* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
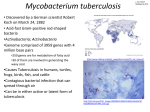
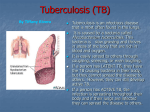
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Mycobacterium leprae Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Bacteria • my·co·bac·te·ri·um too-bur-kyuh-loh-sis • Puss-ball-like appearance • Not gram-stainable • Acid fast stain Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Tuberculosis • Opportunistic pathogen • Is the major contributer to tuberculosis, mostly effects the lungs but can also affect bones, CNS and many organs. The contractors immune health is the largest factor of how strongly they are affected. Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Treatment Active • If you have active TB disease, your doctor will give you several antibiotics to treat the infection and to help prevent resistant bacteria from emerging in your body. You may be taking a combination of antibiotics that may include isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, or ethambutol for 6 to 12 months. Because active TB disease can be fatal if left untreated, regular monitoring and treatment by a doctor are crucial. Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Treatment Resistant • A form of TB, called multidrug-resistant TB, is caused by strains of the tuberculosis bacteria that, through mutation, have developed the ability to resist two or more antibiotic drugs. Worldwide, almost half a million people develop this form of TB annually, and about 150,000 die from this disease. • An even newer form of TB, called extensively drug-resistant TB, resists almost all TB treatments. Fortunately, this form of TB is still relatively rare. Most cases of TB are still highly treatable if the patient follows the full course of antibiotic treatment. Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Pathophysiology • Bacteria in droplets that bypass the mucociliary system and reach the alveoli are quickly surrounded and engulfed by alveolar macrophages. After being ingested by macrophages, the mycobacteria continue to multiply slowly,8 with bacterial cell division occurring every 25 to 32 hours Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis • • • • • • • • • • Presentation Coughing for 3 weeks or longer Weight loss Poor appetite Sweating at night Fever Chills Feeling tired or weak Pain in the chest Coughing up blood or brown-colored material Klebsiella pneumoniae • Gram-negative bacteria • kleb-zee-el-uh noo-mohn-yuh • Responsible for a form of pneumonia Legionella pneumophila • lee-juh-nel-uh pneu-mo-phila • Gram-negative • Responsible for Legionnaires Disease Mycobacterium leprae • My-cobac-terium lep-rae • Gram-negative • Responsible for Hansen’s disease