* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sedimentary Rocks 1
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Ore genesis wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
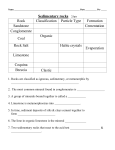
GL4 E1 Key Idea 2 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS The mineralogy and texture of sedimentary rocks are controlled by processes of weathering, erosion and deposition GL4 E1 KI2 a Immature sedimentary rocks are characterised by a wide range of mineral compositions and/or lithic clasts; Mature sedimentary rocks have restricted mineralogies dominated by mineral species resistant to weathering and erosional processes Breccia Sedimentary (fragmental) Immature (wide range of fragments) Angular fragments (little transport) Fragments range in size consider energy current (landslide?) Credit: British Geological Society Immature/Mature Immature rocks - contain easily weathered minerals (eg. first formed minerals from Bowen’s Reaction Series) Immature rocks – normally very little transport (hence angular fragments), poorly sorted Mature rocks – mainly quartz (low temperature minerals from Bowen’s Reaction Series) Mature rocks - fragments often rounded due to long history of weathering and erosion to remove majority of minerals, well sorted Fragment size/shape Longer transport will reduce fragment size and will round fragment shape Geoscience page 88 figure 5.21 (b) and (c) COPY We need to look more closely at Mature sedimentary rocks Why? In order to think of the processes which destroy minerals!