* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T.R.
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Mycobacterium tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
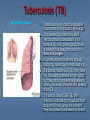
Tuberculosis (TB) By Tiffany Rivera Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that is most often found in the lungs. It is caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This bacteria is slow growing and thrives in areas of the body that are rich in blood and oxygen. It is easily spread to others through coughing, sneezing, or even laughing. If a person has LATENT TB, they have the TB causing bacteria in their body, but they cannot spread the disease to others. However, they can still develop active TB. If a person has ACTIVE TB, the infection is spreading throughout their body and if their lungs are infected they can spread the disease to others. TB most often attacks the lungs (as pulmonary TB) but can also affect the central nervous system, the lymphatic system, the circulatory system, the genitourinary system, bones, joints and even the skin. Symptoms of TB include chest pain, coughing up blood, a prolonged cough for more than three weeks, fever, chills, night sweats, appetite loss, weight loss, paleness, and fatigue. TB is most common in Africa and Asia. TB was found in humans as early as the ancient Egyptians in 2400 BCE. It was one of the main causes of death in the 1920’s, but then seemed to diminish. It made a comeback in recent years, affecting HIV patients and killing them due to their weakened immune systems. Treatment for TB uses antibiotics to kill the bacteria. The two antibiotics most commonly used are rifampicin and isoniazid. It takes 6 to 9 months to entirely eliminate the mycobacteria from the body. The tuberculosis skin test (also known as the PPD test) is a test used to determine if someone has developed an immune response to the bacterium that causes TB. This response can occur if someone currently has TB or if they were exposed to it in the past. Many famous writers have died as a result of having TB. Charlotte Bronte (the author of Jane Eyre), and Robert Luis Stevenson (the author of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde) were among these famous writers.