* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current Biomarker Knowledge and Clinical Practice
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
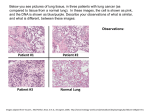
Current Biomarker Knowledge and Clinical Practice in Cystic Fibrosis Gap Analysis of Knowledge and Practice: • Prioritize CF Disease Aspects in Need of Biomarkers • Generate List of Patient Tissue/Fluid Sample Types and Relationship to Disease Aspects Overview: • Review of Cystic Fibrosis Emphasizing Biomarkers • Lung Disease • Suggestions, Recommendations F. Accurso, MD, CF Center Director and Professor of Pediatrics, University of Colorado, Denver, USA (CF Foundation, NHLBI, NIDDK, NCRR, CF Community) Cystic Fibrosis 25 100 20 80 15 60 10 40 5 20 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Age at Death (n=409) 40 45 0 50+ Cumulative Percent Number of Deaths • Definition: Multisystem, genetic disorder leading to early death, primarily from progressive lung disease. • 30,000 individuals in US • Median life expectancy - 35 years (CFF registry, 2004) • Median age at death - 26 years (CFF registry, 2001) Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) • CFTR - Membrane glycoprotein - ABC, c-AMP - Regulates ion flux - chloride, sodium, bicarbonate - 1400 mutations (www.genet.sickkids.on.ca/cftr/) - Delta F508 (70% of alleles in US) • Diagnosis (CFF consensus conference, J Pediatr,1998) - Symptoms and Signs - Physiology - evidence of CFTR dysfunction (sweat electrolytes, nasal potential difference) - Genotype – Two defined mutations - Family History - “Positive Newborn Screen” (Protein Biomarker -Immunoreactive Trypsinogen) CFTR: Need for Protein Biomarkers • Diagnosis in Atypical Cases • Clinical Trial - Proof of Concept Dysfunctional CFTR Cells directly involved in CFTR pathophysiology (Airway Epithelium, Sweat Gland) Cellular Biomarkers of CFTR Presence and/or Function Organs/Tissue Secondarily involved Lung Fluid or Breath, Present in Pancreas Biomarkers of Newborns Intestine Organ Dysfunction Liver and Injury Lung Disease in CF: Clinical Course • Decline in Lung function 100 (CFF registry, 2001) 90 • Acute Exacerbations 80 70 - personal, economic impact 60 - ? decline in lung function. 50 (Phase III trials, unpublished) 40 6 • Structural Lung Injury • Daily treatment - 3-25 medications per day - Oral, inhaled, injectable - Chest Physical Therapy - Nutritional supplementation - Gastrostomy, central line 2001 18 Years 3 CF Pathophysiology Neutrophils Epithelial Cells Lymphocytes (Hubeau et al, 2001) Macrophages (Durieu et al, 1998) Lung Disease in CF: Assessment We do not have a biomarker (biochemical index) or panel of biomarkers that is carefully defined for any Pulmonary clinical use in CF. Assessment History Clinical Yes Research Comment Needs Refinement (CFFTDN) Physical Exam Yes Not quantitative O2 Saturation Yes Acceptable Lung Function Yes Rapidly Improving (CFFTDN) Imaging - x-ray Yes Scoring systems - CT scan Yes Quantitation developing - VQ scan No Not as outcome measure - Mucociliary Cl. No Needs standardization Lung Disease in CF: Assessment Assessment Clinical Research Comment Laboratory - CBC, ESR Yes Acute Exacerbation - CRP Yes Acute Exacerbation - IgE Yes Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis - Pseudomonas Antibodies No Uncertain utility - Quantitative Cultures Yes Good Utility - Sputum Inflammation No Cell Count, IL-8, elastase (some research utility, ?sensitivity) Protein Biomarkers for CF Lung Disease Need Existing Biomarker(s) I. Risk for Rapid decline in lung function No I. Ongoing Lung Structural Injury (Fibrosis, Elastolysis, Remodeling) No I. Identification of Infection - Pseudomonas aeruginosa - MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staph.) - Burkholderia cepacia - NTM – M. avium, M. abscessus - Fungal species No I. Clinical Trials of Antiinflammatories - Stratification - Efficacy ? Sputum Elastase, IL-8, LTB4 Protein Biomarkers for CF Lung Disease Need Existing Biomarker(s) II. Exacerbation - Identification - Susceptibility to exacerbations No No II. Response to treatment No II. Toxicity with treatment No II. Staging No II. Newborn Screening Yes Protein Biomarkers for CF Lung Disease Need Existing Biomarker(s) Clues to Pathogenesis - Intracellular or Membrane (CFTR Presence or Function) No? - Key Pathway (Inflammation, Fibrosis, Antimicrobial Defense) in Organ Dysfunction No - Diagnosis in Atypical Cases (Disease Susceptibility) No Search for Protein Biomarkers in CF Lung Disease: Summary • Neutrophil Associated Molecules • None have been explored in large populations • Panels of more than five markers are only now being investigated. (little multiplex data or “cluster”, “network” or “pattern” analysis) • Proteomic studies are appearing • Bronchoalveolar Lavage - Clinical Utility – Microbial diagnosis - Clues to Pathogenesis Protein Biomarkers of CF Lung Disease: Sputum Elastase (log ug/ml) • Putative Biomarkers - Proteolytic - Cytokines, growth factors - Oxidant/antioxidant - Surfactant proteins • Research Utility - Azithromycin study - Intravenous antibiotics - Interferon gamma study - Hypertonic saline study 2 Control Azithro. 1 p=0.01 for change 0 0 Months 6 (Saiman et al., JAMA, 2003) Protein Biomarkers of CF Lung Disease: Blood/Inflammation • Candidates: CRP, cytokines, growth factors, albumin, oxidant/antioxidant, S-100, • Mostly exacerbation studies Biomarker Development 1. Proteomic Experiments Choose Form Validation Many Steps Make ELISA 2. Multiplex Platforms Many Steps • Microsphere - Luminex • Protein Arrays – Randox • Small Sample Volume, Parallel analyses • 20 Mediators, Candidates can be added Application Protein Biomarkers of CF Lung Disease: Elastolysis • Elastin Breakdown Products - Urinary Desmosine, Isodesmosine (Stone et al. AJRCCM, 1995) • Renewed interest (Ma et al, PNAS, 2003) - Demonstration in sputum, blood - Measurement of Free and Polymerized Forms • Mass Spec improves sensitivity – 100 pg • 9 year old with CF well visit Additional Biomarkers in CF • Breath – Proteins in very low abundance - Volatile gases, pH - Nitric oxide related compounds - Pseudomonas markers (PNAS, 2005) • Nutrition – Very abnormal in CF - Albumin, Retinol Binding Protein - Fat soluble vitamins, Carotene - May confound interpretation of results • Liver Disease – Focal sclerosis - Cytokines, Growth Factors, Elastin products - Confound Pulmonary analyses Protein Biomarker of Pancreatic Disease in CF: Trypsinogen IRT ng/ml N=288 600 400 200 0 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 Age (months) • Residual Trypsinogen at a year of age predicts Better Lung Function throughout childhood 1979 Validation Benefit 2004 Endorsement Samples for Protein Biomarker Identification Sample . Rapid Prog. Lung Pathogenesis Destruct. BAL + + ++++ Sputum +++ +++ +++ Exhaled gases ? ? Breath Cond. ? Blood Stratif Outcome ( Clin Trials) Exacerb. + ++ ++ +++ +++ +++ ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ++ Urine + ++ ? ? ? Saliva + ? ? ? ? + + Epithelium, Circulating Cells – protein expression Current Protein Biomarker Projects Local Biomarkers annual Biomarkers annual Specimen Blood Features Support N Multiplex (Luminex) (Randox) NCRR NHLBI 300 Multiplex NCRR 35 Sputum Glutathione Clinical Trial Blood Sputum Multiplex CFF Industry 30 Elastin products Urine, others Exacerbations CFF 100 Several clinical settings CFF 150 Industry NCRR 15 CFF 15 Novel biomarkers Urine From proteomic studies Inhaled NO Azithromycin Breath, others Multiplex Blood S-100a12 Multiplex Also, 6 CFF and/or Industry sponsored multicenter trials – 300 patients Future Clinical Evaluation Enter Clinic (Ht, Wt, VS) Urine, Blood Pulmonary Function Testing Lab Sputum Induction Lab (Molecular Microbial Dx) Point of Service Testing Exam Room - Clinical Evaluation - Lung Biomarker Profile - Personalize Treatment - Enrollment in Trial