* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding Orbits
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
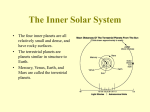
The Sun and It’s Domain Know about the Sun’s Energy Know about the Sun’s Core, Atmosphere, and Sunspots Comprehend the Solar System’s Structure Lesson Overview The Sun’s Energy The Sun’s Core, Atmosphere, and Sunspots The Solar System’s Structure The Sun’s Energy Hermann von Helmholtz and Lord Kelvin proposed that the source of the Sun’s energy was a very slow gravitational contraction Scientists began considering that mass can be converted to energy, and energy into mass The Nuclear Fusion Power of the Sun An atom’s nucleus is made up of protons, positively charged particles; and neutrons, particles with no electrical charge In nuclear fusion, two nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus. They “fuse.” Primary source of the Sun’s energy is a series of nuclear fusion reactions The Sun’s Core, Atmosphere, and Sunspots The equilibrium conditions in the Sun are known as hydrostatic equilibrium Great pressures at the center of the Sun pushes protons close enough together that hydrogen fusion can take place Fusion reactions in the core provide a heat source The Three Modes of Solar Energy Transfer 1. Conduction is the transfer of energy in a solid by collisions between atoms and/or molecules The Three Modes of Solar Energy Transfer, 2. 3. Convection occurs when the atoms of a warm liquid or gas move from one place to another Radiation is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves The Three Layers of the Sun’s Atmosphere 1. 2. 3. Photosphere is the visible part of the Sun and that part of the solar atmosphere that emits light Chromosphere is the region between the photosphere and the corona Corona is the outermost portion of the Sun’s atmosphere The Solar Wind Solar wind is a continuous outflow of charged particles from the Sun Moving at about 249 miles per second near Earth, it plays a significant role in space weather activity The Impact of Sunspots and Solar Flares on Earth’s Climate Sunspots are dark spots appearing on the Sun’s surface caused by the Sun's magnetic field welling up to the photosphere, the Sun's visible "surface". A solar flare is an explosion near or at the Sun’s surface, seen as an increase in activity such as prominences (bulges) http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=nmDZhQAIeXM The Solar System’s Structure The Sun more than 99 percent of the Solar System’s mass 10 times larger in diameter than Jupiter Sun’s diameter is about 862,000 miles How the Solar System Formed Evolutionary theory - how the solar system came to be as part of a natural sequence of events Catastrophe theory refers to an unusual event Modern evolutionary theories - the formation of the Solar System resulted from gravitational forces and pressures on heat and mass Classifying Objects in the Solar System Four innermost planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars – are called the terrestrial planets Next four planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune – are called the Jovian planets Pluto is now considered a dwarf planet Classifying Objects in the Solar System, A planet is a celestial body that: Orbits the Sun Has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a nearly round shape Has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit Sun BINGO Challenge B I N G O Catastrophe Theory Solar Wind Jovian Planets Terrestrial Planets Solar Wind Solar Flares Chromosphere Modern Evolutionary Theories Convection Sunspots Conduction Corona FREE SPACE Helium Solar Flares Dwarf Planet Equilibrium Hydrogen Hydrostatic Equilibrium Neutrons Evolutionary Theories Radiation Protons Nuclear fusion Photosphere The Sun and It’s Domain Know about the Sun’s Energy Know about the Sun’s Core, Atmosphere, and Sunspots Comprehend the Solar System’s Structure