* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
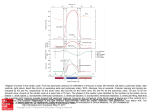
Heart Fist-size Lies in mediastinum Heart Pericardium Parietal Lines wall of sac Visceral Lies on top of the heart Epicardium Heart Pericardial space Potential space Pericardial fluid Heart Wall Layers Epicardium Outermost layer of the heart Connective tissue Houses blood and lymph capillaries with coronary arteries Heart Wall Layers Myocardium Thickest layer Cardiac muscle Heart Wall Layers Endocardium Epithelium Smooth Houses Purkinje fibers Chambers of Heart Atrium Top chambers Receive blood returning from the body Thin walls Chambers of Heart Ventricles Lower chambers Pump blood to the body and lungs Thick walls Septum Wall that divides the right and left side of the heart. Interatrial septum Interventricular septum Heart Valves Atrioventricular valves Tricuspid Valve Right side of the heart Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve Left side of the heart Heart Valves Atrioventricular Valves Chordae tendinae White strings that attach to the cusps Papillary muscles Heart Valves Semilunar valves Pulmonary valve Between right ventricle & pulmonary artery Aortic valve Between left ventricle & aorta Pulmonary Circulation Coronary Sinus, IVC, SVC —> Right Atrium —>Tricuspid Valve —> Right Ventricle —> Pulmonary Valve —> Pulmonary Artery —> Lungs Pulmonary Circulation Veins —> Left Atrium —> Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve —> Left Ventricle —> Aortic Valve —> Aorta and Beyond Pulmonary Systemic Circulation First two vessels to receive blood is the coronary arteries. Aorta carries blood to rest of body via branches. Cardiac Cycle Systole Atrial systole Ventricular systole Diastole Atrial diastole Ventricular diastole Heart Sounds Lubb AV valves close Dupp Semilunar valves close Cardiac Conduction System Sinoatrial Node SA Node Only normal natural pacemaker of the heart Set about 75 bpm Upper Right Atrium Cardiac Conduction System Atrioventricular AV Node Node Can take over for the SA node Set at 40 bpm Lower Right Atrium Cardiac Conduction System Atrioventricular AV Bundle Bundle Top of the interventricular septum Divides into Right and Left Bundle Branches Cardiac Conduction System Purkinje Fibers Actually cause ventricular contraction Scattered throughout the ventricles Electrocardiogram EKG/ECG Measures the electrical activity of the heart Several components Electrocardiogram P wave Shows atrial depolarization or atrial contractions QRS Complex Show ventricular depolarization or contraction Electrocardiogram T wave Most vulnerable time of the heart Ventricular repolarization or resetting Arrhythmia Abnormal heart rhythm Most lethal Ventricular Fibrillation V-Fib Rates Bradycardia Slow rate below 60 Tachycardia Fast rate above 100 Blood Vessels Arteries Carry blood away from the heart. 99.9% of the time it is oxygenated or red blood Pressure is high here. Blood Vessels Arterioles Smaller arteries that connect eventually with the capillaries Blood Vessels Capillaries Smallest One cell thick Simple squamous epithelium Gas exchange done here Blood Vessels Venules Smaller veins that connect the capillaries to the larger veins Blood Vessels Veins Return blood to the heart 99.9% of time is deoxygenated or blue blood. Veins serve as a blood reservoir Blood Vessels Veins Pressure is very low in veins Larger veins have valves To prevent backflow Blood Pressure Force that the blood exerts against the inner walls of the blood vessels Commonly referred to as arterial blood pressure Blood Pressure Systolic pressure Top number of blood pressure Most closely related to ventricular systole Blood Pressure Diastolic Bottom Pressure number of blood pressure Most closely related to ventricular diastole Most important number in hypertension Factors That Influence Blood Pressure Heart action Cardiac output Stroke volume times the heart rate SV = 70 ml/beat Factors That Influence Blood Pressure Blood Volume Average for adults is 5 liters. Less = lower blood pressure Peripheral resistance Vasoconstriction vs vasodilation Blood Pressure Control Baroreceptors Aortic bodies Carotid bodies Sensitive to pressure change Cardioinhibitor reflex Cardioaccelerator reflex