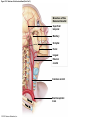
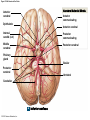
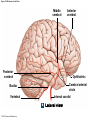
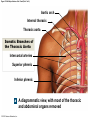
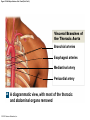
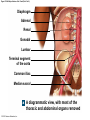
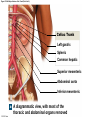
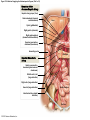
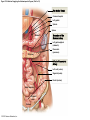
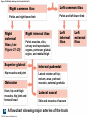
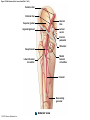
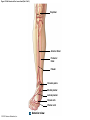
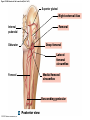
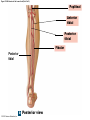
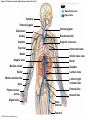
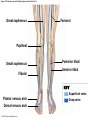
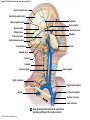
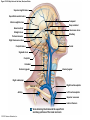
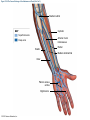
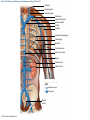
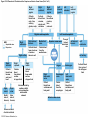
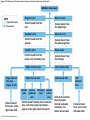
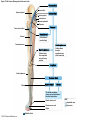
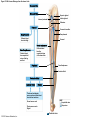
21-1 Classes of Blood Vessels • Arteries • Carry blood away from heart • Arterioles • Are smallest branches of arteries • Capillaries • Are smallest blood vessels • Location of exchange between blood and interstitial fluid • Venules • Collect blood from capillaries • Veins • Return blood to heart © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-1 Blood Vessels • The Largest Blood Vessels • Attach to heart • Pulmonary trunk • Carries blood from right ventricle • To pulmonary circulation • Aorta • Carries blood from left ventricle • To systemic circulation © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-1 Blood Vessels • The Smallest Blood Vessels • Capillaries • Have small diameter and thin walls • Chemicals and gases diffuse across walls © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-1 Blood Vessels • Differences between Arteries and Veins • Arteries and veins run side by side • Arteries have thicker walls and higher blood pressure • Collapsed artery has small, round lumen (internal space) • Vein has a large, flat lumen • Vein lining contracts, artery lining does not • Artery lining folds • Arteries more elastic • Veins have valves © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-1 Structure and Function of Arteries • Arteries • Elasticity allows arteries to absorb pressure waves that come with each heartbeat • Contractility • Arteries change diameter • Controlled by sympathetic division of ANS • Vasoconstriction • The contraction of arterial smooth muscle by the ANS • Vasodilation • The relaxation of arterial smooth muscle • Enlarging the lumen © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-1 Structure and Function of Arteries • Vasoconstriction and Vasodilation • Affect: 1. Afterload on heart 2. Peripheral blood pressure 3. Capillary blood flow © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-1 Structure and Function of Capillaries • Angiogenesis • Formation of new blood vessels • Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) • Occurs in the embryo as tissues and organs develop • Occurs in response to factors released by cells that are hypoxic, or oxygen-starved • Most important in cardiac muscle, where it takes place in response to a chronically constricted or occluded vessel © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-1 Structure and Function of Veins • Veins • Collect blood from capillaries in tissues and organs • Return blood to heart • Are larger in diameter than arteries • Have thinner walls than arteries • Have lower blood pressure © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-2 Pressure and Resistance • Arterial Blood Pressure • Pulse pressure • Difference between systolic pressure and diastolic pressure • Mean arterial pressure (MAP) • MAP = diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-2 Pressure and Resistance • Abnormal Blood Pressure • Normal = 120/80 • Hypertension • Abnormally high blood pressure • Greater than 140/90 • Hypotension • Abnormally low blood pressure © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-4 Cardiovascular Adaptation • Stroke • Also called cerebrovascular accident (CVA) • Blockage or rupture in a cerebral artery • Stops blood flow © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-19 An Overview of the Major Systemic Arteries (Part 1 of 2). Vertebral Right common carotid Right subclavian Left common carotid Brachiocephalic trunk Left subclavian Axillary Pulmonary trunk Descending aorta Aortic arch Ascending aorta Diaphragm Celiac trunk Superior mesenteric Brachial Renal Gonadal Inferior mesenteric Common iliac Radial Internal iliac Ulnar External iliac Palmar arches Deep femoral Femoral © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-19 An Overview of the Major Systemic Arteries (Part 2 of 2). Femoral Popliteal Descending genicular Posterior tibial Anterior tibial Fibular Dorsalis pedis Plantar arch © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-20 Arteries of the Chest and Upper Limb. Right thyrocervical trunk Right vertebral Supplies muscles, skin, tissues of neck, thyroid gland, shoulders, and upper back (right side) Supplies spinal cord, cervical vertebrae (right side); fuses with left vertebral, forming basilar artery after entering cranium through foramen magnum Left common carotid Left subclavian Brachiocephalic trunk Right subclavian Right internal thoracic Right common carotid (see Figure 21– 21) Right thyrocervical trunk Supplies skin and muscles of chest and abdomen, mammary gland (right side), pericardium Right vertebral Right common carotid Left common carotid Aortic arch Thoracoacromial Left subclavian Right axillary Supplies muscles of the right pectoral region and axilla Ascending aorta Lateral thoracic Anterior humeral circumflex Thoracic aorta Posterior humeral circumflex LEFT VENTRICLE Subscapular Deep brachial Intercostals Right brachial Supplies structures of the arm Right radial Right ulnar Supplies forearm, radial side Supplies forearm, ulnar side Ulnar collateral arteries Abdominal aorta Anterior ulnar recurrent Posterior ulnar recurrent Anterior crural interosseous The radial and ulnar arteries are connected by anastomoses of palmar arches that supply digital arteries Deep palmar arch Superficial palmar arch Digital arteries © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Thoracic aorta (see Figure 21–23) 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Branches of the Aortic Arch • Deliver blood to head, neck, shoulders, and upper limbs 1. Brachiocephalic trunk 2. Left common carotid artery 3. Left subclavian artery © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Subclavian Arteries • Leaving the thoracic cavity: • Become axillary artery in arm • And brachial artery distally © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-20 Arteries of the Chest and Upper Limb (Part 1 of 2). © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Brachial Artery • Divides at coronoid fossa of humerus • Into radial artery and ulnar artery • Fuse at wrist to form: • Superficial and deep palmar arches • Which supply digital arteries © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-20 Arteries of the Chest and Upper Limb (Part 2 of 2). © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Common Carotid Arteries • Each common carotid divides into: • External carotid artery – supplies blood to structures of the neck, lower jaw, and face • Internal carotid artery – enters skull and delivers blood to brain • Divides into three branches 1. Ophthalmic artery 2. Anterior cerebral artery 3. Middle cerebral artery © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-21 Arteries of the Neck and Head (Part 1 of 2). Anterior cerebral Middle cerebral Ophthalmic Cerebral arterial circle Carotid canal Posterior cerebral Basilar Internal carotid Carotid sinus Vertebral Inferior thyroid Thyrocervical trunk Transverse cervical Suprascapular Subclavian Axillary Internal thoracic Second rib © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-21 Arteries of the Neck and Head (Part 2 of 2). Branches of the External Carotid Superficial temporal Maxillary Occipital Facial Lingual External carotid Common carotid Brachiocephalic trunk © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Vertebral Arteries • Also supply brain with blood • Left and right vertebral arteries • Arise from subclavian arteries • Enter cranium through foramen magnum © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Anastomoses • The cerebral arterial circle (or circle of Willis) interconnects: • The internal carotid arteries • And the basilar artery © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-22a Arteries of the Brain. Cerebral Arterial Circle Anterior cerebral Anterior communicating Ophthalmic Anterior cerebral Internal carotid (cut) Posterior communicating Middle cerebral Posterior cerebral Pituitary gland Basilar Posterior cerebral Vertebral Cerebellar a Inferior surface © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-22b Arteries of the Brain. Middle cerebral Anterior cerebral Posterior cerebral Ophthalmic Cerebral arterial circle Basilar Vertebral Internal carotid b Lateral view © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Descending Aorta • Thoracic aorta • Supplies organs of the chest • • • • Bronchial arteries Pericardial arteries Esophageal arteries Mediastinal arteries • Supplies chest wall • Intercostal arteries • Superior phrenic arteries © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-23a Major Arteries of the Trunk (Part 1 of 4). Aortic arch Internal thoracic Thoracic aorta Somatic Branches of the Thoracic Aorta Intercostal arteries Superior phrenic Inferior phrenic a A diagrammatic view, with most of the thoracic and abdominal organs removed © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-23a Major Arteries of the Trunk (Part 2 of 4). Visceral Branches of the Thoracic Aorta Bronchial arteries Esophageal arteries Mediastinal artery Pericardial artery a A diagrammatic view, with most of the thoracic and abdominal organs removed © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Descending Aorta • Abdominal Aorta • Divides at terminal segment of the aorta into: • Left common iliac artery • Right common iliac artery • Unpaired branches • Major branches to visceral organs • Paired branches • • • • © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. To body wall Kidneys Urinary bladder Structures outside abdominopelvic cavity Figure 21-23a Major Arteries of the Trunk (Part 3 of 4). Diaphragm Adrenal Renal Gonadal Lumbar Terminal segment of the aorta Common iliac Median sacral a A diagrammatic view, with most of the thoracic and abdominal organs removed © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-23a Major Arteries of the Trunk (Part 4 of 4). Celiac Trunk Left gastric Splenic Common hepatic Superior mesenteric Abdominal aorta Inferior mesenteric a A diagrammatic view, with most of the thoracic and abdominal organs removed © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-24 Arteries Supplying the Abdominopelvic Organs (Part 1 of 2). Branches of the Common Hepatic Artery Hepatic artery proper (liver) Gastroduodenal (stomach and duodenum) Liver Cystic (gallbladder) Right gastric (stomach) Right gastroepiploic (stomach and duodenum) Superior pancreaticoduodenal (duodenum) Ascending colon Superior Mesenteric Artery Pancreas Inferior pancreaticoduodenal (pancreas and duodenum) Middle colic (cut) (large intestine) Right colic (large intestine) Ileocolic (large intestine) Small intestine Intestinal arteries (small Intestine) Rectum © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-24 Arteries Supplying the Abdominopelvic Organs (Part 2 of 2). The Celiac Trunk Common hepatic Left gastric Splenic Spleen Stomach Branches of the Splenic Artery Left gastroepiploic (stomach) Pancreatic (pancreas) Pancreas Inferior Mesenteric Artery Left colic (colon) Sigmoid (colon) Rectal (rectum) Small intestine Sigmoid colon Rectum © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs • Femoral artery • Deep femoral artery • Becomes popliteal artery • Posterior to knee • Branches to form: • Posterior and anterior tibial arteries • Posterior gives rise to fibular artery © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-23b Major Arteries of the Trunk (Part 2 of 2). Right common iliac Left common iliac Pelvis and right lower limb Pelvis and left lower limb Right external Iliac (see Figure 21–25) Right internal iliac Pelvic muscles, skin, urinary and reproductive organs, perineum, gluteal, region, and medial thigh Superior gluteal Hip muscles and joint Obturator Ilium, hip and thigh muscles, hip joint and femoral head Left internal iliac Internal pudendal Lateral rotators of hip; rectum, anus, perineal muscles, external genitalia Lateral sacral Skin and muscles of sacrum b A flowchart showing major arteries of the trunk © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Left external iliac Figure 21-25a Arteries of the Lower Limb (Part 1 of 2). Common iliac External iliac Internal iliac Superior gluteal Lateral sacral Inguinal ligament Internal pudendal Obturator Deep femoral Medial femoral circumflex Lateral femoral circumflex Femoral Descending genicular a Anterior view © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-25a Arteries of the Lower Limb (Part 2 of 2). Popliteal Anterior tibial Posterior tibial Fibular Dorsalis pedis Medial plantar Lateral plantar Dorsal arch Plantar arch a Anterior view © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-25b Arteries of the Lower Limb (Part 1 of 2). Superior gluteal Right external iliac Femoral Internal pudendal Deep femoral Obturator Lateral femoral circumflex Medial femoral circumflex Femoral Descending genicular b Posterior view © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-25b Arteries of the Lower Limb (Part 2 of 2). Popliteal Anterior tibial Posterior tibial Fibular Posterior tibial b Posterior view © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Systemic Veins • Complementary Arteries and Veins • Run side by side • Branching patterns of peripheral veins are more variable • In neck and limbs • One set of arteries (deep) • Two sets of veins (one deep, one superficial) • Venous system controls body temperature © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-26 An Overview of the Major Systemic Veins (Part 1 of 2). KEY Superficial veins Deep veins Vertebral External jugular Subclavian Axillary Cephalic Internal jugular Brachiocephalic Superior vena cava Brachial Intercostal veins Basilic Inferior vena cava Hepatic veins Renal Median cubital Gonadal Radial Lumbar veins Median antebrachial Left and right common iliac Ulnar External iliac Palmar venous arches Digital veins Internal iliac Deep femoral Femoral © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-26 An Overview of the Major Systemic Veins (Part 2 of 2). Great saphenous Femoral Popliteal Small saphenous Fibular Posterior tibial Anterior tibial KEY Superficial veins Plantar venous arch Dorsal venous arch © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Deep veins 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Superior Vena Cava (SVC) • Receives blood from the tissues and organs of: • • • • • Head Neck Chest Shoulders Upper limbs © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-27c Major Veins of the Head, Neck, and Brain. Superior sagittal sinus Superficial cerebral veins Temporal Inferior sagittal sinus Deep cerebral Great cerebral Cavernous sinus Straight sinus Maxillary Petrosal sinuses Right transverse sinus Facial Occipital sinus Sigmoid sinus Occipital Vertebral External jugular Internal jugular Right subclavian Clavicle Right brachiocephalic Left brachiocephalic Axillary Superior vena cava Internal thoracic c Veins draining the brain and the superficial and deep portions of the head and neck. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Superficial Veins of the Head and Neck • Converge to form: • Temporal, facial, and maxillary veins • Temporal and maxillary veins • Drain to external jugular vein • Facial vein • Drains to internal jugular vein © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-27c Major Veins of the Head, Neck, and Brain. Superior sagittal sinus Superficial cerebral veins Temporal Inferior sagittal sinus Deep cerebral Great cerebral Cavernous sinus Straight sinus Maxillary Petrosal sinuses Right transverse sinus Facial Occipital sinus Sigmoid sinus Occipital Vertebral External jugular Internal jugular Right subclavian Clavicle Right brachiocephalic Left brachiocephalic Axillary Superior vena cava Internal thoracic c Veins draining the brain and the superficial and deep portions of the head and neck. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Veins of the Hand • Digital veins • Empty into superficial and deep palmar veins • Which interconnect to form palmar venous arches © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Veins of the Hand • Superficial arch empties into: • • • • Cephalic vein Median antebrachial vein Basilic vein Median cubital vein • Deep palmar veins drain into: • Radial and ulnar veins • Which fuse above elbow to form brachial vein © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-28 The Venous Drainage of the Abdomen and Chest (Part 3 of 3). Median cubital KEY Cephalic Superficial veins Anterior crural interosseous Deep veins Radial Basilic Median antebrachial Ulnar Palmar venous arches Digital veins © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Brachial Vein • Merges with basilic vein • To become axillary vein • Cephalic vein joins axillary vein • To form subclavian vein • Merges with external and internal jugular veins • To form brachiocephalic vein • Which enters thoracic cavity © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-28 The Venous Drainage of the Abdomen and Chest (Part 2 of 3). Vertebral Internal jugular External jugular Subclavian Highest intercostal Brachiocephalic Axillary Cephalic Accessory hemiazygos Hemiazygos Brachial Intercostal veins Inferior vena cava Basilic Phrenic veins Adrenal veins KEY Superficial veins Deep veins Medial sacral © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Veins of the Thoracic Cavity • Brachiocephalic vein receives blood from: • Vertebral vein • Internal thoracic vein • The Left and Right Brachiocephalic Veins • Merge to form the superior vena cava (SVC) © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-29 Flowchart of Circulation to the Superior and Inferior Venae Cavae (Part 1 of 2). Right external jugular Right vertebral Right internal jugular Collects blood from neck, face, salivary glands, scalp Collects blood from cranium, spinal cord, vertebrae Collects blood from cranium, face, and neck Left internal jugular Right subclavian Superficial veins Deep veins Right axillary Right internal thoracic Mediastinal veins Collects blood from structures of anterior thoracic wall Collect blood from the mediastinum Right brachial Right cephalic Right basilic Collects blood from forearm, wrist, and hand Collects blood from lateral surface of upper limb Collects blood from medial surface of upper limb Right radial Right ulnar Radial side of forearm Ulnar side of forearm Venous network of wrist and hand © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Interconnected by median cubital vein and median antebrachial network Left external jugular Left brachiocephalic Right brachiocephalic KEY Left vertebral Superior vena cava Through highest intercostal vein Left internal thoracic RIGHT ATRIUM Azygos Left axillary Hemiazygos Right intercostal veins Esophageal veins Left intercostal veins Collect blood from vertebrae and body wall Collect blood from the esophagus Collect blood from vertebrae and body wall Inferior vena cava Left subclavian Collects blood from veins of the left upper limb 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) • Collects blood from organs inferior to the diaphragm © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-29 Flowchart of Circulation to the Superior and Inferior Venae Cavae (Part 2 of 2). Inferior vena cava KEY Superficial veins Deep veins Right external Iliac (see Figure 21–30) Hepatic veins Phrenic veins Collect blood from the liver Collect blood from the diaphragm Gonadal veins Adrenal veins Collect blood from the gonads Collect blood from the adrenal glands Lumbar veins Renal veins Collect blood from the spinal cord and body wall Collect blood from the kidneys Right common iliac Left common iliac Right internal iliac Left internal iliac Gluteal Internal veins pudendal vein Collects blood from veins of the right lower limb © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Obturator Lateral sacral vein vein Collect blood from the pelvic muscles, skin, and urinary and reproductive organs of the right side of the pelvis Collects blood from the left gluteal, internal pudendal, obturator, and lateral sacral veins Left external iliac Collects blood from veins of the left lower limb 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Veins of the Foot • Capillaries of the sole • Drain into a network of plantar veins • Which supply the plantar venous arch • Drain into deep veins of leg: • Anterior tibial vein • Posterior tibial vein • Fibular vein • All three join to become popliteal vein © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Dorsal Venous Arch • Collects blood from: • Superior surface of foot • Digital veins • Drains into two superficial veins 1. Great saphenous vein (drains into femoral vein) 2. Small saphenous vein (drains into popliteal vein) © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The Popliteal Vein • Becomes the femoral vein • Before entering abdominal wall, receives blood from: • Great saphenous vein • Deep femoral vein • Femoral circumflex vein • Inside the pelvic cavity • Becomes the external iliac vein © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • The External Iliac Veins • Are joined by internal iliac veins • To form right and left common iliac veins • The right and left common iliac veins • Merge to form the inferior vena cava © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 21-30a Venous Drainage from the Lower Limb. Common iliac Internal iliac Superior gluteal External iliac Inferior gluteal Lateral sacral Internal pudendal Obturator Femoral Femoral circumflex Deep femoral Femoral Collects blood from the thigh Great saphenous Great saphenous Collects blood from the superficial veins of the lower limb Small saphenous Collects blood from superficial veins of the leg and foot Popliteal Small saphenous Posterior tibial Fibular Anterior tibial Fibular The dorsal and plantar venous arches collect blood from the foot and toes Dorsal venous arch Plantar venous arch Digital a Anterior view © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. KEY Superficial veins Deep veins Figure 21-30b Venous Drainage from the Lower Limb. Common iliac External iliac Superior gluteal Inferior gluteal Internal pudendal Obturator Femoral Femoral circumflex Deep femoral Deep femoral Collects blood from the thigh Femoral Great saphenous Collects blood from the superficial veins of the lower limb Small saphenous Collects blood from superficial veins of the leg and foot Popliteal Small saphenous Anterior tibial Posterior tibial Anterior tibial Fibular The dorsal and plantar venous arches collect blood from the foot and toes KEY Superficial veins Deep veins Dorsal venous arch Plantar venous arch Digital b Posterior view © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 21-7 The Systemic Circuit • Major Tributaries of the Abdominal Inferior Vena Cava 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Lumbar veins Gonadal veins Hepatic veins Renal veins Adrenal veins Phrenic veins © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.