* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Compounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
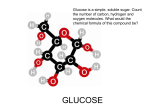
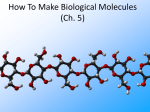
Organic Compounds Organic Compounds • Organic compounds must have carbon and hydrogen. Some examples of organic compounds includes carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. Inorganic Compounds • Inorganic compounds have either one or none of carbon and hydrogen. Water is inorganic as it only has hydrogen and carbon dioxide is also inorganic. H2O CO2 Examples • Identify if the compound is inorganic or organic. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Octane C8 H18 Starch (C6 H10 O5 ) Steel Fe Butane C4 H10 Baking Soda NaHCO3 Olive Oil C18 H34 O2 Carbohydrates H HO CH2OH O H OH H H Carbohydrates: Energy molecules Made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, & Oxygen. OH H OH Carbohydrates • Building block molecules = monosaccharides sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar Carbohydrates • Function: – quick energy (short term) – energy storage – structure • cell wall in plants glucose C6H12O6 sucrose • Examples – sugars – starches – cellulose (cell wall) starch Sugars = building blocks • Names for sugars usually end in -ose – glucose – fructose – sucrose – maltose H HO CH2OH O H OH H H H OH OH glucose C6H12O6 sucrose fructose maltose Building carbohydrates • Synthesis 1 sugar = monosaccharide | glucose | glucose mono = one saccharide = sugar di = two 2 sugars = disaccharide | maltose Building carbohydrates • Synthesis 1 sugar = monosaccharide | glucose | fructose How sweet it is! 2 sugars = disaccharide | sucrose (table sugar) BIG carbohydrates • Polysaccharides – large carbohydrates • starch – energy storage in plants » potatoes • glycogen poly = many – energy storage in animals » in liver & muscles • cellulose – structure in plants » cell walls Building BIG carbohydrates glucose + glucose + glucose… = starch (plant) energy storage glycogen (animal) polysaccharide Digesting starch vs. cellulose starch easy to digest cellulose hard to digest Cellulose • Cell walls in plants – herbivores can digest cellulose well – most carnivores cannot digest cellulose • that’s why they eat meat to get their energy & nutrients • cellulose = roughage – stays undigested – keeps material moving in your intestines Different Diets of Herbivores Cow can digest cellulose well; no need to eat other sugars Gorilla can’t digest cellulose well; must add another sugar source, like fruit to diet Helpful bacteria • How can cows digest cellulose so well? – BACTERIA live in their stomachs & help digest cellulose-rich (grass) meals Eeeew… Chewing cud?