* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 4 landscape development
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
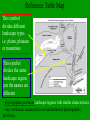
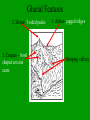
Landscape Development Basic Landscapes Landscapes _________________Earth’s surface visible from any given point on the land or from space. Hill slopes 1. __________________________The angle of slope (gradient) and the shape of hill slopes can be observed, measured, and identified. Stream patterns 2. __________________________streams can be identified and grouped by patterns. ______________________area drained by a stream of Drainage basin system of streams. Soil associations 3.____________________________soils with similar characteristics. - grouped on the basis of composition, particle size and shape, organic content, porosity and permeability, and the maturity of the soil (soil horizons). Landscape Regions Landscape Regions- landscapes with similar characteristics. - in NYS they are grouped by Elevation, type of bedrock and stream drainage pattern 1. _______________a large mass of land which rises to a Mountains great height above its surroundings. 2. _______________Plateaus large regions having horizontal rock structures at high elevations above sea level. - streams cut steep valleys in them (gorges). 3. _______________Plains an extensive region of low elevation where the land is level or gently rolling. Reference Table Map This symbol divides different landscape types. i.e. plains, plateaus or mountains This symbol divides the same landscape region, just the names are different - physiographic provinces-landscape regions with similar characteristics - any continental landmass has several distinctive physiographic provinces. Factors Affecting Landscapes Uplifting forces 1. _______________________Forces which build mountains, enlarge continents, and generally raise or roughen the Earth’s surface. - Earthquakes, folding, faulting, tilting, volcanic activity, continental drift, sea- floor spreading Leveling forces 2. _______________________Forces which lower the elevation of the Earth’s surface through subsidence and erosion. - the major cause of leveling is gravity Factors Affecting Landscapes 3. climate- changes in temperature and moisture. a. arid- steep slopes, angular features. b. humid- smooth with gentle rolling hills c. glaciers- jagged cliffs or U-shaped valleys, polished bedrock, scratched or grooved bedrock Glacial Features Diagrams Factors Affecting Landscapes 4. running water- the most powerful and important erosional agent in shaping landscapes. - responsible for the development of valleys and the hills and ridges between valleys. - streams in arid regions are usually temporary, and often drain into landlocked lakes (lakes that don’t drain into the ocean) Factors Affecting Landscapes 5. soil associations - shallow and poorly developed soils- arid regions, regions with large amounts of rainfall - well developed soilsregions with moderate temperatures and moderate amounts of moisture Bedrock the big factor! Bedrock- the characteristic shape of many landscapes is largely determined by the type of bedrock and its structure. - harder or more resistant the rock- less weathering and erosion. - hard rocks produce steep cliffs (escarpments), mountains and plateaus - soft rocks produce more gradual slopes, weak rocks underlie valleys _____________________ridge that separates two gently escarpment sloping surfaces. _____________________produce circular ridges and domed landscape escarpments. Pay attention to the diagrams! Drainage Patterns Dendritic pattern 1. _______________________branches in a way similar to the limbs or roots of trees. - found on plains and plateaus, where the rock layers are horizontal. Trellis pattern 2. _______________________develops in valley-and-ridge terrain, where rocks of different hardness are folded. Radial pattern 3. _______________________found where streams radiate out from a central point on a large single peak, such as on a volcano or rounded hill. Rectangular pattern 4. _______________________develops in a strongly jointed and faulted area. 5. Annular Pattern - develops where folding has occurred Dendritic Trellis Radial Annular Time and Landscapes: What to look for? 1. young landscape- erosion is beginning. Sharp, craggy hills Steep slope, fast moving streams Narrow V-shaped valleys Time and Landscapes: What to look for? 2. mature landscape- Low rounded hills and broad flat valleys. Streams are no longer eroding downward, but are side cutting. Building meanders and floodplains Time and Landscapes: What to look for? 3. old landscape- Uplands have been eroded to almost sea level - area has become a peneplane- a region that has been reduced by erosion to a nearly flat surface. - Poor drainage system with almost no gradient, Many meanders and wide floodplains Meandering stream Glacial Features 2. Horns- 3-sided peaks 3. Cirques – bowl shaped erosion scars 1. Arêtes- jagged ridges Hanging valleys 5. Kettles & kames – formed by melt water Kame – stream flowing on glacier Kettle- ice blocks 4. Moraines – deposits of glacial till left by 7. Eskers – snaking hill, glaciers stream deposits from under glacier Glacial Features 6. Drumlins – elongated piles of glacial till Marks end of glacier’s advance 8. Outwash plains – melt water deposits, sorted by size, has layers of different sediments Glacial Features U-shaped valley Glacier Animation notes Recessional Moraine Terminal Moraine