* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Installation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
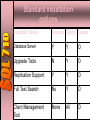
Week 2 - Installation SQL SERVER2000 ENTERPRISE EDITION INSTALLATION Agenda 1. Hardware and Software Requirement 2. Selecting Network Library 3. Standard Installation Options 4. Upgrading to SQL 2000 Server 5. Managing Services 6. Troubleshooting Installation HARDWARE REQUIREMENT Minimum Hardware Requirement • Processor: Intel and compatible systems (166 MHZ Processor or Higher) • Memory: -Minimum 256 MB(All W2K Server family ) -Minimum 64 MB (All NT4 server family) • Hard drive: 250 MB for Typical Installation 270 MB for Full Installation) ( SOFTWARE REQIREMENT Minimum Software Requirement Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 3a Optimizing Hardware •Processor: SMP up to 32 processor ( With Windows2000 Data Center) Hard drive: RAID 1 RAID5 RAID 10 Optimizing Hardware Memory: 64 GB Network: •Network card •Bandwidth •Concurrent Activity on Underlying Network Selecting Network library •SQL Server uses Network libraries to communicate with specific network Protocol and to pass Network packets between a client and a SQL server. •SQL Server simultaneously listen to multiple Network libraries. Server Network Library TCP/IP Socket: Windows Socket TCP/IP Named Pipe: protocol . Any Microsoft supplied transport NWLINK: IPX/SPX Multiprotocol: Windows IPC, Named Pipe, TCP/IP Socket, NWLINK IPX/SPX Appletalk: Appletalk Clients Banyan vines: Banyan Vines Clients Standard Installation options Installation Option minimum Typical Custom Database Server Y Y O Upgrade Tools N Y O Replication Support Y Y O Full Text Search No Y O Client Management Tool None All O Standard Installation Installation Option minimum Typical Custom Client Connectivity Yes Not an option O Yes SQL Server Books Online No Yes Development Tools None de bugger Choice only of tools Code Samples None None Choice of samples Collation Settings Yes Yes Choice of settings Upgrading SQL Server Upgrading from version 7.0: Installs a default instance (Upgrades existing Installation) •Installs a new Named Instance (Retains existing installation) Upgrading from version 6.5: Installs a default or Named instance (Both create new instances) •Use version switching to switch between versions Upgrading from version 6.0: •First upgrade to version 6.5 or 7.0 Reviewing Installation Result Installed component Description SQL Server Service SQL Server, SQL Server Agent, MS DTC, Microsoft search Management Tools Group of Tools for administering SQL Server Databases Master, model, msdb, pubs, Northwind, tempdb Folders & Files Relational database Engine and all tools in c:\Program files\Microsoft SQL Server Default Startup Option A set of default startup options that are written to the windows 2000 Registry Default security mode Windows Authentication –allows users to connect by using windows authentication only Starting, stopping and pausing SQL Server Service • Starting the SQL Server Service allows users to establish new connections • Pausing prevents new connections. Users who are already connected are unaffected • Stopping the SQL Services • Disable login • Perform a checkpoint in each database • Shuts down SQL Server after all currently executing Transact-SQL statements and stored procedures are processed Starting, stopping and pausing SQL Server Agent Service •Starting SQL Server Agent Service allows you to automate activities and activate alerts •Pausing SQL Server Agent Service prevents automatic activities and alerts from occurring •Stopping the SQL Server Agent service prevents automatic activities and alerts from occurring. Tools for starting stopping and pausing Services 1. SQL Server Enterprise Manager 2. SQL Server Service Manager 3. Services and Applications in the computer Management Console 4. Net Command in the Command Prompt Connecting to SQL Server 1. Using Graphical Tools - SQL Query Analyzer - SQL Server Enterprise Manager 2. Using OSQL command line utility - Communicate by ODBC Registering Servers 1. The Server Name or IP address 2. The Named Instance if applicable 3. Windows 2000 Authentication or SQL Server Authentication 4. A Server group, if you plan to manage remote servers or multiple instances. Registration information are stored in Windows 2000 Registry. Installation Troubleshooting Identifying the problem • Review Error Messages • Review the SQLstp.log file • View log information • SQLSTP log • Windows2000 Application log • SQL Server Error log (MSSQL\log) • SQL Server Agent Error log Installation Troubleshooting Symptom:1 The SQL Server Service does not start Problem: Windows 2000 can’t access a domain controller to validate the domain user logon account Solution: Re-establish access to a Domain Controller or reconfigure SQL Server service to use the local system account Installation Troubleshooting Symptom: 2 “Error 1069: The service did not start due to logon failure” Problem: The password for the domain user logon account has changed or expired Solution: Specify a valid password for SQL Server Service. Installation Troubleshooting Symptom: 3 The SQL Server Service does not start Problem: SQL Server entries in the Windows 2000 Registry are corrupted Solution: Rerun setup, and under Advanced Options, click Registry Rebuild to rebuild the SQL server registry entries. Installation Troubleshooting Symptom: 4 The SQL Server Agent Service does not start Problem: The Domain User logon account does not have permission to access SQL Server Solution: Add domain user logon account to the windows 2000 local group Administrators or the sysadmin role in SQL Server. Installation Troubleshooting Symptom: 5 A SQL Server Management tool can’t connect to SQL Server Problem: SQL Server Service has not been started Solution: Verify that the SQL Server service has started Installation Troubleshooting Symptom: 6 “A connection could not be established to [ servername]” Problem: The client and server network library do not match. Solution: Modify the default network library on the client, add a network library to the server or both. Installation Troubleshooting Symptom: 7 “A connection could not be established to [ servername]” Problem: You don’t have permission to administer the computer running SQL Server Solution Log on to the Windows 2000 with an account that has permission to administer the computer running SQL Server, or connect with SQL server login account, such as sa.