* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is a Silicon Transient Voltage Suppressor and how does it
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
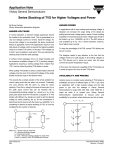
Application Note Vishay General Semiconductor What is a Silicon Transient Voltage Suppressor and how does it work? By Bruce Hartwig Senior Automotive Applications Engineer Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS’s) are devices used to protect vulnerable circuits from electrical overstress such as that caused by electrostatic discharge, inductive load switching and induced lightning. Within the TVS, damaging voltage spikes are limited by clamping or avalanche action of a rugged silicon pn junction which reduces the amplitude of the transient to a nondestructive level. In a circuit, the TVS should be “invisible” until a transient appears. Electrical parameters such as breakdown voltage (VBR), standby (leakage) current (ID), and capacitance Transient Voltage Clamped Transient + Transient Current Protected Load TVS - should have no effect on normal circuit performance. The TVS breakdown voltage is usually 10 % above the reverse standoff voltage (VR), which approximates the circuit operating voltage to limit standby current and to allow for variations in VBR caused by the temperature coefficient of the TVS. When a transient occurs, the TVS clamps instantly to limit the spike voltage to a safe level, called the clamping voltage (VC), while conducting potentially damaging current away from the protected component. IC Failure Threshold + 30 V + 12 V TVS’s are designed, specified and tested for transient voltage protection, while a Zener diode is designed and specified for voltage regulation. For transient protection, the designer’s choice is a TVS. The surge power and surge current capability of the TVS are proportional to its junction area. Surge ratings for silicon TVS families are normally specified in kilowatts of peak pulse power (PPP) during a given waveform. Early devices Transient Peak + 20 V Figure 2. Transient Current is Diverted to Ground Through TVS; the Voltage Seen by the Protected Load is Limited to the Clamping Voltage Level of the TVS TVS Clamping Voltage (Vc) were specified with a 10/1000 µs waveform (10 µs rise to peak and 1000 µs exponential decay to one half peak), while more recent product introductions are rated for an 8/20ìs test waveform. Power ratings range from 5 kW for 10/1000 µs, down to 400 W for 8/20 µs. This power is derived from the product of the peak voltage across the TVS and the peak current conducted through the device. Normal Operating Voltage Figure 1. Transients of Several Thousand Volts can be “clamped” to a Safe Level by the TVS Packaging covers a broad spectrum according the need. Discrete axial leaded components are available in peak pulse power ratings of 400 W, 500 W, 600 W, 1.5 kW and 5 kW. The higher power devices are most frequently used across power buses. www.vishay.com 256 Document Number: 88436 Revision: 02-Feb-07 Application Note Vishay General Semiconductor Figure 3. Transient Voltage Suppressors are Offered in Axial, Surface-Mount and Array Packages For lower power, high density applications, suppressor arrays are available in both DIP and small outline surface mount configurations. Arrays are normally used across data lines for protecting I/O ports from static discharge. Specialized low capacitance TVSs are available for use in high data rate circuits to prevent signal attenuation. Integrated circuits normally feature on-chip protection which is usually provided by internal resistor-diode networks or SCR’s. There is insufficient space on a microchip to provide more than minimal protection, so the higher power, external protection of a TVS should be added in those applications where damaging transient voltage threats exist. TVSs have circuit operating voltages available in increments from 5 V up through 376 V for some types. Because of the broad range of voltages and power ratings available, (as well as the universal presence of transient voltages) TVSs are used in a remarkably wide variety of circuits and applications. The loss to U.S. industry due to transient voltages exceeds $ 10 billion per year. TVS devices are an important part of the solution. Document Number: 88436 Revision: 02-Feb-07 Vishay General Semiconductor has become the world’s leading supplier of silicon TVS protection. www.vishay.com 257