* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Origin of Earth
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
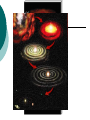
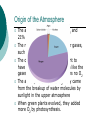
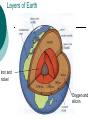
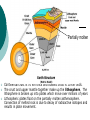
The Origin of Earth Six facts must be considered when formulating a hypothesis about the origin of Earth: 1. Planets revolve around the sun in the same direction. 2. The orbits are all nearly circular 3. The orbits are in the same flat plane. 4. The sun rotates in almost the same plane as the planets and in the same direction as the they revolve. 5. Most of the planets rotate in the same direction as the sun 6. Seven of the nine planets have moons. Protoplanet Hypothesis 5 billion years ago a cloud of gas and dust at least 10 billion kilometres in diameter rotated slowly in space. As time passed the cloud shrank under its own gravity. Most of the material condensed at the center. The compression made the interior so hot that fusion began and the core of the cloud formed the sun. Friction caused eddies in the disk rotating around the core, which condensed into the protoplanets and later the planets and moons. Origin of the Oceans When Earth first formed, it had neither oceans nor atmosphere The protoplanet heated up b/c of the radioactive minerals, compression, and meteorites. Iron melted and sank to the centre of Earth, forming the core. As the molten iron sank, it melted other materials that released water and gases. Steam and gases escaped to the surface in volcanic eruptions. The steam condensed into water that accumulated as oceans. Origin of the Atmosphere The atmosphere contains 78% N2 and 21% O2 The remaining 1% is mostly other gases, such as Ar, CO2, He, and H2O The original atmosphere is thought to have come from volcanoes, much like the gases now emitted, which contains no O2 The atmosphere first free O2 likely came from the breakup of water molecules by sunlight in the upper atmosphere When green plants evolved, they added more O2 by photosynthesis. When Earth formed 5 billion years ago, much of the planet was molten (liquid) Heavier elements such as iron and nickel (atomic #s 26 and 28) sank to the middle of the earth and lighter elements such as oxygen and silicon (atomic #s 8 and 16) floated to the top. Layers of Earth Iron and nickel Oxygen and silicon Partially molten Continental crust is 70 km thick and oceanic crust is 10 km thick. The crust and upper mantle together make up the lithosphere. The lithosphere is broken up into plates which move over millions of years Lithospheric plates float on the partially molten asthenosphere. Convection of melted rock is due to decay of radioactive isotopes and results in plate movement.