* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 – Gastrointestinal Tract Infections
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Probiotics in children wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Rotaviral gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
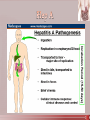
Bacterial Food Poisoning Bacterial Enteritis and Enteric Fevers Bacterial infection of the stomach, esophagus and intestines Gastrointestinal disease caused by other pathogens By ingestion of food contaminated with preformed toxins Also might contain metals, pesticides and other toxic substance The symptoms more rapid compared to infections S.aureus – food handler Soil organisms such as water, feces, sewage (nature food contamination) Others: Campylobacter jejune, Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium perfringens, C.botulinum and Bacillus cereus Feces – physical determination, isolation and component analysis Food – contaminated Gastric juice / fluid Basically in uncooked or inadequate cooked food. And unrefrigerated.such as?? Releasing endotoxin A or D Bacteria producing toxin instead of multiply Causing symptoms – abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea n vomiting Clostridium perfringens – undercooked meats and gravies, late onset and lasting, only during sporulation, gas gangrene and anaerobic cellulitis Clostridium botulinum – minor in GI but major in nervous system Bacillus cereus – contaminated rice / meat dishes, vomiting, short time onset and period of infection Pseudomonas cocovenenans – bongkrek disease (coconut) – cause fatal Enteritis – an inflammation of intestine; not intoxication Invade and damage the intestinal mucosa or deeper tissue Small intestine – diarrhea Large intestine – dysentery (severe including mucus, blood and pus) Leading to enteric fever such as typhoid fever By genus Salmonella – typhi, choleraesuis and enteritidis Detection using serotype identification – molecular/special test Other than typhi can cause typhoid fever Normal flora of poultry, wild birds and rodents The particular animal infected seriously / just carrier – 90% pet reptiles carrier Normal flora of poultry, wild birds and rodents The particular animal infected seriously / just carrier – 90% pet reptiles carrier Infected hen to the laying eggs Trace from contaminated food and water In daily life – improper preparation of food (uncooked egg and meat/dairy product) Abdominal pain, fever and diarrhea with blood and mucus Onset 8 – 48 hours after ingestion Fever – endotoxin release during lysis Self-limiting lasts 1 – 4 days No need of antibiotic Infant and elderly more severe S.typhimurium and S. paratyphi cause more serious condition – enterocolitis Incubation period up to 10 days Cause fever and chills for 1 – 3 weeks No antibiotic suitable – increase spectrum of normal flora of GIT Maintain the sanitary water and food supplies Primarily – caused by S.typhi In faulty and sewage system- uncooked shellfish, raw fruit and raw vegetable Bacteremia and septicemia Patient having headache, malaise and fever due to toxication Invade mucosa and excrete thru stool Infect lymphoid tissue such as Peyer’s patches (rose spots) Antibiotic – fluoroquinolones, chloramphenicol Bacillary dysentery – serovar A (dysenteriae), B (flexneri), C (boydii) and D (sonnei) In day-care-centre, 10 organisms enough to cause infection Contaminated food, finger, flies, feces and fomites Vibrio vulnificus and V. Parahemolyticus In poor country Mild and not true cholera If caused by Vibrio cholerae – rice water stool – chronic cholera Test of microscopic observation until serological test - IgA Largely caused by V. parahemolyticus Contaminated fish and shellfish Endotoxin released 12 hr after entering body Last fo 2 -5 days Caused by E.coli O157:H7 Others are Campylobacter, rotavirus, Giardia, Entamoeba, Salmonella Strain that is enterotoxigenic (ETEC) or enteroinvasive (EIEC), enterohemorrhagic (EHEC) (also cause hemorrhagic uremic syndrome-HUS) Caused by Campylobacter pylori Is a cofactor for stomach cancer Penetration so called as perforation Drinking too much alcohol Regular use of aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Taking aspirin or NSAIDs once in awhile is safe for most people. Smoking cigarettes or chewing tobacco Being very ill, such as being on a breathing machine Radiation treatments Feeling of fullness -- unable to drink as much fluid Hunger and an empty feeling in the stomach, often 1 - 3 hours after a meal Mild nausea (vomiting may relieve symptom) Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen Upper abdominal pain that wakes you up at night Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a special test performed by a gastroenterologist in which a thin tube with a camera on the end is inserted through your mouth into the GI tract to see your stomach and small intestine. During an EGD, the doctor may take a biopsy from the wall of your stomach to test for H. pylori. Upper GI is a series of x-rays taken after you drink a thick substance called barium. Aslo known as rotavirus Infecting infants and children Causing watery diarrhea within 2 days 3rd virus causing fatality in children Contain dsRNA and observe using EM Diagnosis of stool using ELISA Also caused by species of Enterovirus, Clostridium difficile and can inflammed nervous system In the United States, rotavirus infection outbreaks are common during the winter and spring months. It is particularly a problem in childcare centers and children's hospitals because rotavirus infection is very contagious. Usually this happens when kids don't wash their hands often enough, especially before eating and after using the toilet. have fever, nausea, andvomiting, often followed by abdominal cramps and frequent, watery diarrhea. Kids may also have a cough and runny nose. Some rotavirus infections cause few or no symptoms, especially in adults. An inflammation of liver, caused by viruses Can also caused by amoeba and toxic chemical substance Hep A – infectious hepatitis (fecal-oral route) Hep B – serum hep (blood) Hep C – NANB hep (parenterally – blood) – liver transplant Hep D – delta hep (blood)along wt HBV Hep E – NANBNC hep (enterically – fecal oral) Giardiasis Amoebic Dysentery and chronic amebiasis Balantidiasis Cryptosporidiosos Cyclosporiasis Penicillin and Aspergilus Strongyloidiasis Tapeworms Fluke Trichinosis Hookworm Ascariasis Trichuriasis Pinworm