5.1 .2. Disseminated gonococcal infection
... •Gonococcus create PPNG which can split Beta-Lactam cycle of penicillin through plasmid, that can cause it lose antibiotic effect. •Drug resistance strains caused by chromatosome mutation can change permeability of bacteria cell wall which cause the resistance to penicillin increase to 2-4 times •Th ...
... •Gonococcus create PPNG which can split Beta-Lactam cycle of penicillin through plasmid, that can cause it lose antibiotic effect. •Drug resistance strains caused by chromatosome mutation can change permeability of bacteria cell wall which cause the resistance to penicillin increase to 2-4 times •Th ...
Antibiotic Resistance - e-Bug
... normal/good bacteria. – Many antibiotics prescribed by the doctor are broad spectrum – These kill the body’s good bacteria as well as the bad – With the good bacteria gone there is more room for bad microbes to ...
... normal/good bacteria. – Many antibiotics prescribed by the doctor are broad spectrum – These kill the body’s good bacteria as well as the bad – With the good bacteria gone there is more room for bad microbes to ...
Highlights on antibiotic resistance Antibiotic resistance in
... resistance in these bacteria is defined as resistance to third-generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides. The increasing trend of combined resistance means that, for patients who are infected with these multidrugresistant bacteria, only few therapeutic options remain available, ...
... resistance in these bacteria is defined as resistance to third-generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides. The increasing trend of combined resistance means that, for patients who are infected with these multidrugresistant bacteria, only few therapeutic options remain available, ...
Fight the Resistance
... what is expected for actual rates -- 15 to 36 percent -- of strep throat among kids with sore throat. ...
... what is expected for actual rates -- 15 to 36 percent -- of strep throat among kids with sore throat. ...
Microreviews in Cell and Molecular Biology
... been seen to have a reversal of resistance compared to previous years. Some reports, including some from the World Health Organization (WHO), generated ineffective data in relation to antibiotic resistance [3]. All factors have to be taken into consideration when discussing this issue because extern ...
... been seen to have a reversal of resistance compared to previous years. Some reports, including some from the World Health Organization (WHO), generated ineffective data in relation to antibiotic resistance [3]. All factors have to be taken into consideration when discussing this issue because extern ...
Helicobacter Pylori - Diagnostic Endoscopy Centre
... Twenty percent of people with the organism will develop a peptic ulcer at some time in their life. Presence of Helicobacter increases the risk of stomach cancer by about sevenfold. How is Helicobacter diagnosed? The Helicobacter organism is detected in two ways: By obtaining samples of stomach ...
... Twenty percent of people with the organism will develop a peptic ulcer at some time in their life. Presence of Helicobacter increases the risk of stomach cancer by about sevenfold. How is Helicobacter diagnosed? The Helicobacter organism is detected in two ways: By obtaining samples of stomach ...
McKenna.2011.SciAm.Gram negative resistance
... also across classes (as vancomycin resistance did in the 1990s from Enterococcus to S. aureus, creating VRSA). - They are spreading with particular speed in countries where antibiotics are easily accessed over the counter; before NDM-1 emerged, other carbepenemase resistance was flagged by researche ...
... also across classes (as vancomycin resistance did in the 1990s from Enterococcus to S. aureus, creating VRSA). - They are spreading with particular speed in countries where antibiotics are easily accessed over the counter; before NDM-1 emerged, other carbepenemase resistance was flagged by researche ...
Microbiological Contamination \A\A - B. Braun Melsungen AG
... According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), MRSA currently causes about 1 % of all staphylococcus infections and more than 50 % of health-care associated staphylococcus infections. After Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus is the second most common pathogen causi ...
... According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), MRSA currently causes about 1 % of all staphylococcus infections and more than 50 % of health-care associated staphylococcus infections. After Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus is the second most common pathogen causi ...
marbocyl 10
... Indications: In cattle: Treatment of respiratory infections caused by sensitive strains of Pasteurella multocida, Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica and Mycoplasma bovis. Treatment of acute mastitis caused by E. coli strains sensitive to marbofloxacin during the lactation period. In sows: Treatmen ...
... Indications: In cattle: Treatment of respiratory infections caused by sensitive strains of Pasteurella multocida, Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica and Mycoplasma bovis. Treatment of acute mastitis caused by E. coli strains sensitive to marbofloxacin during the lactation period. In sows: Treatmen ...
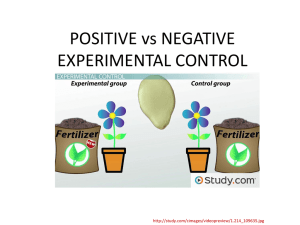
Positive vs Negative controls
... any bacterial growth on this plate. If you do, it is an indication that your swabs, plates, or incubator are contaminated with bacteria that could interfere with the results of the experiment. POSITIVE CONTROL: Wipe a swab on an existing colony of bacteria and wipe it on the growth plate. Shows your ...
... any bacterial growth on this plate. If you do, it is an indication that your swabs, plates, or incubator are contaminated with bacteria that could interfere with the results of the experiment. POSITIVE CONTROL: Wipe a swab on an existing colony of bacteria and wipe it on the growth plate. Shows your ...
basics
... Goal of treatment is the eradication of Brucella canis from the animal (as indicated by a decline in antibodies to negative status [seronegative status] and no bacteria in the blood [bacteremia] for at least 3 months), but sometimes the result of treatment is persistent low antibody titers, with n ...
... Goal of treatment is the eradication of Brucella canis from the animal (as indicated by a decline in antibodies to negative status [seronegative status] and no bacteria in the blood [bacteremia] for at least 3 months), but sometimes the result of treatment is persistent low antibody titers, with n ...
Top margin 1
... antibiotics slowed the epidemic in Europe in the 1950s-1970s, it is again becoming a public health issue due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains which contaminate 490,000 people each year, particularly in the former Soviet Union. This infectious disease spreads very quickly since it is s ...
... antibiotics slowed the epidemic in Europe in the 1950s-1970s, it is again becoming a public health issue due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains which contaminate 490,000 people each year, particularly in the former Soviet Union. This infectious disease spreads very quickly since it is s ...
Top margin 1
... antibiotics slowed the epidemic in Europe in the 1950s-1970s, it is again becoming a public health issue due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains which contaminate 490,000 people each year, particularly in the former Soviet Union. This infectious disease spreads very quickly since it is s ...
... antibiotics slowed the epidemic in Europe in the 1950s-1970s, it is again becoming a public health issue due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains which contaminate 490,000 people each year, particularly in the former Soviet Union. This infectious disease spreads very quickly since it is s ...
New medicine to help in the fight against - EMA
... European Union (EU) for Zavicefta (ceftazidime/avibactam), a new treatment option against multi-drug resistant bacteria. The lack of availability of medicines to treat patients with infections caused by resistant bacteria has become a major problem in recent years. It is estimated that at least 25,0 ...
... European Union (EU) for Zavicefta (ceftazidime/avibactam), a new treatment option against multi-drug resistant bacteria. The lack of availability of medicines to treat patients with infections caused by resistant bacteria has become a major problem in recent years. It is estimated that at least 25,0 ...
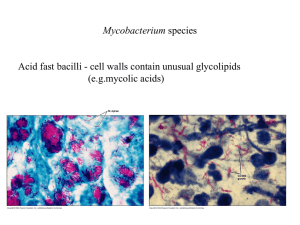
Tuberculosis
... Tuberculosis Know the facts. What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, also called TB, is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attacks the lungs but it can also affect other parts of the body and can be fatal if not treated properly. TB is spread through the air when so ...
... Tuberculosis Know the facts. What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, also called TB, is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attacks the lungs but it can also affect other parts of the body and can be fatal if not treated properly. TB is spread through the air when so ...
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
... • If you have active TB disease, your doctor will give you several antibiotics to treat the infection and to help prevent resistant bacteria from emerging in your body. You may be taking a combination of antibiotics that may include isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, or ethambutol for 6 to 12 months ...
... • If you have active TB disease, your doctor will give you several antibiotics to treat the infection and to help prevent resistant bacteria from emerging in your body. You may be taking a combination of antibiotics that may include isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, or ethambutol for 6 to 12 months ...
Session 2 Presentation: Introduction to DR TB
... usually mean that a patient yielding such organisms would fail to respond to treatment with the drug concerned in normal dosage, i.e. a dosage that will cause a response in patients infected with sensitive organisms.” – Mitchison DA. “What is drug resistance?” Tubercle Suppl 1969; 50: 44-47. ...
... usually mean that a patient yielding such organisms would fail to respond to treatment with the drug concerned in normal dosage, i.e. a dosage that will cause a response in patients infected with sensitive organisms.” – Mitchison DA. “What is drug resistance?” Tubercle Suppl 1969; 50: 44-47. ...
Tuberculosis
... - resistance occurs by inactivation of catalaseperoxidase or by mutation of enzyme in mycolic acid synthesis pathway ...
... - resistance occurs by inactivation of catalaseperoxidase or by mutation of enzyme in mycolic acid synthesis pathway ...