* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Living things are . . .
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
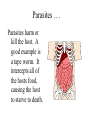
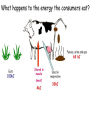
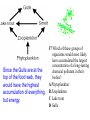
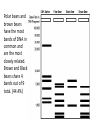
STAAR Review Ecology Biomes Identified by biotic and abiotic factors • Biotic – what kinds of plants and animals live in it. • Abiotic – Nonliving characteristics such as soil type, rainfall amounts, and average temperature cycles. Temperate Desert Forest Tundra Name the Biome Grasslands Tropical Tiaga Rainforest What are they referring to? • Biosphere – The entire area of the planet that supports life. • Biome – An area defined by specific abiotic and biotic factors. • Community – The groups of living things in an area and how they relate. Ecology – The study of the relationships among living things • Symbiosis is a close relationship between two living things. • When both are helped it is called mutualism • When one is helped and there is no effect on the other it is called commensulism • When one is helped and the other is harmed it is called parasitism Mutualism . . . Sharks are cleaned by a little fish known as a Remora. The shark never eats them since they clean bacteria off of the shark. Since both species are helped, this is mutualism. Commensulism . . . Orchids live high in tree-tops on the branches of large trees. They do not harm the tree, but they are helped by being raised up into the sunshine and receiving water. Parasites . . . Parasites harm or kill the host. A good example is a tape worm. It intercepts all of the hosts food, causing the host to starve to death. 35 Clown fish are small reef fish that seek protection from predators by sheltering themselves among the stinging tentacles of sea anemones. Clown fish are very territorial and can potentially scare off predators of sea anemones. This relationship is an example of -A neutralism This is not a type of symbiosis Incorrect Since both are helped, it B mutualism is of mutual benefit or C parasitism Neither is harmed so this is incorrect D commensalism Means only one is being helped and the relationship has no effect on the other – also incorrect What is helped? Both the ants and the tree. This is the definition of: All energy on the earth comes from the sun. 18 Energy used by producers in a grassland Used by producers food web is provided byF sunlight G photosynthesis H oxygen J carbon dioxide This is a process, not an energy source. H and J are elements which are types of matter, not energy. So our answer should be: F Energy Diagrams At one end of the diagram are plants. They are called producers since they are capable of turning sunlight into food by photosynthesis. They pass 10% of the energy they absorb to animals that eat them. Consumers 1st Order Consumers eat only plants and are also called herbivores. 2nd Order Consumers eat only animals and are called carnivores. 3rd Order Consumers animals that eat other animals, they are also known as carnivores 39 Wolves and hawks are at the same Trophic trophic level level because they — Means 1st , A both live on land 2nd or 3rd B are both large mammals Order C both eat primary consumers Consumer D have similar hunting patterns 10% Energy Rule – Only 10% of the energy moves up to the next trophic level. Decomposers Energy Pyramid Pyramid of Numbers Biomass Pyramid If we apply the 10% rule, 10% of 43 Approximately how much the 1000 kcal of the plant is of the energy available in the consumed or 100 kcal, and 10% tissues of the producer is of that is 10 kcal which is 1% of eventually incorporated into the original 1000kcal, but only 3 the tissues of a secondary kcal is available to the tissues so consumer? it is A. A Less than 1% B Between 20% and 30% C Approximately 50% D More than 50% Food Chain – One of many feeding relationships in a community • Arrows in a food chain show the direction of energy flow. • This is not the only feeding relationship for these organisms. • When several or all of the food relationships are shown it’s a . . . Food Web Food Webs • Food webs attempt to show all the feeding relationships in a community. • The direction of the arrows shows the direction of energy flow. • At the bottom of every web and every chain is a plant. These are the only things that can turn sunshine into food. Since the Gulls are at the top of the food web, they would have the highest accumulation of everything but energy. 37 Which of these groups of organisms would most likely have accumulated the largest concentration of a long-lasting chemical pollutant in their bodies? A Phytoplankton B Zooplankton C Lake trout D Gulls • Prey are the animals that are eaten as a food source for the . . . • Predator This is the hunter animal. The population of the predator must be less than the prey or they do not have enough food. Population (100s) Predator and Prey Time (months) Prey Predator To increase the predator population you could do what? 24 Which of the following is most likely to cause increases in a predator population? F Fewer prey G A reduction inReduces competition available food – Nope! H More parasites Less predators, they J A period of drought Less and prey, would bepredators sick or dying! they’d be gone looking for water! Population (100s) Carrying Capacity Time (months) P rey P redat or • This is the maximum number of a specific population that an area can support with enough food and living requirements. It is shown by a line on population graphs for a specific species. 2 Because of this animal’s adaptations, it would be most successful at — F competing with birds G making its own food H hiding from predators J running very rapidly And the answer is? • H hiding from predators. • Its not a plant, so it can’t make food. • It has no wings, so it can not compete with birds. • Although it has long legs, it doesn’t seem balanced for running. Succession Primary Succession – building soil Secondary Succession Water Cycle • Precipitation (rain and snow) fall on plants and ground. • Plants respire and evaporate water back into clouds. • The ground filters the water run-off into the lakes where it evaporates again. 21 The diagram shows physical changes that occur in the water cycle. Which of these shows condensation? AQ B R Precipitation C S Run Off of ground water D T Evaporation Carbon Cycle • Glucose C6H12O6 is produced by plants, eaten by animals. Photosynthesis • Animals and plants exhale CO2 which is taken in by plants to make glucose Cellular Respiration Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Cycle • Lightening and bacteria in the ground “fix” Nitrogen into a form usable by plants. • It is absorbed by plants, through their roots as nitrates, so they can be used to build amino acids essential for building proteins, enzymes and the nitrogen bases of DNA. Man’s Effects on the Environment • Ozone O3 is a protective layer at the top of the atmosphere. • However, when it occurs near the ground, it is very harmful to all living things, it is SMOG Man’s Effects on the Environment • More than 90% of fresh water is locked in ice at the polar caps and in glaciers. • Much of the fresh water is polluted by land run-off, dumping of wastes and excess heat directly into lakes, oceans and rivers. Man’s Effects on the Environment Global warming, also called the Greenhouse Effect is caused by excess burning of fossil fuels and destruction of our oxygen producing protista in the oceans, and deforestation on land. Less plants means less oxygen and more CO2. 54 Which of these activities can help conserve natural resources? What is the phrase for ecology? F Recycling cardboard boxes G Washing small loads of laundry H Driving large cars J Building wooden fences Yes! Recycle! Not saving water! Wasting fuel! Cutting down trees that give oxygen and clean air! All animals and plants have adaptations that help them survive in their environment. Examples of Plant Adaptations: Support/food storage: Above ground (prop) roots, Stiff cell walls in stems and trunks (vascular tissue that also carries water and food), Starch storage in roots. Prevention of water loss: Waxy cuticle, stomata on leaves, reduced leaf surface area (cactus), seed coats. Reproduction: Seed dispersal by wind and animals, colors to attract pollinators, pollen, coevolution with insects. Defense: Toxins, thorns, bark. Examples of Animal Adaptations: Protection and prevention of dehydration: exoskeletons, armor, scales, skin, kidneys. Defense/Predation: Claws, teeth, well developed eye lens, sense of smell, speed, camouflage, armor, mimicry. Reproduction: Eggs, internal fertilization, placentas, care of young, nesting. Life is very Diverse. Diversity is a measure of how many different types of organisms live in an area. For example, a rainforest is a very diverse habitat (many different species of insects, plants and animals). A desert is not as diverse (lots of the same kind of cactus and a few species of animals). A species is a group of animals that can breed and produce fertile offspring. (Poodles and Dalmatians can make Doodles/Palmations. They are the same species. Lions and tigers are not. There are no ligers/tions) Populations of animals adapt to their environment by Natural Selection. 1.All species have variations (caused by genetic makeup…Mutations can cause variation). 2. Variation is inherited. 3. More species are produced than will live. 4. Those species that survive to reproduce will pass their characteristics (genes) on to the next generation those that don’t become extinct. 5. Over time, characteristics and behavior that allow the species survive are “selected” for. Unfavorable traits won’t be passed on. If two populations of organisms become separated by a barrier, each separate group may have different selection pressures on it and change in different ways. Eventually they may not be able to reproduce and become separate species. This process is called speciation. Phylogenetic Trees are diagrams that show the relatedness (Phylogeny) of organisms based on physical and chemical similarities. C Present D E F G B 100mya A A is the common ancestor. B is extinct. E and F are the most closely related. Scientist look at both physical and biochemical similarities (like DNA and protein comparisons) to see how organisms are related. Which two organisms in this chart are the least related? The silkworm moth and the screwworm fly. Polar bears and brown bears have the most bands of DNA in common and are the most closely related. Brown and Black bears share 4 bands out of 9 total. (44.4%)