* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download viruses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
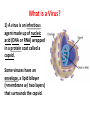
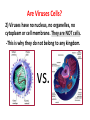
Doesn’t belong to any kingdom -It’s not a plant or an animal. -It’s not a fungi, protist, or bacteria. WHAT IS A VIRUS? What is a Virus? 1) A virus is an infectious agent made up of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) wrapped in a protein coat called a capsid. Some viruses have an envelope, a lipid bilayer (=membrane w/ two layers) that surrounds the capsid. Are Viruses Cells? 2) Viruses have no nucleus, no organelles, no cytoplasm or cell membrane. They are NOT cells. -This is why they do not belong to any kingdom. vs. Are Viruses Living? 3) Criteria Yes Kind of √ Reproduce √ Energy Use Adapt No √ Cells √ Homeostasis √ Nucleic Acids (must have both) Growth Organization √ √ √ Are Viruses Living? 4) Are they considered living? No, they would have to meet all 8 qualifications to be considered alive. 5) Even though viruses do have genetic material (DNA or RNA) and it can change (adapt), they cannot reproduce on their own, they’re not cells, they cannot maintain homeostasis, they do not grow (rather, they’re “assembled”), and they do not have organization. Classification of Viruses 6) Viruses can be classified based on: a. Nucleic Acid type (DNA/RNA) b. Shape of Nucleic Acid 7) c. Shape of Capsid d. Presence of Envelope Hosts 8) Viruses are like parasites—they depend entirely upon another living organism (= a host) for its existence in such a way that it harms that organism. 9) Bacteriophage—viruses that infect bacteria Capsid (protein coat) – inside contains either RNA or DNA 10) Influenza and HIV, for example, infects human cells. DNA or RNA Surface Marker Capsid (protein coat) Viral Replication 11) Viral Replication is how a virus makes copies of itself. A virus CANNOT reproduce by itself—it must invade a host cell and take over the cell’s “machinery”, make copies of itself, and eventually will cause the cell to burst (lyses), releasing more viruses. This kills the host cell. Virus attaches to cell. Step 3 Step 2 Step 1 Virus copies itself. Step 4 DNA/RNA is copied. DNA/RNA injected into cell. Cell bursts (lyses) and releases new viruses. Step 5 Viral Transmission 12) Outside the host cell, a virus is a lifeless particle with no control over its movements. It is spread by: •Air •In water •In food •By body fluids Viruses as Pathogens 13) Many viruses cause disease = pathogenic -Pathogen = disease-causing agent (could be a bacterium, protist, fungus) 14) Human diseases caused by viruses: Warts, common cold, Influenza (flu), Smallpox, Ebola, Herpes, AIDS, Chickenpox, Rabies 15) Some viruses can be prevented with vaccines, but NOT treated with antibiotics (antibiotics treat bacteria). Benefit of Viruses 16) Genetic Engineering—harmless virus carries good genes into cells.