* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unix and shell programming
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Computer terminal wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
MTS system architecture wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
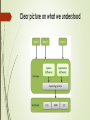
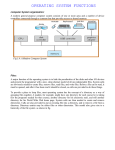
Unix and shell programming - 15CS35 SEMESTER – III 04-08-2016 Syllabus and course outcomes Link for syllabus Operating system The operating system (OS) is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs and applications. It is like a traffic cop -- it makes sure that different programs and users running at the same time do not interfere with each other. The operating system is also responsible for security, it ensuring that unauthorized users do not access the system. Diagram Classification of Operating systems Multi-user: Allows two or more users to run programs at the same time. Some operating systems permit hundreds or even thousands of concurrent users. Multiprocessing : Supports running a program on more than one CPU. Multitasking : Allows more than one program to run concurrently. Multithreading : Allows different parts of a single program to run concurrently. Real time: Responds to input instantly. overview Operating systems provide a software platform on top of which other programs, called application programs, can run The application programs must be written to run on top of a particular operating system. Interacting With the Operating System As a user, you normally interact with the operating system through a set of commands. For example, the DOS operating system contains commands such as COPY and RENAME for copying files and changing the names of files, respectively The commands are accepted and executed by a part of the operating system called thecommand processor or command line interpreter. Graphical user interfaces allow you to enter commands by pointing and clicking at objects that appear on the screen. System A group of interdependent items that interact regularly to perform a task. A computer system refers to the hardware and software components that run a computer or computers. An information system is a system that collects and stores data. System often simply refers to the operating system. Operating system Definition An operating system (OS) Is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. Application programs usually require an operating system to function. Types of operating systems Single- and multi-tasking A single-tasking system can only run one program at a time, while a multi-tasking operating system allows more than one program to be running in concurrency. Single- and multi-user Single-user operating systems have no facilities to distinguish users, but may allow multiple programs to run. A multi-user operating system extends the basic concept of multi-tasking with facilities that identify processes and resources Continued….. Distributed A distributed operating system manages a group of distinct computers and makes them appear to be a single computer. Embedded Embedded operating systems are designed to be used in embedded computer systems. They are designed to operate on small machines Clear picture on what we understood Memory Management Memory management refers to management of Primary Memory or Main Memory. Main memory is a large array of words or bytes where each word or byte has its own address. Main memory provides a fast storage that can be accessed directly by the CPU. For a program to be executed, it must in the main memory. Allocates the memory and De-allocates the memory Processor Management In multiprogramming environment, the OS decides which process gets the processor when and for how much time. This function is called process scheduling. An operating system keep track of Keeps tracks of processor and status of process.. Also it Allocates and De-allocates the processor (CPU) to a process. Device Management An Operating System manages device communication via their respective drivers. OS does: Keeps tracks of all devices. Program responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. Decides which process gets the device when and for how much time. Allocates the device in the efficient way and De-allocates devices. File Management A file system is normally organized into directories for easy navigation and usage. These directories may contain files and other directions. OS does: Keeps track of information, location, uses, status etc. The collective facilities are often known as file system. Decides who gets the resources. Allocates the resources. De-allocates the resources. Other Important Activities of OS Security Control over system performance Job accounting Error detecting aids Coordination between other software's and users Components of Unix System Unix Operating System has primarily three components Kernel − Kernel is the core part of Linux. It is responsible for all major activities of this operating system. It consists of various modules and it interacts directly with the underlying hardware. System Library − System libraries are special functions or programs using which application programs or system utilities accesses Kernel's features. System Utility − System Utility programs are responsible to do specialized, individual level tasks. What is Unix ? The UNIX operating system is a set of programs that act as a link between the computer and the user. The computer programs that allocate the system resources and coordinate all the details of the computer's internals is called the operating system or kernel. Users communicates with the kernel through a program known as the shell. The shell is a command line interpreter; it translates commands entered by the user and converts them into a language that is understood by the kernel. Unix was originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie Continued… There are various Unix variants available in the market. Solaris Unix, AIX, HP Unix and BSD are few examples. Linux is also a flavor of Unix which is freely available. Several people can use a UNIX computer at the same time; hence UNIX is called a multiuser system. A user can also run multiple programs at the same time; hence UNIX is called multitasking. Following are some of the important features of Unix Operating System Portable Open Source Multi-User Multiprogramming Hierarchical File System Shell Security ARCHITECTURE Unix Architecture Components Kernel: The kernel is the heart of the operating system. It interacts with hardware and most of the tasks like memory management, task scheduling and file management. Shell: The shell is the utility that processes your requests. When you type in a command at your terminal, the shell interprets the command and calls the program that you want. C Shell, Bourne Shell and Korn Shell are most famous shells which are available with most of the Unix variants. Continued… Commands and Utilities: There are various command and utilities which you would use in your day to day activities. cp, mv, cat and grep etc. Files and Directories: All data in UNIX is organized into files. All files are organized into directories. These directories are organized into a tree-like structure called the file system. Features Main Features of UNIX This section contains a brief overview of the main features of UNIX. multi-user more than one user can use the machine at a time supported via terminals (serial or network connection) multi-tasking, more than one program can be run at a time hierarchical directory structure, to support the organization and maintenance of files portability Hierarchical File System 28 29 Shells What is a shell? A command interpreter “protects you from the kernel” It really protects the kernel from you FSU COP 4342 Unix Tools Spring 2004 30 Many Shells Bourne shell (sh) Creator Steve Bourne in the early 80’s First shell Used for shell programming C shell (csh) Created at UCB their Unix implementation in the early 80’s Users wanted more familiar syntax More features (for interactive uses) than sh (e.g. job control and history) 31 Many Shells Korn shell (ksh) Created by David Korn in the mid 80’s Compatible with sh but having most features of csh Features history editing (a.k.a. command-line editing) Was available on System V Public-domain version is pdksh T-shell (tcsh) has all csh features and less bugs Bourne-again shell (bash) Offered by FSF (free software foundation) Similar to ksh and csh Command-line editing 32 What’s my shell? Check your prompt Usually bash uses $ Usually csh uses % Usually tcsh uses > Superuser “root” usually is # UNIX Commands Structure To give a command to a UNIX system you type the name of the command, along with any associated information, such as a filename, and press the <Return> key. The typed line is called the command line UNIX uses a special program, called the shell or the command line interpreter The components of the command line are: the command; any options required by the command the command's arguments (if required). For example, the general form of a UNIX command is: command [-option(s)] [argument(s)] POSIX Single UNIX Specification Unix Commands UNIX commands: – Internal (builtin) and external command Some commands are internal, built into the shell. cd command is built-in. (the shell interprets that command and changes your current directory). ls command is an external program stored in the file /bin/ls. • The shell does not start a separate process to run internal commands. External commands require the shell to fork and exec a new sub process; this takes some time, especially on a busy system. Check a command is internal or external: – $type cd – cd is a shell builtin Internal and External Commands Unix commands are grouped into two categories-Internal and External. Internal There is a set of commands which are part of the shell and to execute them the shell does not need to search the given path in the PATH variable. These are also called shell builtins or Internal Commands. External Commands that are available as independently compiled C programs usually located in the /bin or the /usr/bin directory are called External Commands. 37 Internal and External Commands Internal commands built into the shell the shell performs the command E.g. chdir or cd External commands Require the shell to fork and exec and a subprocess will start E.g. ls FSU COP 4342 Unix Tools Spring 2004 Continued… Example: $ type ls ls is /bin/ls the above command returns the location or the path of the ls command .Therefore ls is an external command. $ type echo echo is a shell builtin the 'echo' command is an Internal Command or a shell builtin. $ type LS LS: not found 39 Summary on same…!! Shell checks what type of command the user is trying to run Check if built-in Else check if absolute path Else check alias (except bash) Check for executable in search path Search path is a list of dir that the shell must check An environment variable PATH lists these dir Look at an example Search path is specified in the shell start up files System Boot-up If you have a computer which has UNIX operating system installed on it, then you simply need to turn on its power to make it live. As soon as you turn on the power, system starts booting up and finally it prompts you to log into the system, which is an activity to log into the system and use it for your day to day activities. Login Unix To log in Have your userid (user identification) and password ready. Contact your system administrator if you don't have these yet. Type your userid at the login prompt, then press ENTER. Your userid is case-sensitive, so be sure you type it exactly as your system administrator instructed. Type your password at the password prompt, then press ENTER. Your password is also case-sensitive. If you provided correct userid and password then you would be allowed to enter into the system. Read the information and messages that come up on the screen something as below. UI to check calendar you need to type cal command as follows − Change Password All Unix systems require passwords to help ensure that your files and data remain your own and that the system itself is secure from hackers and crackers. Here are the steps to change your password − To start, type passwd at command prompt as shown below. Enter your old password the one you're currently using. Type in your new password. Always keep your password complex enough so that no body can guess it. But make sure, you remember it. You would need to verify the password by typing it again. UI Listing Directories and Files All data in UNIX is organized into files. All files are organized into directories. These directories are organized into a tree-like structure called the file system You can use ls command to list out all the files Following is the example of using ls command with -l option. UI Who Are You? While you're logged in to the system, you might be willing to know : Who am I? The easiest way to find out "who you are" is to enter the who am i command − Who is Logged In? Sometime you might be interested to know who is logged in to the computer at the same time. There are three commands are available to get you this information, based on how much you'd like to learn about the other users: users, who, and w. Logging Out When you finish your session, you need to log out of the system to ensure that nobody else accesses your files while masquerading as you. just type logout command at command prompt, and the system will clean up everything and break the connection System Shutdown Flexibility in using commands $Wc note; ls –l note Command line can overflow $echo “ this is >a three line >text message” o/p This is A three line Text message To break – press ctrl+z When things go wrong Terminal and keyboard have no uniform behaviroul pattern Backspacing will not work all time Wen you use backspace u can see ^H^H Ctrl+h or delete hey Killing a line Ctrl+u Break by Ctrl+d Ctrl+z Knowing the user terminal About tty Print the file name of the terminal connected to standard input. tty syntax tty [OPTION]... Options -s, --silent, --quiet Print nothing, only return an exit status. --help display this help and exit. --version output version information and exit. Continued…. tty examples $tty Running tty by itself will display the current tty session as shown below: /dev/pts/0 stty About stty $Stty changes and prints terminal line settings. Description stty displays or changes the characteristics of the terminal. displaying its characteristics and setting characteristics Root root is the user name or account that by default has access to all commands and files on a Linux or other Unix-like operating system. The root directory, which is the top level directory on a system That is, it is the directory in which all other directories, including their subdirectories and files reside. The root directory is designated by a forward slash ( / ). Root privileges are the powers that the root account has on the system. root's powers are the ability to modify the system in any way desired and to grant and revoke access permissions Login in terminal Su: Acquiring superuser status $su Password:****** #pwd /home/sh Prompt changes but directory dosen’t From super user access we can switch to other user by using $su – username Without password Administrators Privileges Change the contents or attributes of any file like its permissions and ownerships He can delete the file even if the directory is write protected Initiate or kill any process Change any user password without knowing the existing one Set system clock with date Address all users concurrently ----- wall Limit the file size fir each users Control overall access with FTP as well. Date setting Wall : communicating with users It address all users simultaneously #wall Welcome all for the day 3 session All the user who are currently logged in will this message Ulimit Restricts the size As super user we can also modify the same. Continued… user management Creating the user involves the following parameters UID and user Name GID and group name The home directory The login shell Mailbox in var/mail The password ----------------------------------------------------- Most of these are found in single line identifying the user in /etc/passwd useradd and usermod , userdel Adds the new user to the system All parameters related to the user should be provided in command line Example: #useradd –u 210 –g dba –c “the rdbms” –d /home/oracle –s /bin/ksh – m oracle Usermod and userdel #usermod #userdel /etc/passwd and /etc/shadow All user information except the password encryption is now stored in /etc/passwd The encryption itself is stored in /etc/shadow Discussions Thank you