* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Invasive” Plants - MSU Department of Geography
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Invasive species wikipedia , lookup
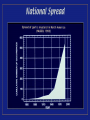
What Invasive Species are affecting Forest Ecosystems and Waterfowl? By Jay Rendall Minnesota Department of Natural Resources What are “Nonnative Invasive Species”? Definitions Exotic, alien, introduced, nonnative, nonindigenous species a species that is not a native species (Minn. Stat. 84D) the condition of a species being beyond its natural range or natural zone of potential dispersal (OTA 1993) Definitions “Nonnative” “Naturalized” “Invasive” Invasive Species Concepts “We are in a period of the worlds history when the mingling of thousands of kinds of organisms is setting up terrific dislocations in nature." - Charles Elton, The Ecology of Invasions Local Spread 100 80 60 40 20 0 1962 1966 1970 1974 Increase in purple loosestrife biomass in a USFWS refuge. 1978 “Invasive Species” affecting Forest Ecosystems “Invasive Species” affecting Waterfowl and Wetlands Waterfowl and Invasive Species Interactions: • Eurasian Milfoil increase leads to native aquatic plant decrease (Knapton and Petrie 1999, Madsen 1991) • Curly-leaf pondweed and common carp populations can lead to turbid conditions rather than clear-water, macrophyte dominated conditions in shallow lakes. Waterfowl and Invasive Species Interactions: • Several studies have documented the negative impacts of common carp on shallow water ecosystems such as reduction of wild celery and increased cycling of nutrients. • Zebra mussels filter water leads to increase of native aquatic plants including wild celery and may contribute to decline of Eurasian milfoil (Knapton and Petrie 1999) Invasive Species and Climate Change Interactions • If tree composition of forests begin to change due to climate change, invasive species may have an advantage in the transition period — and may become more dominant than without climate change. • Kudzu and many other species currently limited by climate to southern states may extend their range northward into the northern latitudes. Invasive Species and Climate Change Interactions • Incidences of diseases and parasites could increase under climate change (Leach 1999). • If climate change leads to ecological disruption, the task of predicting the probability of successful invasions will be more difficult (Leach 1999).