* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ACCESS
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Open data in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
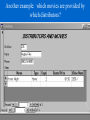
Microsoft Access Database Creation and Management The first step in creating a database table is to create its structure. Always create the design of the table before entering data. You begin by specifying the fields you want to include and their characteristics. • Primary Key: – A field that uniquely identifies each record in a table. – Used to sort or index a database. – No two records can have the same primary key. • Input Mask – Allows you to simplify data entry for fields that have the same format. – You create the standard format (the mask) • Specify field sizes Access Modifying the Data Table • Widen out or narrow down columns to improve appearance. DO NOT CUT OFF WORDS. • Add new records. • Add new structure items. Manipulating a Database • Sort records into a particular order. – Sort columns in ascending or descending order – Can also sort adjacent columns. Access sorts adjacent columns from left-to-right. – If columns are not in the correct order for sorting, you must rearrange the columns. Access: Samples Manipulating a Database • Filter: Displays only a subset of the entire table that matches your criteria. Every single field shown – You can filter on a single field and one criteria – You can filter on a single field with multiple criteria – Advanced Filter: Filter By Form • Allows you to specify criteria for multiple fields • Query Design – Specify the exact criteria you wish to view. – View only the fields you wish to see: All other fields not shown. Common Query Operators • • • • • Text Criteria “Fred Jones” Greater than > >1000 Less than < <1000 Equal to = =1000 Greater than or equal to >= > =1000 Less than or equal to <= < =1000 Creating Relationships • Relationships are used to link tables together. • Relationships are based upon common fields in both tables. • Drag the name from one table over to the next table and a connecting line will appear. Access INFORMATION STORED SEPARATELY BUT CAN BE RELATED THROUGH KEY JOINS Another example: which movies are provided by which distributors? Forms Access • Forms are used to customize your data entry screen. You see only the relevant items in the location where you want them. • Forms are created for the convenience of the user. • You can change locations of fields and colors very easily in the Design screen. • Forms are used to update Data Tables. Reports • Reports are used to “Dress Up” or summarize your data. Access • Reports can be made from a Table or Query. • You can use a Wizard to create your reports or you can customize them to fit your needs. – You can specify sorting orders and you can also group data. Basic Database Definitions • Table – All the data relating to a particular subject. • Record – An individual entry in a table. – Like a file folder. • Field – Piece of information in a record. – Last Name, First Name, Address, City Access Database Objects • Table Object – Data Table: Basic area where your data is stored and manipulated. • Query Object – Results of a question or condition you outline. – All students at KSU who belong to the CBA. • Form Object – Data entry screen that you can customize . – Used to add new records. • Report Object – Used to print and emphasize specified information. Database Views • Design View – Lets you see the structure of the database and create its properties. • Datasheet View – Lets you see the actual data.