* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CNA Unit 3 - Lesson 3rev-20
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
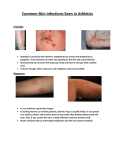
Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Terms and Definitions • Asepsis – the absence of germs • Aseptic – free of microorganisms • Contaminated – exposed to germs • Germ - microorganism • Infection – invasion of the body by a disease-producing (pathogenic) microorganism • Micro - small Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Microorganism – a very small living thing (a germ) that can only be seen with a microscope • Pathogens – microbes that cause disease • Resistance – ability to fight off • Toxin – a poisonous substance • Transmitted – transferred or spread Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Lymphatic System • Organs Tonsils Lymph nodes (with lymph fluid) Spleen Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Figure 3.1 – Lymphatic System Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Lymphatic System • Lymphatic System Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Lymphatic System • Functions Produces antibodies to fight infection Manufactures white blood cells Filters impurities such as dead cells and bacteria • Aging process Less resistant to disease and infections Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Wound healing takes longer. • Related health problems Infections (pneumonia, influenza, etc.) HIV, AIDS Hepatitis Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Microorganisms (Microbes) Bacteria and viruses are the most common in the spread of disease. • Grow best in the following conditions: Warm environment Dark environment Moist environment Where there is a food supply Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Found everywhere Everything we use in daily living – food, water, objects we touch An object used by others Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Bacteria Small microorganisms that can cause infection – Major bacterial infections are listed below. • Staphylococcus (staph) • Streptococcus (strep) • Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) • Syphilis • Escherichia coli (E. coli) Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Gonococcus (GC) • Clostridium difficile (C. diff) • Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) • Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) • Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Bacteria • Staphylococcus • Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Streptococcus • Syphilis Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Bacteria • E. Coli • E. Coli Outbreak Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Clostridium Difficile • C.Diff Information • Gonococcus Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Bacteria • MRSA • MRSA Information Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Vancomycinresistant enterococci (VRE) • Vancomycinresistant Staphylococcus Aureus (VRSA) Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Viruses Tiny microorganisms much smaller than bacteria that can cause infection. Major viral infections are listed below. • Hepatitis • Herpes • Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) • Influenza • Common cold Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Measles • Herpes zoster (chicken pox/shingles) • Ebola Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Hepatitis A,B,C,D,E • Hepatitis A and E viruses- spread by contaminated food and water or by coming in direct contact with contaminated stool (feces).Fecal or Oral • Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses- spread when an uninfected person comes in contact with blood, semen, or vaginal fluid (including menstrual blood) that is infected with one of these viruses. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Hepatitis B and C • Definition Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Herpes Simplex Virus • Herpes type 1 (HSV-1, or oral herpes) ex. fever blisters or cold sores Cause- oral secretions, sharing eating utensils Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Herpes type 2 (HSV-2, or genital herpes) ex. sores around the genitals or rectum. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Herpes Simplex Virus • How is the Herpes Infections and Spread? • Symptoms? • Diagnosed? • Treated? No cure, meds for symptom relief Ex Zovirax, Valtrex and warm baths Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) • HIV- causes AIDS • HIV/AIDS weakens a person’s ability to fight infections and cancer. • HIV transmission- unprotected sex or with needle sharing. • You CANNOT get HIV from: touching, hugging, public bathrooms or swimming pools. Sharing cups, utensils, or telephones with someone who has HIV/AIDS. • Bug bites Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Acute HIV Infection Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control HIV • (HIV) test detect antibodies to HIV or the genetic material (DNA or RNA)of HIV in the blood or another type of sample. This determines whether an HIV infection is present. • NO CURE- Meds used to treat s/s Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Influenza • Caused by- influenza A or B viruses • Definition- extremely contagious respiratory • Spread- inhale droplets in the air that contain the flu virus, make direct contact with respiratory secretions through sharing drinks or utensils, or handle items contaminated by an infected person • S/S- cough, chest discomfort, congestion, FEVER • DX- by symptoms • Tx- antiviral meds tx symptoms Nurse Assistant Common cold In a Long-Term Care Facility • Cause-more than 200 different viruses are known to cause the common cold Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Rhinoviruses -- causing 10% to 40% of colds • Coronaviruses -- causing 20% of colds • Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) -- responsible for 10% of colds Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Common Cold • Definition • Spread by Droplet (ex sneezing, coughing), touching a surface ,contaminated with cold germs (ex. computer keyboard, doorknob, or eating utensil, for example -- and then touching your nose or mouth. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Common Cold • S/S- congestion, itchy and sore throat • Dx- Symptoms • TX- to alleviate symptoms – Decongestants reduce swelling in nasal passages, relieves the feeling of pressure and improves airflow through your nose. – Antihistamines block histamine that is produced by the body in response to allergens or irritant – Cough Syrup- Expectorant or Suppressant Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Measles - Rubella, Rubeola • Cause- measles virus Morbillivirus • Spread- Airborne Transmission, Droplet, Contact Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Symptoms- dusky red maculopapular eruption, fever, lymph nodes in your neck may swell -macule- flat like freckle -papule- elevated like a pimple • Dx-Blood test or viral culture • Tx-Take medicines to lower your fever. Also, get plenty of rest and drink lots of fluids Nurse Assistant Herpes zoster (chicken pox/shingles) In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • • • • • Caused by the varicella zoster virus Spread by contact and airborne S/S- very itchy, blistery rash, fever Dx- Symptoms Home Tx- resting and taking medicines to reduce fever and itching (oatmeal baths) Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Ebola • Texas Nurse Union Report • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f -K1m6IsxKI • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= GimY45M-z4o Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • http://www.today.com/health/insideebola-isolation-unit-how-doctorsnurses-protect-themselves2D80215459 Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility How Microorganisms (Bacteria and Viruses) Are Spread • Direct contact (See Figure 3.2.) Touching the resident Bathing the resident Secretion from the resident Urine from resident Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Feces from resident Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility How Microorganisms (Bacteria and Viruses) Are Spread Figure 3.2 – Direct Contact Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility How Microorganisms (Bacteria and Viruses) Are Spread • Indirect contact – touching objects (See Figure 3.3.) Dishes Bed linen Clothing Instruments Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Belongings Figure 3.3 – Indirect Contact Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility How Microorganisms (Bacteria and Viruses) Are Spread • Droplet spread within 3 feet (See Figure 3.4.) Sneezing Talking Coughing Chewing gum (especially blowing bubbles and popping them) Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Figure 3.4 – Droplet Spread Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility How Microorganisms (Bacteria and Viruses) Are Spread • Vehicle contamination (See Figure 3.5.) Food Drugs Water Blood Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Airborne transmission Dust particles Moisture in the air Figure 3.5 – Vehicle Contamination Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Symptoms of Bacterial/Viral Infections • Drainage from wound, eyes, ears, or nose • Reddened or inflames area • Increased heat in an area • Pain • Swelling • Fever Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Confusion Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Other Harmful Microorganisms • Yeast infection (Candida albicans) can affect mouth, genital tract, or skin. • Scabies, head and body lice are transmitted by direct or indirect contact. They may affect head and body, especially genitals, hands, and feet. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Portal of Entry – Microorganisms Enter the Body (See HO 1.) *CNA • Break in the skin or mucous membrane (Staphylococci) • Respiratory tract (common cold) • Genitourinary tract (syphilis, AIDS, bladder and kidney infections) • Gastrointestinal tract (salmonellosis, hepatitis) • Circulatory system (meningitis, malaria) Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Portal of Exit – Microorganisms Leave the Body *CNA • Excretions from respiratory tract • Excretions from genital tract Semen Vaginal secretions • Drainage of wounds • Urine Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Feces • Blood • Saliva • Emesis • Excretions from the digestive tract Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility The Susceptible Host *CNA A person with low resistance or poor immunity – The elderly resident is a susceptible host. • Due to aging process, decreased immune system • Some diseases and conditions predispose the elderly to infection. Diabetes mellitus Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Congestive heart failure Dehydration Malnutrition Immobility Hospitalization Diminished pain sensitivity symptoms Decreased mental ability (unable to describe illness) Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility The Susceptible Host Tumors Drugs Physical or emotional stress • Nosocomial infection *Infection that develops when a person is in a health care facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Studies show that nosocomial infections are common in long-term facilities with a prevalence of 1.6 to 15% of all residents being affected. Most common infections are the following: • Urinary tract infections (UTIs) • Respiratory infections • Gastrointestinal infections • Skin infections Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility The Susceptible Host • Acute phase of infection may be missed because of several underlying factors. Afebrile Resident may be receiving medications such as aspirin or steroids for other diseases that keep the temperature from rising. Decreased sensitivity to pain. Resident may develop confusion. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Fluid and nutritional balance are not maintained. Skin loses fat and becomes thin. Gastric acid decreases. Decreased urinary flow and the presence of catheters may lead to urinary tract infection. Decreased cough reflex and less mucus, due to dehydration or medication. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Body Substance Precautions (BSP) Precautions used by all health care providers to minimize the risk of exposure to disease through contact with body fluids (See HO 2.) • Hands Wash before and after contact with resident. NOTE: Long nails, artificial nails, chipped nail polish, and hand jewelry can harbor harmful microorganisms. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control After using gloves. If hands come in contact with blood and/or body fluids containing blood, wash immediately with soap and water and report to charge nurse. Always wash hands before clocking out. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Body Substance Precautions (BSP) • Use personal protective equipment (PPE) when necessary. PPE includes gloves, apron, or gowns, goggles, and masks. Gloves should be worn when contact is likely with the following: • Any body opening • Blood Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • All moist body fluids • Mucous membranes (nose, mouth, etc.) • Nonintact skin (pressure ulcers, skin tears) • Dressings • Used tissues or wipes • Surfaces or items contaminated with blood or body fluids • Specimen containers being transported Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Body Substance Precautions (BSP) Gowns or plastic aprons should be worn if blood splattering might occur. Remove and discard aprons after completing the task. Face and eye protection – Wear goggles for eye protection when it is likely that eyes will be splashed with body substances. Use a mask to protect the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth. Discard masks after use and place reusable goggles/face shields in a specified container for cleaning. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Body Substance Precautions (BSP) • Disposable razors should never be recapped. Discard in a sharps container. • Blood spills should be cleaned up according to facility policy. • Laboratory specimens and containers should be handled and labeled carefully according to facility policy. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • All laboratory specimens and containers should be labeled with a biohazard symbol. (See Figure 3.6.) • Laboratory specimens should not be stored in a refrigerator containing food or drink. Figure 3.6 – Biohazard Symbol Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control • The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), located in Atlanta, Georgia, and the Missouri Department of Health issue guidelines to protect people and prevent the spread of infection. • Control of infection at the source Maintain health; have illness and infections treated. Report any open lesions or weeping skin rash to supervisor before having contact with the residents. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Notify your supervisor if you are ill or infected. Correct handwashing technique. Facility disinfection and sterilization. Housekeeping. Keep work area neat and clean. Clean linen properly. Dispose of soiled disposable articles properly. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control • Control of infection at the transmission level Wash hands before and after caring for each resident. Long nails, acrylic nails, hand jewelry, and chipped polish can harbor infectious microorganisms. Facility policy for catheter care. Follow Body Substance Precautions. If several resident have the same symptoms, report to the charge nurse immediately. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Wear gloves to wipe up any spills of blood and blood products per facility’s policy. Treat bloody linens as a biohazard; bag at point of contact and dispose per facility policy. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control • Control of infection at the resident level Know resident, report any abnormal change in behavior or symptoms. Cleaning and giving care from clean to dirty. Observe residents who are receiving antibiotics for side effects and report these immediately (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rashes, yeast infections, thrush). Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Prevent pressure ulcers by giving good nursing care. (See Unit V, Lesson Plan 11, Preventing and Caring for Pressure Ulcers.) Do not share articles of personal care among residents. Personal care items should be labeled with the resident’s name. Work toward maintaining nutrition and activity of the resident. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control Use gloves when doing mouth care, perineal care, skin care, and other procedures involving body fluids. Wear masks, gloves, goggles, and gown as per facility policy when caring for the resident who might cough or spray mucus discharge. • Specific control measures Handwashing – the single most important means of preventing the spread of infection Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Our hands carry germs. • Good handwashing technique prevents spread of germs. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control • Wash your hands for at least 15 seconds. When you first come on duty and before going home Before and after contact with each resident Before and after glove use After contact with any waste or contaminated material Before any contact with food Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Before and after going to the bathroom, breaks, or smoking After coughing, sneezing, or blowing nose • Wash resident’s hands before meals and at other appropriate times (e.g., after going to the bathroom). • Any water faucet is always considered contaminated or dirty. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control • Turn the facet off with a clean, dry paper towel. • Use soap from a dispenser, rather than bar soap. Bar soap accumulates pools of soapy water in the soap dish, which is a good medium for germ growth. • Never use the resident’s bar soap to wash your hands. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • When washing hands, hold hands below elbows to allow water to run down the fingertips so germs do not contaminate your arms and uniform. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control Linen changing • Keep linen away from uniform. • Avoid shaking or fluffing linen. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Place used linen in a nonporous bag (e.g., plastic bag) at the side of the bed. Never put linen directly on the floor. Placed closed bagged linen in designated soiled linen container. Do not overfill bags because they tend to rupture if they are dropped. • Change linen any time it is soiled. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control Sanitation • Clean, label, and cover all individual utensils and return to bedside table after each use. NOTE: Disposable items should not be reused. Return soiled dishes to dietary department after each meal. Damp-wipe overbed tables. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • Each resident should have his/her own hygiene supplies and equipment. The equipment should be cleaned regularly and labeled with the resident’s name. • Transfer belts should be kept clean and washed weekly and whenever necessary. • When cleaning an item or part of the body, start with the cleanest area and work toward the dirtiest area. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Infection Control Disinfection • Disinfection is a process of destroying as many harmful microorganisms as possible. • See facility’s procedure regarding disinfecting thermometers, utensils, shower chairs, bathtubs, bed frames, mattresses, and denture cups. NOTE: Disinfection is accomplished by thoroughly cleansing an object by hand. Unit III: Safety Sterilization – used on metal or rubber objects that are reusable Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control • A process that kills all microorganisms • Requires special processing and handling NOTE: Sterilization is accomplished using chemical/mechanical methods. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Important Factors • Be aware of and follow specific measures to take for each type of transmission-based precaution. A “Stop Sign Alert” card should be posted on the door of each resident who is on transmission-based precautions. Follow recommendations given to protect everyone. Gowns, gloves, and/or masks may be required for the nurse assistant. • Always organize your work before going into the room. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Gather all supplies and linens needed. Inform other staff members if you need their assistance. • Remember to wash hands before and after contact with the resident. This is the single most important means of preventing the spread of infection. • Gloves do not eliminate the need to wash your hands; they just provide a barrier between you and potentially infectious microorganisms. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Important Factors • Never touch unnecessary articles in the room or one’s face, hair, contact lens, or glasses when wearing gloves. • Always wear gloves when handling or picking up any medication patches. • Remove gloves before leaving the resident’s room. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Conclusion Understanding germs and the importance of controlling them in the long-term care environment is essential for controlling infection. Handwashing is so simple but often neglected. Take time to protect everyone – yourself, your family, coworkers, and the residents. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Steps of Procedure for Washing Hands 1. Remove wristwatch and/or rings if necessary. Roll up your sleeves. (Wash wristwatch and rings if they come into contact with contaminated material.) 2. Turn on water with knee, foot, or hand controls; adjust temperature so it is comfortable for you. CAUTION: Do not touch controls during the rest of the procedure. 3. Wet hands thoroughly, including 2 to 3 inches above wrists. Hold hands with wrists lower than elbows and fingertips pointed downward. 4. Apply a generous amount of soap to hands. Do not use bar soap. 5. Scrub hands for at least 15 seconds. Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control a. Wash palms and back of hands with at least 10 circular motions. Nurse Assistant In a Long-Term Care Facility Unit III: Safety Lesson Plan 3: Infection Control Steps of Procedure for Washing Hands b. Wash fingers and between fingers with at least 10 circular motions. c. Wash wrists with at least 10 circular motions. d. Wash round and under fingernails. 6. Rinse wrists and hands well. Keep wrists lower than elbows. 7. Dry hands well with paper towel or fresh clean towel, using one for each hand. 8. Turn off faucet with clean, dry paper towel. 9. Discard paper towel. Be careful not to touch the part that touched the faucet. 10. Use a clean paper towel to turn knob on door or pull door open.