* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
ContactPoint wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
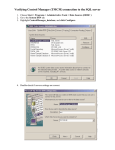
OnDemand Operations Document ODBC Access Reqest BMC Remedy OnDemand June, 2012 BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Table of Contents Table Of Contents ___________________________________________________________________________________ 1 Document History ___________________________________________________________________________________ 2 Introduction ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3 How do Applications Access the Data ___________________________________________________________________ 3 Using a Firewall System with SQL Server Database Engine _________________________________________________ 3 Generic Network Diagram _____________________________________________________________________________ 5 Process Flow _______________________________________________________________________________________ 6 Process Description _________________________________________________________________________________ 7 Considerations ______________________________________________________________________________________ 7 How to Create ODBC DSN ? ___________________________________________________________________________ 8 Customer Sign-Off _________________________________________________________________________________ 12 Basic Design and Implementation _____________________________________________________________________ 13 Information Requirement.....................................................................................................................................................13 FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 1 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Document History S.No. 1 Document Change Created Initial Document Modified By Moin Ul Haque Africawala Modification Date Version June-2012 Draft 2 3 4 FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 2 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Introduction ODBC, Open Database Connectivity, is an open standard method of accessing data. The data to be accessed needs an interpreter (driver), which understands the format of the stored data, and a connection manager that determines how the connection needs to be made. All this information is stored in a so-called Data Source Name (DSN). Data Source simply means where the data is kept. It can be a file — typically, a database on a Database Management System (DBMS) — or even a live data feed. The purpose of a Data Source is to gather all the technical information needed to access the data — the driver name, network address, network software, and so on — into a single place and make the data access transparent to the user. For example, a user should be able to look at a list of databases — that could include Payroll, Inventory and Employees — choose Payroll from the list, and have the application connect to the payroll data, all without knowing where the payroll data resides or how the application got to it. How do Applications access the Data? When an application needs to access the data from those databases, it calls the Driver Manager and passes the name of the machine Data Source or the path of the file Data Source – depending on what is being used. When a machine Data Source name is passed, the Driver Manager searches the system to find the driver used by the Data Source. It then loads the driver and passes the Data Source name to it. The driver uses the Data Source Name to find the information it needs to connect to the Data Source. Finally, it connects to the Data Source, typically prompting the user for a user ID and password, which, generally, are not stored. When a file Data Source is passed, the Driver Manager opens the file and loads the specified driver. If the file also contains a connection string, it passes this to the driver. Using the information in the connection string, the driver connects to the Data Source. If no connection string is passed, the driver generally prompts the user for the necessary information. Using a Firewall System with SQL Server Database Engine Many companies use a firewall system to isolate their networks from unauthorized access from the Internet. A firewall can be used to restrict access to your network by forwarding only requests targeted at specific TCP/IP addresses in the local network. Requests for all other network addresses are blocked by the firewall. You can allow Internet applications to access an instance of the SQL Server Database Engine in the local network by configuring the firewall to forward network requests that specify the network address of the instance of the Database Engine. FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 3 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request To work with a firewall, the instance of the Database Engine must listen on the network address that the firewall is configured to forward. A TCP/IP network address for SQL Server Database Engine consists of two parts: an IP address associated with one or more network cards in a computer, and a TCP port address specific to an instance of SQL Server. Default instances of the Database Engine use TCP port 1433 by default. Named instances, however, dynamically assign an unused TCP port number the first time the instance is started. The named instance can also dynamically change its TCP port address on a later startup if the original TCP port number is being used by another application. SQL Server only dynamically changes to an unused TCP port if the port it is currently listening on was itself dynamically selected; if a statically assigned port is in use by another application, SQL Server displays an error and continues to listen on other ports. It is unlikely, however, that another application would use 1433 since that port is a well-known registered address for the SQL Server Database Engine. When using a named instance of Database Engine with a firewall, use SQL Server Configuration Manager to configure the named instance to listen on a specific TCP port. You must pick a TCP port that is not used by another application running on the same computer or cluster. The network administrator should configure the firewall to forward communication to SQL Server for the IP address and TCP port that the instance of the Database Engine is listening on (either TCP port 1433 for a default instance, or the TCP port you configured for a named instance). Also, because Microsoft SQL Server uses UDP port 1434 to establish communications links from applications, have the network administrator configure the firewall to forward requests for UDP port 1434 on the same IP address. For example, consider a computer running one default instance and two named instances of the SQL Server Database Engine. The computer is configured such that the network addresses that the three instances listen on all have the same IP address. The default instance would listen on TCP port 1433, while the other named instances could listen on TCP ports 1434 and 1954, respectively. The network administrator would then configure the firewall to forward network requests for UDP port 1434 and TCP ports 1433, 1434, and 1954 on that IP address. FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 4 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Generic Network Diagram Customer Computer Customer Firewall / NAT Customer Switch Customer Router Internet BMC Router BMC Firewall / NAT BMC Switch BMC Database Server FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 5 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Process Flow ODBC Access Request Customer Start Customer Change Process End N Customer Sends ODBC Request / Information Customer Receives Information for Change Customer Security Sign-Off ? (Y / N) Test Changes Successful ? (Y / N) Y End Y BMC Y BMC Receives Request/ Information BMC Documents the information required for the Change BMC Security Sign-Off ? (Y / N) N N Notify Customer of Access Deniel End BMC Change Process FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 6 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Process Description 1) Gather information from customer of what is the exact requirement and how many nodes will be involved in using this privileged access to the BMC Databases. 2) After the information is received, get approval from BMC Security Group Manager. 3) If the Request is denied, then ODBC Access will not be granted. 4) Once approval is received from the BMC Security Group manager, a Customer representative needs to sign off (see customer sign off shown below) and acknowledge the risk associated with the opening of firewall ports on their end and also has to accept the impact / liability of any data loss in the interim. 5) Once approval and customer sign-off are received from both BMC Security Group Manager and the Customer Representative, then all required information (see Information Requirements shown below) needs to be gathered to process the request made to the technical support team for completion of activities associated with opening the firewall ports and getting credentials for database access. 6) A change request needs to be opened and assigned to the BMC Security team with all required customer information, as well as the current SQL Server port to be used for firewall port configuration. 7) A Service Request needs to be opened and assigned to the Database Team for creating Read-only Access to the Reporting Database of the customer. (Please refer to Database Access Request). 8) Once all activities have been completed, credentials are shared with the customer. 9) Once the customer receives the credentials for database access, then they will need to test connectivity. Considerations 1) ODBC connectivity can only be granted to those customers who have purchased the Dashboard and Analytics Product or the Reporting Server Product. 2) ODBC access will only be provided to the Reporting Database (Daily Snapshot of the Production Database) and not the actual Production Database. FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 7 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request How to Create ODBC DSN ? (1) If creating ODBC on Windows Server Click Start --> Administrative Tool --> Data Sources (ODBC). If creating ODBC on a Windows 7 machine Click Start --> Type ODBC --> Click Data Sources (ODBC) [ as shown below] (2) ODBC Data Source Administrator will pop-up. Click Add to Create a new User DSN. (3) Select SQL Server and Click Finish. FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 8 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request (4) Type in the Name of the DSN you wish to have and Enter the SQL Server Name / IP you wish to connect to. Click Next. (5) Now Select (With SQL Server authentication using a login ID and password entered by the user ). Now enter Database Login ID and Password. Click Next. (Note : If the network connection is successful, then after hitting Next you will be prompted for next screen else it will give you an error, stating unable to make connection to the server / credentials provided.) FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 9 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request (6) Under "Change the default database to:) put in the name of the database provided to you when the credential information is shared. Click Next. (7) Click Finish.. (8) After clicking finish you will get a confirmation page, where you can test the connectivity of the New Data Source Created. Click "Test Data Source"... FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 10 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request (9) If the entered information is correct the Test will be successful. Click OK. (10) You can see the New User DSN we just created under the List. FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 11 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Customer Sign-Off The customer understands and accepts the security risk associated with opening the firewall port. The customer is responsible for any data loss while connected to the database. The customer is responsible for any negative impact made on the system (example: fetching large amounts of datasets which can choke server performance). The customer will not misuse the access credentials. If a high-privileged account is being used for setting up ODBC, then the customer is accountable and accepts the responsibility for any data changes made abruptly / accidently. The customer understands that the access granted to them is on a shared server and the risk associated with the access is very high, therefore the customer agrees to use extreme caution while connected to the database. BMC will not be held accountable for any data changes occurred during this process. I understand the risks, and agree to accept responsibility and accountability for all the information shown above. Company Name: ________________________________ Customer Representative/Title: ________________________________ Signature: ___________________ Date: ___________________ FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 12 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL BMC Remedy on Demand ODBC Access Request Basic Design and Implementation Information Requirements 1) IP Address Information (Customer). 2) IP Address Information (BMC). 3) SQL Server Port Number (BMC). 4) SQL Server Database Information (BMC). 5) Generic SQL ID creation (BMC needs to know of any naming convention to follow). Above information is required in order to fulfill the change. BMC will provide with the information required and Customer has to implement the change on their end. BMC Network team will work on their end to make sure that all the required information and action is carried out so that the customer will be able to execute their task as required. Once everything is setup, BMC database Team will create a generic ID and will share the credentials to the customer to check the connectivity on their end. FOR INTERNAL USE ONLY PAGE 13 OF 13 CONFIDENTIAL Business runs on IT. IT runs on BMC Software. Business thrives when IT runs smarter, faster, and stronger. That’s why the most demanding IT organizations in the world rely on BMC Software across both distributed and mainframe environments. Recognized as the leader in Business Service Management, BMC offers a comprehensive approach and unified platform that helps IT organizations cut cost, reduce risk and drive business profit. For the four fiscal quarters ended September 30, 2008, BMC revenue was approximately $1.83 billion. Visit www.bmc.com for more information.