* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download antigens
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
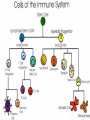
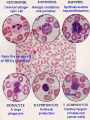
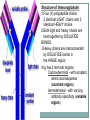
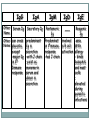
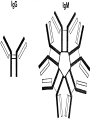
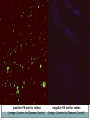
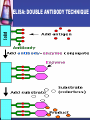
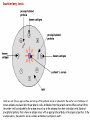
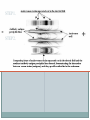
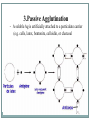
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Faculty of Allied Medical Sciences Clinical Immunology & Serology Practice (MLIS 201) Over View Prof. Dr. Ezzat M Hassan Prof. of Immunology Med Res Inst, Alex Univ E-mail: [email protected] Clinical Immunology & Serology Practice (Code: MLIS 201) Teaching Objectives: 1- To know the elements of serological reactions 2- To define serological reactions 3- To describe the basics of primary and secondary serological reactions ANTIGENS Definition: Any molecular structure that when introduced is capable of Antibody production. Parts of Antigen Carrier portion - responsible for the molecular weight of antigen Epitope or Determinant - determines specificity of antigen Two Properties of Antigens 1. IMMUNOGENICITY - inherent ability of a substance to induce the specific immune response resulting in the formation of immune lymphocytes or antibodies Factors influencing Immunogenicity (Summary) 1-Foreigness : Foreign substances are immunogenic 2- Molecular size: High molecular weight increase immunogenicity 3- Chemical structure complexity: High complexity increase immunogenicity 4- Route of administration: Parenteral routes are more immunogenic to oral route SC>IP>IV>Intragastric Factors influencing Immunogenicity (Summary) (cont.) 5- Degradability of the immunogen 6-Genotype of the recipient 7- immunogen dose: Appropriate dose Low dose High dose optimum antigenicity low- zone tolerance high-zone tolerance 8- Adjuvant: Substance when injected with an immunogen enhance immunogenicity 2. ANTIGENICITY/SPECIFICITY - the ability to react specifically with the antibody or cell that caused it to be produced ANTIBODIES Definition: Spec. glycoproteins, produced by plasma cells in response to antigenic stimulation of B lymphocytes. Immunoglobulins. Structure of Immunoglobulin 1.Four (4) polypeptide chains: 2 identical LIGHT chains and 2 identical HEAVY chains. 2.Both light and heavy chains are held together by DISULFIDE BONDS. 3.Heavy chains are interconnected by DISULFIDE bonds in the HINGE region. 4.Ig has 2 terminal regions: Carboxyterminal - with constant amino acid sequence (constant region). Aminoterminal - with varying antibody specificity (variable region) Classes of Immunoglobulins IgG IgA IgM IgD IgE Molecular Weight Daltons 150 T 160-400 T 900 T 180 T 190 T Halflife 21-23 days 5-6 days 5 days 2-3 days 2-3 days Subclasses 4 2 2 - - Domains 4 4 5 4 5 Activate Complement? Yes Alt pathway only Yes No. No. IgG Other Name Serum Ig Other can cross Notes placenta except -major Ig in 2º Immune response IgA Secretory Ig predominant Ig in secretion -with J chain -exist as monomerin serum and dimer in secretion IgM Pentameric Ig IgD ___ IgE Reagenic Ig Predominat involved asso. in 1ºimmune in B cell With response activation allergy - binds -has J chain basophils and mast cells elevated during parasitic infections Complement System COMPLEMENT SYSTEM - A set of serum proteins that play a role in cytolytic destruction of cellular antigen by specific antibody. - reaction is nonspecific to the target cell - destroyed at 56ºC for 30 minutes - the in vitro study of antigen-antibody reaction - laboratory study of the activities of the components of blood serum that contributes to immunity Immunologic Reactions: Primary - combination of Ag-Ab; non-visible reaction Secondary - demonstrable Ag-Ab rxn (e.g. precipitation, agglutination) PRIMARY IMMUNOLOGIC TESTS. IMMUNOASSAYS Ligand - any substance that will complex to another substance; (the substance to be measured. A. FLUORESCENCE IMMUNOASSAY Fluorescent Probes used: a. FITC (Fluorescein isothiocyanate) b. Phycocyanin c. Texas red d.Tetramethyl rhodamine -emits green light***mostly used -emits red light -emits red light -emits red orange light Techniques: 1. Direct/Single Layer Immunofluorescent Assay 2. Indirect/Double Layer Immunofluorescent Assay positive FA test for rabies (Image: Centers for Disease Control) negative FA test for rabies (Image: Centers for Disease Control) C. ENZYME IMMUNOASSAY colorimetric reaction Enzymes Used: a. b. c. d. ALP Horseradish Peroxidase Glucose oxidase B-galactosidase Techniques: 1. Direct 2. Indirect 3. Sandwich/Double Ab 4. Competitive Binding 5. Enzyme Inhibition ELISA: DOUBLE ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE Secondary tests PRECIPITATION AGGLUTINATION COMPLEMENT FIXATION NEUTRALIZATION I.PRECIPITATION RXNS - Antigens involved are soluble antigens. Types of Precipitation reaction: 1. Single diffusion, Single Dimension Px serum w/ soluble Ag (+) rxn - formation of pptn line Gel/Agar impregnated w/ known Ab 2. (RADIAL IMMUNODIFFUSION) - uses a plate containing agar with known antibody - Px serum is placed on the wells - Diameter of the pptn line is directly proportional to the concentration of the target antigen 5. Immunoelectrophoresis (IEP) - useful procedure for the ID of monoclonal proteins (Bence Jones Protein) - utilizes both double diffusion and electrophoresis a. Ags migrate under an electric current (-) Ag (+) b. Rgt. Ab Added. Diffusion through gel (-) (+) Antibody c. (+) rxn - Pptn arcs formed (-) (+) STEP 1. STEP 2. II. AGGLUTINATION REACTIONS - Ags involved are particulate antigens. Types of Agglutination Rxn 1.Direct Agglutination (e.g. Blood Typing) 2. Antiglobulin Technique (CoombsTest)/Indirect Agglutination - anti-human IgG is added to bridge the gap between the cells - to demonstrate incomplete antibodies 3.Passive Agglutination - A soluble Ag is artificially attached to a particulate carrier (e.g. cells, latex, bentonite, celloidin, or charcoal 6. Hemagglutination - Agglutination of rbc due to antibody, viruses, bacteria, or other biologic substance. - It is not the antigen of RBC but the artificially attached Ag (after undergoing tx) that are made to react with the Ab - ex. TPHA Study Questions: 40 Compare between: Different Classes of Immunoglobulins Assignment Write notes on A- Primary Ag-Ab reactions شروق ابو الحسن – شروق كمال – غادة عز الدين – فاطمة على – مروة اشرف B- Secondary Ag-Ab reactions صالح ميلود – محمد زغلول – محمد فوزى – محمود محمد رمضان Thanks