* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Fossils - Parkway C-2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
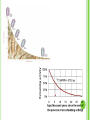
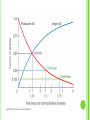
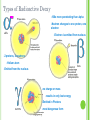
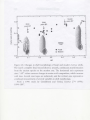
FOSSILSEvidence from Once-living Organisms Fossils found in SEDIMENTARY ROCKS The lower the sediment layer is, the older the fossils of the layer will be.- Law of Superposition As time elapses, more and more sediment layers form to create the layers of sedimentary rocks. EXAMPLES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS DIFFERENT ROCK LAYERS OF THE EARTH Relative dating places rocks in their proper sequence of formation, e.g. which formed first, second etc. Although relative dating cannot give us numeric dates for events that took place, it does provide useful information on what event followed or preceded another event. Relative dating is still very valuable to scientists and still widely used. The discovery of radioactive dating has supplemented relative dating techniques. Oldest? Youngest? Can you put the events in order? Relative Dating combined with Radioactive Dating Absolute (Radioactive) Dating of Fossils using the half- life of elements oHalf Lives for Radioactive Elements Radioactive Parent Stable Daughter Half life Potassium 40 Argon 40 1.3 billion yrs Rubidium 87 Strontium 87 48.8 billion yrs Thorium 232 Lead 208 14 billion years Uranium 235 Lead 207 704 million years Uranium 238 Lead 206 4.5 billion years Carbon 14 Nitrogen 14 5730 years Half-Life of an element is the TIME it takes for HALF of the atoms present to RADIOACTIVELY decay into a stable element. Types of Radioactive Decay -100x more penetrating than alpha -Neutron changes to one proton, one electron -Electron is emitted from nucleus -2 protons, 2 neutrons -Helium atom -Emitted from the nucleus -no charge or mass -results in only lost energy -Emitted in Photons -most dangerous form C-14 Decay 1/2 C-14 100% C-14 50% C-14 5730 years 1/4 C-14 1/8 C-14 12.5% C-14 25% C-14 50% N-14 75% N-14 5730 years PARENT = C-14 DAUGHTER = N-14 87.5% N-14 5730 years MOLDS Are “trace fossils” Are not the organisms themselves, but is evidence that the organism has been there Depressions in a surface Smurf Mold EXAMPLES OF MOLDS Lobster Fish Trilobite CASTS Three-dimensional trace of organism Protrudes out of surface of rock EXAMPLES OF CASTS Insect Trilobite Eurobrontes (dinosaur footprints) IMPRINTS Different from molds—are not indented or depressed into its surface Different from casts—do not protrude from surface Thin layer of carbon which forms from where the organism was EXAMPLES OF IMPRINTS Fish Leaf BODY PARTS Actual parts of an organism left behind from the past Example: bones, organisms preserved in amber or ice EXAMPLES OF BODY PARTS A baby mammoth has been uncovered in the permafrost of north-west Siberia. Approx. 9,000 years old. Skull of horned and hornless deer From the Dominican Republic, Miocene epoch (23.8 to 5.3 mya) The 67-million-year-old Tyrannosaurus rex skeleton known as Sue stands on display at Union Station in Wash D.C. Gradualism- pg439 Punctuated Equilibrium-pg439