* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oral cavity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
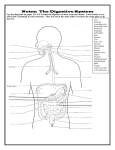
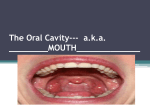
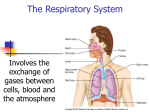
Head & Neck Surgery Course r f . s Oral cavity: surgicalm anatomy e i n l r o . w w w Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Introduction Schematic representation of oral cavity and floor of mouth m i rl-n o . ww w r f . es A: philtrum; B: upper labial frenulum; C: opening of Stensen's duct; D: labial commissure; E: hard palate; F: soft palate; G: intermaxillary commissure; H: base of tongue; I: lateral border of tongue, dorsal view; J: tip of tongue, dorsal view; K: tip of tongue, ventral view; L: lateral border of tongue, ventral view; M: ventral surface of tongue; N: lingual frenulum; O: floor of mouth; P: opening of Wharton's duct; Q: vestibular gingiva; R: vestibule. Introduction Mucosal features of oral cavity w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Introduction Coronal section w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Introduction Physiology Functions • Speech • Mastication • bolus preparation and initiation of deglutition w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: anatomy Boundaries • Anteriorly: – Vermilions (superiorly and inferiorly) o . ww m i rl-n • Posteriorly: the oral cavity is w separated from the oropharynx by – the anterior tonsillar pillars – circumvallate papillae (inferiorly) – junction of hard and soft palate (superiorly) r f . es Oral cavity: anatomy Skeleton r f . es • Mandible • Maxilla w o . ww • Palatine bone m i rl-n Oral cavity: anatomy Skeleton w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: anatomy Skeleton w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: anatomy Muscles • Masticatory muscles – – – – • Temporal Masseter Internal pterygoid External pterygoid w Muscles of facial o . ww expression m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: arterial supply w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: arterial supply w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: venous supply w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: innervation • • • • • Greater palatine nerve (V2) r f Lingual nerve (V3 and VII) . s e m i n XII CN l r o . w Inferior alveolar nerve (V3) w w Posterior, midldle and anterior superior alveolar nerve (V2) Oral cavity: innervation w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: innervation w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: innervation w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: innervation w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Oral cavity: lymphatics • m i rl-n r f . es o . 1st echelon nodes:ww w level I,II,III • Then IV, V • Skip metastasis! Sites of oral cavity • • • • • • • lips alveolar ridges buccal mucosa retromolar trigone hard palate floor of mouth mobile tongue w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Tongue: anatomy •The sulcus terminalis divide the anterior and posterior tongue •Tongue base ends at the vallecula o . ww m i rl-n w •Foramen cecumarea(where the thyroid descends) r f . es Tongue: muscles •There are 8 muscles of the tongue •They are classified as intrinsic and extrinsic muscles w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Tongue: muscles There are 4 paired intrinsic muscles of the tongue Superior Longitudinal Inferior longitudinal Verticalis Transversus muscle w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Tongue: muscles r f . es Function of the intrinsic muscles Inferior and superior longitudinal muscles - Move tip up and down o . ww m i rl-n w Transverse muscle -Narrows and lengthens the tongue Vertical Muscle - Flattens and depresses the tongue Tongue: muscles The 4 extrinsic muscles are Genioglossus-from the mandible Hyoglossus- from the hyoid bone Styloglossus- from the styloid process Palatoglossus- from the palatine aponeurosis w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Tongue: muscles r f . es Function of the extrinsic muscles Genioglossus- protrusion of tongue apex from the mouth Hyoglossus- depression of the tongue Styloglossus- elevates and retracts the tongue Palatoglossus- elevates and retracts the tongue w o . ww m i rl-n Tongue: arterial supply r f . es •lingual artery •Other contributors include the ascending palatine and tonsillar branch of the facial artery w o . ww m i rl-n Tongue: venous supply r f . es •lingual vein w o . ww m i rl-n Tongue: innervation Sensory nerves o . ww m i rl-n w Motor innervation r f . es Tongue: innervation Sensory nerves Lingual branch of V2-General sensation for the anterior two thirds of tongue m i rl-n o . ww Chorda tympani of CN VII- taste for anterior 2/3 w r f . es Lingual branch of CN IX- General sensation and taste for posterior 1/3 Superior laryngeal CN X- root of tongue and lingual base sensation. Tongue: innervation Motor innervation o . ww m i rl-n All tongue muscles are innervated by XII except the palatoglossusinnervated by X w r f . es Hard palate: anatomy • The palate forms the roof of the mouth and intervenes between the nasal and oral cavities. w o . ww m i rl-n • It consists of the palatine process of the maxilla, the horizontal plates of the palatine bone. r f . es Hard palate: anatomy • Three foramina open on the oral aspect of the hard palate w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Foramina that open on the oral aspect of the hard palate Incisive Fossa – Slight depression posterior to central incisor teeth – Nasopalatine nerve o . ww m i rl-n Greater palatine foramina w – Medial to 3rd Molar – Greater palatine vessels and nerve Lesser palatine foramina – Lesser Palatine nerves and vessels to soft palate r f . es Hard palate: arterial supply Greater palatine artery • branch of the third part of the maxillary artery o . ww m i rl-n • it descends with its accompanying nerve in the palatine canal. w Superior Alveolar Arteries • terminal branches of the internal maxillary artery r f . es Hard palate: arterial supply • The greater palatine emerges on r f . es the hard palate from the greater m i rl-n palatine foramen o . ww • runs forward in a groove on the w inferior surface of the bony palate almost to the incisor teeth • supplies the gums and the mucosa and glands of the hard palate. Hard palate: arterial supply • The superior alveolar arteries (anterior, middle, posterior) provide blood o . ww m i rl-n supply to the maxillary w gingiva, alveolar ridge, and dentition r f . es Hard palate: venous supply m i rl-n o . ww w r f . es • The venous drainage is to the pterygoid plexus and subsequently to the internal jugular venous system. Hard palate: innervation • The nasopalatine nerves w o . ww m i rl-n • Greater Palatine Nerves r f . es Hard palate: innervation • The nasopalatine nerves – branches of V2 – They enter the palate at the incisive foramen – they supply the anterior part of the hard palate behind the incisor teeth. w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Hard palate: innervation • Greater Palatine Nerves – Greater (and Lesser) Palatine run through the palatine canal and exit at the Great and Lesser Palatine Foramens, respectively. w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Hard palate: innervation • Greater Palatine Nerves – Parasympathetic postganglionic secretomotor fibres from the pterygopalatine ganglion run with the nerves to supply the palatine mucous glands. w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Perineural Spread • Tumors spreading by perineural extension can be discovered by radiographic enlargement of the palatine foramina or widening of the palatine canals or the foramen rotundum. w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Upper Alveolar Ridge m i rl-n o . ww w r f . es • The upper alveolar ridge consists of mucosa overlying the alveolar process of the maxilla and extends from the gingivobuccal sulcus to the junction of the hard palate medially. Inferior Alveolar Ridge m i rl-n o . ww w r f . es • The inferior alveolar ridge consists of mucosa overlying the alveolar process of the mandible and extends from the gingivobuccal sulcus to the junction of the floor of the mouth. Floor of the mouth (FOM): anatomy • FOM extends from the inferior alveolar ridge to the anterior tongue w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Floor of the mouth (FOM): anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Floor of the mouth (FOM): anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Floor of the mouth (FOM): anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Floor of the mouth (FOM): anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Floor of the mouth (FOM): anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Lips and buccal mucosa: anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Lips and buccal mucosa: anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Retromolar trigone: anatomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Head & Neck Surgery Course r Oral cavity: surgical options f . s e m i and technique l-n ww r o w. Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Surgical approaches to the oral cavity (a) Peroral r f . (Mandibular swing): s e m i l-n (b) Mandibulotomy w w w r o . lower lip-splitting incision or visor flap (c) Lower cheek flap (d) Visor flap (cervical degloving) (e) Upper cheek flap a) Peroral es.fr w o . ww m i rl-n Peroral partial glossectomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Peroral Pelvectomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Peroral approach to the palate w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Peroral resection of tumor of the upper alveolus w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Marginal mandibulectomy-Pull Trough operation (peroral) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es b) Mandibulotomy (Mandibular r f . s e swing) m i -n w w w l r .o Transmandubular resection of oral/oropharyngeal cancer • “Mandibular swing” r f . es • Midline lip splitting or visor flap m i rl-n • Mandibulotomy anteriorly, incise w o . ww along floor of mouth to anterior tonsillar pillar • Identify hypoglossal nerve and lingual nerve • Divide styloglossus and stylopharyngeus muscle • Need tracheotomy Partial glossectomy via lip split mandibulotomy (Mandubular swing) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es c) Lower cheek flap fr . w ww i n l r o . s me Marginal mandibulectomy via lower cheek flap (Pull Through operation) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Marginal mandibulectomy via lower cheek flap (Pull Through operation) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Marginal mandibulectomy via lower cheek flap (Pull Through operation) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Segmental mandibulectomy – Commando operation via lower cheek flap w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Segmental mandibulectomy – Commando operation via lower cheek flap w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Segmental mandibulectomy – Commando operation via lower cheek flap w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es d) Visor flap (cervical degloving) fr . w ww i n l r o . s me Marginal mandibulectomy-Pull Trough operation (visor flap) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Anterior Segmental mandibulectomy via visor flap w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Anterior Segmental mandibulectomy via visor flap w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Partial glossectomy via visor flap (Mandubular swing) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es e) Upper cheek flap w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Partial maxillectomy (upper cheek flap) for tumor of hard palate/upper alveolus w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es f) Other approaches w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Midfacial degloving approach for tumor of hard palate/upper alveolus w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Total glossectomy via mandibular lingual release (Pull Through) w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Appendix: mandible management w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Patterns of tumor invasion of the mandible w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Patterns of tumor invasion of the mandible w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Mandible management • Patterns of tumor invasion of the mandible dictate mandible management m i rl-n – Marginal mandibulectomy o . ww w r f . es – Segmental mandibulectomy Marginal mandibulectomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Marginal mandibulectomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es Segmental mandibulectomy w o . ww m i rl-n r f . es