* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thevenin and Max Power
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
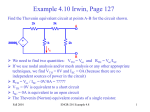
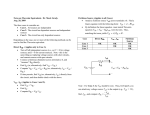
EE301 AC Thèvenin and Max Power Transfer Learning Objectives Apply Thèvenin’s Theorem to AC circuits Explain under what conditions a source transfers maximum power to a load Determine the value of load impedance for which maximum power is transferred from the circuit Thévenin’s theorem for AC ETh is the open circuit voltage at the terminals, ZTh is the input or equivalent resistance at the terminals when the independent sources are turned off. Review Determining ETh Remove the load (open-circuit) and measure the resulting voltage. Eth = open ckt voltage Determining ZTh With the load disconnected, turn off all independent sources. sources – 0 V is equivalent to a short-circuit. Current sources – 0 A is equivalent to a open-circuit. Voltage ZTh is the equivalent resistance looking into the “dead” circuit through terminals a-b. Zth Applying Thévenin equivalent Once ETh and ZTh have been found, the original circuit is replaced by its equivalent and solving for ILD and VLD becomes trivial. I LD ETh = ZTh + Z LD VLD Z LD = ETh ZTh + Z LD Example Problem 1 Convert the source below into a Thévenin equivalent and determine the current through load Zab. Example Problem 2 Convert the source below into a Thévenin equivalent. ZLOAD Example Problem 3 Convert the source below into a Thévenin equivalent and determine the power dissipated by the load. Conjugates The conjugate of C is written as C*, which has the same real value but the opposite imaginary part: C a jb C C a jb C Review Review Maximum power transfer theorem Maximum power is transferred to the load when RLD = RTh. PMAX E 2 Th 4 RTh Max Power Transfer in AC Circuits In AC circuits, max power transfer occurs when load impedance (ZL) is the complex conjugate of the Thévinin equivalent impedance (ZTh). ZTH RTH jX TH Z LD RLD jX LD This means the load has a capacitor if the Thèvenin impedance includes an inductor XLD cancels out XTH! Max Power Transfer in AC Circuits Since RLD=RTH, and the reactances cancel out, the resulting PMAX equation is the same as with DC! Z LD RLD jX LD IL ZTH RTH jX TH ETh ETh ZTh Z LD ( RTh RLD ) j ( X Th X LD ) ETh ETh E Th since RTh RLD RTh RLD RTh RTh 2 RTh 2 PL I L2 RLD ETh2 4 RTh ETh ETh2 RTh RLD 2 4 RTh 2 RTh Max Power Transfer in AC Circuits #1 Mistake with AC Max Power is not using the REAL value of resistance when calculating Pmax Transform ZTH into rectangular form to determine RTH ZTH ZXTH RTH jX TH Pmax ETh2 when Z LD ZTh 4 RTh Example Problem 4 Determine the load ZLOAD that will allow maximum power to be delivered to the load the circuit below. Find the power dissipated by the load. Example Problem 5 Determine the load ZLD that will allow maximum power to be delivered to the load the circuit below. Frequency is 191.15 Hz. Find the maximum power. What will happen to power if the frequency is changed to 95.575?