* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Volcano (1997 film) wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
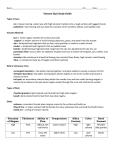
Types of Volcano Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in other words, it has a low viscosity. This low viscosity means that the lava from a basalt volcano flows a long way, resulting in a volcanic cone with a flat, shield-like shape. Basalt is very dark in colour and has a silica content of only 50%. Basalt is also very dense and has a high specific gravity. Examples of shield volcanoes include the Dunedin and Lyttleton volcanoes, and Rangitoto Island. The ‘Organ Pipes’ on Mt Cargill are an example of a basalt formation. Andesite is an intermediate type of magma, and its qualities are between those of basalt and ryholite. It has a silica content of 60% and is grey in colour. Andesite has a medium viscosity, and it flows like cold treacle. Because if flows more slowly than basalt, it forms volcanic cones with a much steeper shape, called cone volcanoes. Examples of cone volcanoes include Mt Taranaki and Mt Ruapehu. Rhyolite magma is the most viscous type of magma – it flows like tar. It is light in colour and has a silica content of 70%. Rhyolite has a low density and a low melting point. Because of its high viscosity, rhyolitic volcanoes tend to be very explosive. The viscous magma builds up until there is enough pressure in the magma chamber to push it out. If sides of the volcano are left behind, it is called a dome volcano, like Tarawera. Sometimes, if the explosion is very large, nothing is left behind except a large hole in the ground, called a caldera. Examples of a caldera include Lake Taupo and Lake Rotorua. a.