* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homeostasis- maintaining stable, constant internal environments
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
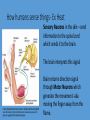
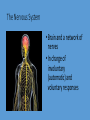
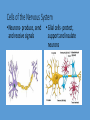
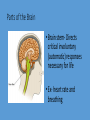
Homeostasis- maintaining stable, constant internal environments • 2 things are required for homeostasis• 1- organism must be able to sense when changes have taken place in the external and internal environments • 2- must be able to respond with appropriate adjustments to keep internal environment stable. How humans sense things- Ex Heat Sensory Neurons in the skin – send information to the spinal cord which sends it to the brain. The brain interprets this signal Brain returns direction signal through Motor Neurons which generate the movement- aka moving the finger away from the flame. The Nervous System • Brain and a network of nerves • In charge of involuntary (automatic) and voluntary responses Cells of the Nervous System • Neurons- produce, send and receive signals • Glial cells- protect, support and insulate neurons Parts of the Brain • Brain stem- Directs critical involuntary (automatic) responses necessary for life • Ex- heart rate and breathing Parts of the brain • Cerebellum- balance and posture • Cerebrum- conscious though, language, voluntary movement Parts of the Brain • Hypothalamusregulates physiological processes important to homeostasis • Ex- water balance, body temperature, feeding and sleep • Also part of the Endocrine system Endocrine System • In charge of hormones – “chemical messengers” • Hormones play a large role in homeostasis • Ex- regulate sugar balance Hormones • Travel through the blood • Only work on cells that have that specific hormone’s receptor • Receptors- proteins on the cell membrane that are shaped to fit the hormone. How it works- Dehydration • 1- Sensory Neurons detect water • 4- The receptors simulate shortage due to amount of the kidney cells to reabsorb sodium in the blood water • 2- Neurons in the Hypothalamus simulate the release of a • At the same time the hormone Vasopression from the Endocrine systems is Pituitary gland working the nervous system • 3- Hormone travels through the can also trigger thirst. blood until it hits the kidney cells Then what? • How does the body know when to stop producing Vasopressin? • Feedback systems are established through out the body • 2 types of feedback systems Negative Feedback • Body uses this system to shut off the response the body has started • Ex- once the water balance has been regained the body signals the hypothalamus to reduce the release of Vasopressin Positive Feedback • Adjusts internal conditions towards initial conditionaka it makes initial change keep happening till its complete • Ex- Small clot forms due to bleeding positive feedback causes more clotting factors to build up increasing the blood clot size