* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B5 Revision questions - Blackpool Aspire Academy
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
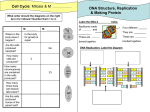
B5 – Growth and development Revision questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. What is a ‘specialised cell’? Define ‘tissue’ and ‘organ’. What is a ‘zygote’ and what is an ‘embryo’? How does a zygote develop into an embryo? After which cell stage, 4,8,16 or 32, do embryonic cells become specialised? What is the key difference between an adult stem cell and embryonic stem cells? What are ‘meristem cells’? What do meristem cells do that other plant cells do not do? Name two types of tissues in plants. Name four types of organs in plants. Meristem cells can form new tissues and organs in plants when cuttings are taken. Why might someone want to take a cutting of a plant, rather than grow a new one from seed? What is the name of a plant hormone that stimulates meristem cells to divide? What is phototropism? Why is phototropism beneficial to lants? How does light affect the distribution of auxin in a shoot tip? What is mitosis? The cell cycle is the growth followed by division of stem cells. What two things happen during cell growth? What two things happen during mitosis? What is meiosis and how is it different to mitosis? Why is it important that meiosis is used to produce gametes? Where do the chromosomes found in zygotes originate from? What is the correct name for the shape of DNA? What are the four bases that make up DNA and how do these bases always pair up? How does the cell know which amino acids should be used to make a protein? How does altering the order of bases in the DNA code affect the protein that is made from the code? Where is the genetic code kept in a cell? Where are proteins produced? What is the name of the molecule that transfers a copy of the gene from the nucleus to the cytoplasm? If all body cells contain the same genes, why do different cells produce different proteins? What is gene switching? What is the difference between an embryonic stem cell and a specialised cell in terms of gene switching? Suggest how stems cells could be used in medicine. Suggest two ethical issues surrounding the use of embryonic stem cells. Why is stem cell research regulated by the government? Dolly the sheep was made by taking a specialised cell and making it form a new embryo. Explain, in terms of gene switching, what must have happened to this specialised cell so that it could act like a zygote.