* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ecology
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
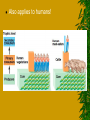
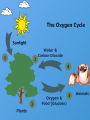
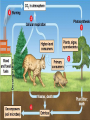
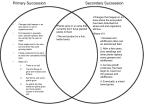
Ecology The study of interactions of living organisms with one another and with their environment Habitat is the place a plant or animal lives, while its niche is its total way of life. Niche Abiotic The physical non – living parts of a habitat. include climate, soil, temperature, water, air, sunlight, humidity, pH, and atmospheric gases. Biotic The living organisms in a habitat. includes plants, animals, fungi, & microorganisms. They may be producers, consumers, or decomposers. Organism Any single living thing Population Members of the same species living in one place. Community All the populations living in an area (habitat). Ecosystem Is made up of a community and all the physical aspects of a habitat (such as soil, water, and weather). Biosphere All living & nonliving things on earth. Biome Ecosystems covering wide areas & with similar climates & organisms There are many types of Biomes: •Water •Tropical rain forest •Deserts •Temperate forest • Coniferous forests •Savannas •Chaparral •Tundra •Temperate grasslands Water Water – Marine – Fresh Aquatic Biomes Oceans cover about 75% of the Earth’s surface Light and the availability of nutrients are the major factors that shape aquatic communities. Deserts Temperature: very hot, and cold (Antarctica!) Rainfall: dry Plants: none, deep rooted shrubs, succulents. – waxy coating to prevent water loss – many seeds that remain dormant until it rains Sunlight: extreme Habitats: burrows, active at night Animals: ants, birds, rodents, lizards, snakes, & hawks. Temperate forests Temperature: cold winter, hot summer Rainfall: high precipitation Plants: deciduous trees (oak, hickory, maple) Habitats: rich soil, leaf litter, burrow Animals: invertebrates, mice, shrew, squirrels, birds, bobcats, foxes, bears, & mountain lions. Most destroyed by loggers & urban development. Coniferous forests Taiga Temperature: long cold winters, short wet summers Rainfall: considerable precipitation (snow) Plants: cone bearing evergreens – (spruce, pine, fur) Habitats: soil thin & acidic Animals: moose, elk, bears, wolves, hares, migratory birds. Heavily logged. Largest terrestrial biome! Tropical forests Temperature: warm Rainfall: varied - heavy Plants: thorny shrubs, deciduous trees, & succulents. (very diverse) Sunlight: little reaches the forest floor. Habitats: floor –> canopy. – Poor soil, due to high temp & heavy rains (leaching). Animals: monkeys, birds, snakes, bats, frogs – tree dwelling. Savannas Temperature: warm year round Rainfall: moderate rainfall Plants: grasses & scattered trees. – growing point below ground & resistance to periods of drought. Habitats: migratory – Poor soil, lack of moisture, grazing animals, & fires inhibit most trees. Animals: large grazing mammals, insects, burrowing animals, predators (lions & cheetahs). Chaparral Temperature: mild winter, hot summer Rainfall: rain in winter, dry in summer Plants: dense shrubs with tough evergreen leaves. Seasonal plants. – Food reserves in roots allow for rapid growth after frequent fires. – Seeds only germinate after hot fire. Animals: deer, birds, rodents, lizards & snakes Tundra Temperature: extremely cold Rainfall: little Plants: no trees, shrubs, grasses, mosses, and lichens. – Permafrost prevents deep root penetration Sunlight: little light for much of the winter, constant daylight in summer Habitats: migratory (summer is a breeding ground), high altitude, permafrost, soil continually saturated due to poor drainage and slow evaporation. Animals: well insulated (oxen & caribou), lemmings, fox, snowy owl. During the summer, clouds of mosquitoes fill the air due to the Producer Make their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Includes plants, algal protists, and some other bacteria. Consumer Can’t make their own food. – Herbivores – plant eating – Carnivores – feed only on animals – Omnivores – feed on plants and animals Decomposers Breaks down dead plants and animals – Called Detritus Recycles nutrients. They are called Detritivores form the excrement into a small ball and roll it into a hole that was previously dug in the soil. They lay an egg on the ball of dung and cover it with soil to serve as a nursery for their larvae. How Organisms Interact Predation Parasitism Mutualism Commensalism Competition Predation Act of one organism feeding on another Parasitism One organism feeds on and usually lives on or in another. Mutualism A symbiotic relationship in which both participating species benefit. Commensalism A symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped. Energy of Life FOOD CHAIN: diagram showing the relationship between organisms and their food supply. Energy of Life Food web – A network of interconnecting food chains Keystone species – A species whose impact on its community is larger than its biomass or abundance indicates – Occupies a niche that holds the rest of its community in place Energy of Life Trophic structure – A pattern of feeding relationships consisting of several different levels Each level receives only one-tenth the energy available to the previous level. 90% of the energy is lost as heat. A pyramid of production – Illustrates the cumulative loss of energy transfer in a food chain (90%) Energy of Life Producers – Support all other trophic levels – Autotrophs – Photosynthetic producers – Plants on land – Cyanobacteria in water Consumers – Heterotrophs – – – Primary consumers (1) Secondary consumers (2) Tertiary consumers (3) 1 2 3 Also applies to humans! Succession Succession: the series of ecological changes that every community undergoes over long periods of time. – A success of change gradually replaces other species Succession Primary succession – Begins in a virtually lifeless area with no soil Secondary succession – When a disturbance destroyed an existing community but left the soil intact Disturbance = Storms, fire, floods, droughts, overgrazing, or human activity Cycles All the organisms in a community as well as the abiotic environment Components of ecosystems – Energy flow – Passage of energy through the ecosystem – Chemical cycling – Transfer of materials within the ecosystem Oxygen Cycles OXYGEN CYCLE: 1. 2. 3. 4. Plants take in water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight Through photosynthesis, plants produce oxygen and food (glucose) to provide their energy Animals take in oxygen and food (glucose) produced by plants Through cellular respiration, animals produce water, carbon dioxide, and energy for their use. Water Cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Water comes to Earth in the form of precipitation and is stored in oceans, lakes, and rivers. All living things take in water and release water to the atmosphere. Plants release water through TRANSPIRATION: loss of water through the leaves of plants Animals release water through evaporation and respiration. Once in the atmosphere, water condenses in clouds and precipitation occurs. The sun provides the heat energy required for the cycle to continue. Carbon Cycle Carbon is the major ingredient of all organic molecules The return of CO2 to the atmosphere by respiration closely balances its removal by photosynthesis The carbon cycle is affected by burning wood and fossil fuels Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen is an essential component of proteins and nucleic acids Nitrogen has two abiotic reservoirs – Air – Soil Nitrogen fixation converts N2 to nitrogen used by plants – Carried out by some bacteria and cyanobacteria