* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 1 Geometry Basic Constructions
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of the compass wikipedia , lookup
Cardinal direction wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
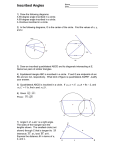
Name_________________________________ Date UNIT 1 Geometry Page 2 Opening Exercise Page 3 Definition of Circle Pages 4-5 Basic Constructions: Practice using the Compass Pages 6-10 Perpendicular Bisectors Pages 11-13 Bisecting an Angle Pages 14-15 Copying an angle Pages 16-18 Constructing an Equilateral Triangle Pages 19-21 Constructing an Equilateral Triangle Inscribed in a Circle Pages 22-23 Constructing a line perpendicular to another line through a given point Pages 24-26 Constructing a line parallel to another line through a given point Pages 27-30 Constructing a Square Inscribed in a Circle Page 31 Constructing a Rectangle that is not a square inside a circle Pages 32-34 Constructing Triangle Midsegments Online Activity Page 35 Constructing the Median of a Triangle 1 Name_____________________________ Date Opening Exercise Materials needed: Ruler, pencil Directions: 1.) There is a point on your paper labeled P 2.) Plot 20 points that are exactly 3 inches away from point P 2 On the previous page, you should have ended up with something that either looked like a circle or was becoming a circle. If you kept on plotting points, you would eventually have a circle. Definition of Circle: 3 Next, we are going to start CONSTRUCTIONS What is a Construction? Activity Materials needed: Compass, Straight edge, pencil Directions: Using this page and the next, construct 8 circles with each having a different radius. Label the center point of each circle with a letter. 4 5 Name________________________________ Date: Opening Exercise Plot 20 points that are exactly the same distance from both points A and B 6 Name___________________________ Date: PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS LINE SEGMENT: PERPENDICULAR: 7 BISECTOR: Line segment DE is bisecting line AC 8 Constructing the Perpendicular Bisector of Line Segment Activity: Using the steps below construct the perpendicular bisector of line segment AB 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Place the compass at one end of line segment. Adjust the compass to slightly longer than half the line segment length. Draw a circle with the center being the end point Keeping the same compass width, draw a circle with the center being the other end point. Place ruler where the circles cross, and draw the line segment. Do the 2 circles that you drew have the same radius? _____ 9 Directions: Construct the perpendicular bisector of Line segment AB. 1.)Label the point where the line segments intersect as C 2.) Label the endpoints of the line you drew D and E State 2 angles that are 90 degrees __________ and __________ Do the 2 circles that you drew have the same radius? _____ Is point D the same distance from A that it is from B? _____ How do we know? Point D is on both circles with centers A and B. Since the circles are equal, the radii are equal. 10 Name____________________ Date: Bisecting an Angle Angle: FACTS ABOUT ANGLES 1.) Angles that are less than 90 degrees are called _____________________ 2.) Angles that are Greater than 90 degrees are called ________________________ 3.) Angles that EXACTLY 90 degrees are called ______________________________ 4.) The three interior angles of every Triangle add up to ________________________ 5.) The four interior angles of every 4 sided figure (Quadrilateral) add up to ______________ 6.) A straight line is ___________________________ 7.) A circle is ____________________________ 8.) When two angles add up to 180 degrees, they are called ______________________________ 9.) When two angles add up to 90 degrees, they are called ______________________________ 11 Activity: Using the steps below construct the angle bisector of angle ABC 1.)Draw an circle that is centered at the vertex of the angle. This circle can have a radius of any length. However, it must intersect both sides of the angle. ** We will call these intersection points P and Q . This provides a point on each line that is an equal distance from the vertex of the angle. 2.) Draw a circle centered at point P with the same radius 3.) Draw a circle centered at point Q with the same radius 4.) Draw the bisector through the intersection point of the two circles. 12 Practice Constructing the ANGLE BISECTOR 13 How to Copy an angle 1.) Draw a ray that will be one of the sides of the new angle and label the end point P 2.) On the original angle, draw a circle with the center being the vertex. The circle can be any size. However, it must intersect both sides of the angle. 3.) Draw a circle centered at the point P of the ray that you drew 4.) Using the compass, measure the opening of the original angle by placing the compass point and pencil on the points where the circle intersects the sides 5.) Keeping the compass radius the same, put the point of the compass on the point where the circle intersected the ray that you drew and draw a circle. 6.) Draw the other side of the angle through the intersection point of the 2 circles 14 Practice copying Angles Copy the following 2 angles 15 Name__________________________________ Date: EQUILATERAL TRIANGLES Properties of Equilateral Triangles 1.) 2.) 16 Constructing an Equilateral Triangle **There are multiple ways to perform this construction. We will go over a couple of them Steps 1.) Draw a line segment of any length and label the end points A and B 2.) Place the point of the compass on point A and open up the compass so that the other end is on point B and draw a circle 3.) Repeat step 2 with the point of the compass on Point B and draw a circle 4.) Draw two line segments connecting points A and B to the intersection point of the circle 17 Practice Construct 2 Equilateral Triangles 18 Name______________________________ Date: Equilateral Triangle Inscribed in a Circle We already have talked about Equilateral Triangles, but what does it mean to be “Inscribed”? When you think of INSCRIBED, think INSIDE! INSCRIBED – INSCRIBED NOT INSCRIBED All three vertex points are not touching circle Constructing an equilateral Triangle Inscribed in a circle 19 Steps ***You may not be able to draw the entire circle for this 1.) Draw a circle of any size 2.) Keeping the same opening of the compass, place the point anywhere on the outer edge of the circle and draw a circle 3.) Keeping the same opening of the compass, place the point of the compass on the intersection point of your 2 circles and draw another circle 4.) Continue this process all the way around the circle until there are 6 points of intersection on your original circle 5.) Label these points in order 1,2,3,4,5,6 6.) Use line segments to Connect points 1,3,5 20 Practice Construct an Equilateral Triangle Inscribed in a Circle 21 Name__________________________ Date: Constructing a line Perpendicular to another line through a given point Steps 1.) Place compass on point P and draw a circle. The circle must intersect the line segment twice. Label the two points of intersection C and D. You have created a new line segment 2.) Construct the perpendicular bisector of line segment CD 3.) The line you draw is perpendicular to the given line segment and should go through the given point 22 Practice Construct a line perpendicular to the given line through the given point 23 Name______________________ Date: Parallel Lines Parallel Lines- On a coordinate grid, parallel lines have the same slope 24 Constructing a line parallel to another line through a given point Steps 1.) Draw a line segment that goes through both segment AB and point P. Label point C where the line you drew intersected segment AB 2.) Draw a circle with the center being point C 3.) Keeping the compass opening the same, draw a circle with the center being point P 4.) Next we are going to copy angle PCB with point P being the vertex of our new angle 25 Practice: Construct a line parallel to the given line that goes through the given point 26 Name_________________________ Date: Properties of Square What is a Square? 27 Constructing a Square Inscribed in a circle Steps: 1.) Construct a circle of any size. Make sure and mark the center point 2.) Using a straight edge, draw the diameter of the circle. Label the end points of the diameter A and B 3.) Construct the perpendicular bisector of the diameter. Label the points where the perpendicular bisector intersects the circle C and D 4.) Connect point A, B, C, D 28 Practice: On this page construct a square inscribed in a circle twice 29 Challenge: Can you figure out how to construct a Rectangle inscribed in a circle. Try it on your own NOTE: This rectangle CAN NOT be a square 30 Constructing a rectangle inscribed in a circle Steps: 1.) Follow steps 1 thru 5 of constructing a Hexagon inscribed in a circle 2.) Connect points 1,2,4,5 31 Name____________________________ Geometry Date: Triangle Midsegment Online Assignment 1.) Go online and look up “Midsegment of Triangle” Below, write down the definition of a Midsegment How many midsegments does a triangle have? _________ What are the 2 special properties of MIDSEGMENTS? 1.) 2.) 32 2.) Label the Triangle below with points A, B, C Research how to construct a midsegment and construct one of the midsegments of the triangle. Label the points D and E 3.) State 2 angles that are congruent to one another 33 4.) Triangle ABC is shown below. Construct all three midsegments of the triangle and label the points D,E,F 5.) After you have constructed all three midsegments, a smaller triangle is created inside the bigger one. How do the perimeters of the two triangles compare to each other? 34 Name_____________________ Date: Median of a triangle Definition of Median of Triangle- Below draw a triangle and construct All 3 medians of the triangle The three medians of the triangle intersected at one point. What is this point called? _________________________________ 35