* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EE6201
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electronic musical instrument wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Transmission tower wikipedia , lookup
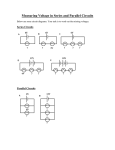
LP-EE6201 LESSON PLAN LP Rev. No: 01 Sub Code & Name: EE6201 CIRCUIT THEORY Unit: I & II Branch: ECE ,EEE Date: 20/11/2014 Semester: II Page 1 of 5 UNIT I BASIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS 12 Ohm’s Law – Kirchoffs laws – DC and AC Circuits – Resistors in series and parallel circuits – Mesh current and node voltage method of analysis for D.C and A.C. circuits – Phasor Diagram – Power, Power Factor and Energy UNIT II NETWORK REDUCTION AND NETWORK THEOREMS FOR DC AND AC CIRCUITS 12 Network reduction: voltage and current division, source transformation – star delta conversion. Thevenins and Novton & Theorem – Superposition Theorem – Maximum power transfer theorem – Reciprocity Theorem. Objective: To expose the students to the basic concepts in analysis of dc/ac electric circuits and the important theorems of circuit analysis. Session No 1 2 3 Topics to be covered Introduction to Circuit theory Ohm’s laws, Kirchoff laws Voltage and Current sources DC circuits Resistors in series and parallel circuits Time Allocation (min) 50 Books Referred Teaching Method PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 6 Voltage and Current division Voltage, Current source transformations Dependent current and voltage sources Mesh analysis of dc circuits Power delivery Super mesh analysis 7 Nodal analysis 50 PPT 8 Super node analysis 50 PPT 9 Star-Delta transformation 50 PPT 10 Superposition theorem-DC circuits 50 PPT 11 Thevenin’s theorem-DC circuits 50 PPT 12 Norton’s theorem-DC circuits 50 PPT 4 5 50 1,2,3,4,7 PPT LP-EE6201 LESSON PLAN LP Rev. No: 01 Sub Code & Name: EE6201 CIRCUIT THEORY Unit: I & II Branch: ECE,EEE Date: 20/11/2014 Semester: II Page 2 of 5 Units 1 and 2 : Continued Session No Topics to be covered Time Allocation (min) 50 Books Referred Teaching Method 13 Thevenin’s theorem with dependent sources 14 Norton’s theorem with dependent sources 50 PPT 15 Maximum power transfer theorem-DC circuits 50 PPT 16 Reciprocity theorem-DC circuits 50 PPT 17 Problems 50 PPT 18 Inductance and Capacitances Basics of AC circuits Average RMS values of common waveforms 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 23 Phasor diagram AC circuits – R load, L load and C load AC circuits- RL , RC, RLC load Voltage, Current, Power and Power factor, Energy Impedances in series and parallel Admittance, Susceptance, Conductance Mesh Analysis – AC circuits 24 Nodal Analysis – AC circuits 50 PPT 25 50 PPT 26 AC circuits – Voltage and Current division Source transformation AC circuits –Star Delta transformation 50 PPT 27 Superposition theorem-AC circuits 50 PPT 28 Thevenin’s theorem-AC circuits 50 PPT 29 Norton’s theorem-AC circuits 50 PPT 30 Maximum power transfer theorem-AC circuits Reciprocity theorem-AC circuits CAT-I 50 PPT 19 20 21 22 50 PPT 1,2,3,4,7 PPT LP-EE6201 LESSON PLAN LP Rev. No: 01 Sub Code & Name: EE6201 CIRCUIT THEORY Unit: III Branch: ECE,EEE Date: 20/11/2014 Semester: II Page 3 of 5 UNIT – III: RESONANCE AND COUPLED CIRCUITS Series and parallel resonance – their frequency response – Quality factor and Bandwidth - Self and mutual inductance – Coefficient of coupling – Tuned circuits – Single tuned circuits Objective: To expose the students to the concept of resonance and its application to coupled circuits Session No 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 Topics to be covered Series resonance Impedance at resonance Q factor, Variation of Capacitor and Inductor voltage with frequency Bandwidth for a series resonant circuit Time Allocation (min) 50 Books Referred Teaching Method PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT Parallel resonance, Q factor, Variation of Capacitor and Inductor voltage with frequency Bandwidth for a parallel resonant circuit 50 PPT 50 PPT Resonant frequencies for series-parallel combinations Frequency response for series and parallel resonant circuits Magnetically coupled circuits, Dot convention, Self inductance Mutual inductance Coefficient of coupling Circuits with coupled inductances 50 PPT Tuned circuits Singly tuned circuits 50 1,2,3,4,7 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT LP-EE6201 LESSON PLAN Sub Code & Name: EE6201 CIRCUIT THEORY LP Rev. No: 01 Unit: IV Date: 20/11/2014 Branch: ECE, EEE Semester: II Page 4 of 5 UNIT IV TRANSIENT RESPONSE FOR DC CIRCUITS 12 Transient response of RL, RC and RLC Circuits using Laplace transform for DC input and A.C. with sinusoidal input – Characterization of two port networks in terms of Z,Y and h parameters. Objective: To familiarise the students to the Laplace transform concept for applying it to obtain transient response for DC & AC inputs and to discuss briefly the concepts of two port networks. Session No Topics to be covered Time Allocation (min) 50 Books Referred Teaching Method 42 Laplace Transform 43 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 48 Transient response of RL,RC circuits with dc input Transient response of LC,RLC circuits with dc input Transient response of RL,RC circuits with switched dc inputs Transient response of RL,RC circuits with ac sinusoidal input Transient response of LC,RLC circuits with ac sinusoidal input Parameters of Two port Networks (T and Π) 49 44 45 46 47 PPT 50 PPT 1,2,3,4,7 50 PPT 50 PPT Characterization in terms of Z parameter 50 PPT 50 Characterization in terms of Y parameter 50 PPT 51 Characterization in terms of h parameter 50 PPT CAT II LP-EE6201 LESSON PLAN LP Rev. No: 01 Sub Code & Name: EE6201 CIRCUIT THEORY Unit: V Branch: ECE ,EEE Date: 20/11/2014 Semester: II Page 5 of 5 UNIT V ANALYSING THREE PHASE CIRCUITS Three phase balanced / unbalanced voltage sources – analysis of three phase 3-wire and 4-wire circuits with star and delta connected loads, balanced & un balanced – phasor diagram of voltages and currents – power and power factor measurements in three phase circuits. Objective: To familiarize the students with the analysis of three phase circuits Session No Topics to be covered 52 3 phase circuits, Star and delta connection Balanced voltage sources 3 phase circuits with Unbalanced voltage sources Analysis of 3 phase, 3 wire star connected circuits with balanced loads Analysis of 3 phase, 3 wire delta connected circuits with balanced loads Analysis of 3 phase, 4 wire star connected circuits with balanced loads Analysis of 3 phase, 3 wire star connected circuits with unbalanced loads Analysis of 3 phase, 3 wire delta connected circuits with unbalanced loads Analysis of 3 phase, 4 wire star connected circuits with unbalanced loads Phasor diagrams of voltages and currents in 3 phase circuits Power measurement in a three phase circuits by Three Wattmeter method Power measurement in a three phase circuits by Two Wattmeter method Power factor measurements in 3 phase circuits 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 CAT III Time Allocation (min) 50 Books Referred Teaching Method PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 1,2,3,4,7 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT 50 PPT LP-EE6201 LESSON PLAN LP Rev. No: 01 Sub Code & Name: EE6201 CIRCUIT THEORY Unit: Branch: ECE,EEE Date: 20/11/2014 Semester: II Course Delivery Plan: Week Units 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 5 TEXT BOOKS : 1)William H. Hayt Jr, Jack E. Kemmerly and Steven M. Durbin, “Engineering Circuits Analysis”, Tata McGraw Hill publishers, 6th edition, New Delhi, (2002). 2)Sudhakar A and Shyam Mohan SP, “Circuits and Network Analysis and Synthesis”,Tata McGraw Hill, (2007). REFERENCES: 3)Paranjothi SR, “Electric Circuits Analysis,” New Age International Ltd., New Delhi, (1996). 4) Joseph A. Edminister, Mahmood Nahri, “Electric circuits”, Schaum’s series, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi (2001). 5). Chakrabati A, “Circuits Theory (Analysis and synthesis), Dhanpath Rai & Sons, New Delhi, (1999). 6). Charles K. Alexander, Mathew N.O. Sadik, “Fundamentals of Electric Circuits”, Second Edition, McGraw Hill, (2003). 7).Prof T. Nageswara Rao, “ Electric Circuit Analysis”, A.R Publications. Prepared by Approved by Dr.S.Ganesh Vaidyanathan, K.Sundara Raman, P.Muhukumaran, C.Suganthi, M.H.Masood Professor, Assoc. Prof, Asst. Prof, Asst.Prof, Asst.Prof 20.11.2014 Dr.S.Ganesh Vaidyanathan, Dr.K.R.Santha Signature Name Designation Date HOD/EC, HOD/EE 02.01.2015