* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology Unit
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
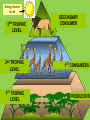
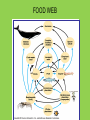
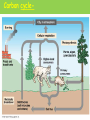
Ecology Unit What is ecology? Ecology- the scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environments, focusing on energy transfer Environments have two key factors: Biotic factors- all living organisms inhabiting the ecosystem-soil bacteria, fungi, animals, plants Abiotic factors- nonliving parts of the environment (i.e. temperature, soil, light, moisture, air currents) Ecosystem- the biotic and the abiotic factors which interact marine terrestrial Community- several interacting populations that inhabit a common environment and are interdependent. Population-a group of organisms of one species live in the same place, interbreed and produce fertile offspring Organism- any unicellular or multicellular form exhibiting all of the characteristics of life, an individual. •The lowest level of organization EARTH BIOMES The types of plants & animals are Determined by 2 Factors Temperature Precipitation Biosphere- life supporting portions of Earth composed of air, land, fresh water, and salt water. •The highest level of organization Habitat vs. Niche Niche - the role a species plays in a community (job) Habitat- the place in which an organism lives out its life (address) Feeding Relationships • There are 3 main types of feeding relationships 1. Producer- Consumer 2. Predator- Prey 3. Parasite- Host Feeding Relationships Producer- all autotrophs (plants), they trap energy from the sun • Bottom of the food chain Feeding Relationships Consumer- all heterotrophs: they ingest food containing the sun’s energy • Herbivores • Carnivores • Omnivores • Decomposers Feeding Relationships ConsumerHerbivores – Eat plants • Primary consumers • Prey animals Feeding Relationships Consumer-Carnivores-eat meat • Predators – Hunt prey animals for food. Feeding Relationships Consumer- Carnivores- eat meat • Scavengers – Feed on carrion, dead animals Feeding Relationships Consumer- Omnivores -eat both plants and animals Feeding Relationships Decomposers Fungi & Bacteria Breakdown dead plants and animals into nutrient They can exist at all levels of a food web Energy Source for all 3RD TROPHIC LEVEL SECONDARY CONSUMER 2ND TROPHIC LEVEL 1ST CONSUMERS 1ST TROPHIC LEVEL PRODUCERS Passing of energy in a food web Trophic Levels Biomass- the amount of organic matter in a habitat. • As organisms move up a food chain, both available energy and biomass decrease. Most energy is loss as heat • Energy is transferred to a trophic level, but is reduced, only about 10% is passed to the next level. FOOD CHAINS FOOD WEB Toxins in food chains increase as they move upward This is called Biological Magnification Nutrient Cycles Cycling maintains homeostasis (balance) in the environment. •3 cycles to investigate: 1. Water cycle 2. Carbon cycle 3. Nitrogen cycle Animation Carbon cycle- tutorial Nitrogen cycleNitrogen-fixing bacteria: Some live in a symbiotic relationship with plants of the legume family (e.g., soybeans, clover, peanuts).