* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1, Section 5 – The Theory of Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
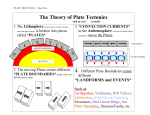
Chapter 1, Section 5 – The Theory of Plate Tectonics *J. Tuzo Wilson: proposed that the lithosphere is broken into sections called plates *Plates carry continents or parts of the ocean floor as they move I. How Plates Move a. Theory of plate tectonics: i. Movement of plates in lithosphere powered by convection currents ii. Plates collide, pull apart, or grind past each other = changes in Earth’s surface 1. creates volcanoes, mountain ranges, and deep ocean trenches iii. plate movement is incredibly slow – only 1 – 24 cm. per year! II. Plate Boundaries a. Extend deep into lithosphere b. Three types: i. Divergent boundary: place where two plates move apart 1. Usually found at mid-ocean ridges where sea-floor spreading occurs 2. Sometimes form a rift valley on land ii. Convergent boundary: place where plates come together/collide 1. density determines which plate slips below the other a. oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust (subduction will occur) b. two plates carrying continental crust will collide and form mountains iii. Transform boundary: two plates slip past each other (moving in opposite directions) 1. earthquakes often occur here