* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download in the kidney - Faculty Sites
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
NURS 1950: Pharmacology
1
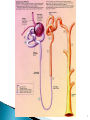
Objective 1: list two (2) major physiological
functions of the kidneys
Objective 2: list the four (4) processes
carried out by the nephron
Objective 3: name the part of the nephron
responsible for each of the processes
1
2
Objective 4: name the pituitary hormone that
influences the urine volume
Objective 5: name the adrenocortical
hormone that influences the urine volume
Objective 6: list the four (4) ways in which
fluid is normally lost from the body
1
3
Objective 7: describe the actions of diuretics
Diuretics act to
Deplete
blood volume
Excrete
sodium
Vasodilate
peripheral arterioles
(how is unknown)
1
4
Diuretics work in the kidney at
various sites of the nephron
Can interfere with the action of
aldosterone causing loss of sodium
◦ Where goes sodium, so goes water
5
6
7
What happens with diuretics
◦ Decrease excess water
◦ Loop diuretics + 0.9% NaCl = loss of
calcium
◦ Decrease excess NaCl
◦ Decrease cerebral edema (Mannitol)
◦ Decrease increased IOP (Diamox)
8
Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic (a
sugar);
◦ in the brain, its presence causes
water to be drawn to it
Works the same way in the eye:
◦ the excess intraocular fluid is drawn
to the mannitol in the hyperosmotic
plasma
9
◦ Diamox very weak diuretic
Useful in treating glaucoma
10
◦ Aminophylline
◦ Theophylline
◦ Caffeine
◦ Theobromine
Diuretic effect from improved blood
flow to kidney
Generally not used for diuretic
effect
11
Action of the thiazides
◦ Act on the distal tubules of the kidney
Block reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions
from the tubule
The unreabsorbed Na and Cl ions pass into the
collecting ducts, taking water with them
Thiazides have antihypertensive properties because
of direct vasodilation effect on peripheral arterioles
◦ Expected outcomes from treatment
Decreased edema and improvement of
symptoms RT excess fluid accumulation
Reduction in BP
12
Assessments
◦ Mental status
◦ Diabetics require baseline blood glucose
◦ Assess hearing
◦ Assess for symptoms of acute gout
SE to expect: orthostatic hypotension
◦ Usually in initial stages of treatment
◦ Teach client safety measures
13
SE to report
◦ GI irritation, N/V, constipation
◦ Electrolyte imbalance, dehydration
◦ Hyperuricemia
◦ Hyperglycemia
◦ Hives, rash
Thiazides can interact with
◦ Digoxin, corticosteroids
◦ Lithium, NSAIDs
◦ Oral hypoglycemic agents
14
Thiazides
can interact with
◦ Digoxin, corticosteroids
◦ Lithium, NSAIDs
◦ Oral hypoglycemic agents
15
Thiazide diuretics include
◦ Bendroflumethiazide (Naturetin)
◦ Chlorothiazide (Diuril)
◦ Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) {Esidrix,
HydroDiuril}
◦ Polythiazide (Renese)
◦ Trichlomethiazide (Naqua,
Metahydrin, Diurese)
16
Thiazide-like
drugs include
◦Chlorthalidone (Hygroton)
◦Indapamide (Lozol)
◦Metolazone (Zaroxolyn)
17
Drugs
that affect the loop of
Henle
◦ Bumetanide (Bumex)
◦ Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin)
◦ Furosemide (Lasix)
◦ Torsemide (Demadex)
18
Act in the loop of Henle in the kidney
◦ Inhibits Na and Cl reabsorption
Some increase blood flow to glomeruli
Inhibits electrolyte absorption in
proximal tubule
◦ Lose sodium, chloride, potassium,
magnesium, sodium bicarbonate
19
Onset
of diuretic effect varies,
but is within 1-2 hours. IV,
drugs work within 5-10
minutes
Peak effect within 1-2 hours
Duration approximately 6
hours
20
Maximum mg/day
◦ Bumex 10 mg per 24 hours
◦ Edecrin 400 mg per 24 hours
◦ Lasix 1000 mg/24 hours
Cross sensitivities
◦ Sulfonamides and Lasix, Demadex
SE to expect
◦ Oral irritation
◦ Dry mouth
◦ Orthostatic hypotension
21
SE to report with loop diuretics
◦
◦
◦
◦
GI irritation, abdominal pain
Electrolyte imbalance, dehydration
Hives, pruritus, rash
Some can cause loss of hearing and hyperglycemia
(interfere with hypoglycemic agents)
22
Drug interactions
◦ Alcohol, barbiturates, narcotics
◦ Aminoglycosides
◦ Cisplatin
◦ NSAIDs
◦ Corticosteroids
◦ Probenecid
◦ Digoxin
23
Loop diuretics include
◦ Bumetanide (Bumex)
◦ Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin)
◦ Furosemide (Lasix)
◦ Torsemide (Demadex)
24
Why
is there concern about the
electrolyte balance?
25
Weak antihypertensives
Mechanism of action unknown
Do work in distal renal tubule
◦ Retains potassium
◦ Excretes sodium
◦ Some have anti-aldosterone activity
26
Maximum dosing per 24 hrs
◦ drug dependent
SE to expect with Midamor:
◦ anorexia, N/V, flatulence and HA
SE to report:
◦ electrolyte imbalance, dehydration,
27
SE to expect and report with
Aldactone and Dyrenium:
◦ mental confusion, HA, diarrhea,
electrolyte imbalance, dehydration,
gynecomastia, reduced libido, breast
tenderness
Dyrenium can also cause allergic
reaction (hives, pruritus, rash)
28
Generally, drug interactions for the K+
sparing agents
◦ Lithium, ACE inhibitors, salt substitutes, K+
replacement
◦ NSAIDs,
Potassium-sparing drugs include
◦ Amiloride (Midamor)
◦ Spironolactone (Aldactone)
◦ Triamterene (Dyrenium)
29
Potassium-sparing
drugs include
◦ Amiloride (Midamor)
◦ Spironolactone (Aldactone)
◦ Triamterene (Dyrenium)
30
Why is an adequate fluid intake important
with diuretic therapy?
If the client has to get up during the night to
void, what will they probably do?
31
What are some good dietary sources of
potassium?
If a client is on Aldactone, what would you tell
them about high potassium foods?
32
Assessments to make
Teaching to include:
33
Drugs include
◦ Antibiotics
Fosfomycin (Monurol)
Quinolones : cinoxacin, nalidixic
acid, norfloxacin
Methenamine madelate
Nitrofurantoin
34
Fosfomycin (Monurol)
◦ Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis
◦ Reduces adherence of bacteria to epithelial cells
of urinary tract
◦ Single dose therapy
SE to expect:
◦ nausea, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, flatulence
SE to report:
◦ perineal burning, dysuria
Indicates UTI is not responding to treatment
Drug interactions
◦ Drugs such as metoclopramide that increase GI
motility
35
Norfloxacin (Noroxin) has wide range of activity
against gram negative and gram positive bacteria
Expensive
Reserve for resistant/recurrent infections
SE to report
◦ Hematuria as crystals can form in urinary tract
◦ HA, tinnitus, dizziness, tingling sensations,
photophobia
Various drug interactions can occur
◦ Assess client’s current drug therapy, monograph
of quinolone being used
36
◦ Converts to ammonia and formaldehyde in acidic urine
◦ Used in clients susceptible to chronic, recurrent UTIs
◦ Preexisting infections treated with antibiotics
Implementation
◦ DO NOT crush the tablets
◦ pH testing of urine: report over 5.5
SE to expect
◦ N/V, belching
SE to report
◦ Hives, pruritus, rash
◦ Bladder irritation, dysuria, frequency
Drug interactions
◦ Acetazolamide, sodium bicarbonate
◦ Sulfamethizole
37
◦ Interferes with several bacterial enzyme systems
◦ Effective only in the urinary tract
SE to expect:
◦ N/V, anorexia, urine discoloration
SE to report:
◦ Dyspnea, chills, fever, erythematous rash, pruritus
◦ Peripheral neuropathies
◦ Second infection
Drug interactions
◦ Magnesium containing products can decrease
absorption
38
Bethanecole chloride (Urecholine)
Neostigmine (Prostigmin)
Oxybutynin chloride (Ditropan)
Phenazopyridine (Pyridium)
Tolterodine (Detrol)
39
◦ Parasympathetic nerve stimulant
◦ Causes contraction of detrusor urinae muscle
Results in urination
May also stimulate gastric motility
Can increase gastric tone
Can restore impaired rhythmic peristalsis
SE to expect
◦ Flushing of skin, HA
SE to report
◦ N/V, sweating, colicky pain, abdominal cramps
◦ Diarrhea, belching, involuntary defecation
40
◦ Anticholinesterase agent
◦ Binds to cholinesterase
Prevents destruction of acetylcholine
Effects are: miosis; increased tone of
intestinal, skeletal, and bladder muscles
Bradycardia; stimulation of secretions of
salivary and sweat glands
Constriction of bronchi and ureters
Neostigmine used to prevent and treat
postoperative distension and urinary retention
◦ Assess for pregnancy, intestinal or urinary
obstruction, peritonitis
◦ Assess coronary status
41
Antispasmodic agent—acts directly on
smooth muscle of the bladder
◦ Delays initial urge to void
◦ Do not use if glaucoma, myasthenia
gravis, ulcerative colitis, obstructive
uropathy
SE to expect
◦ Dry mouth, urinary hesitance, retention
◦ Constipation, bloating
◦ Blurred vision
Report any SE that are intensified
42
Produces local anesthetic effect in urinary
tract
Acts about 30 min. after administration
Used to relieve burning, pain, urgency,
frequency in UTI
Reduces bladder spasms
SE to expect
◦ Reddish-orange urine color
SE to report
◦ Yellow sclera or skin
43
Muscarinic receptor antagonists
Inhibit muscarinic action of acetylcholine on
bladder smooth muscle
Used to treat overactive bladder
Do not use if glaucoma, ulcerative colitis,
obstructive uropathy
S/E to expect
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
Dry mouth
Urinary hesitance, retention
Constipation, bloating
Blurred vision
Report if the effects intensified
44
Objective 18: Discuss patient
education guidelines for drugs that
affect the urinary system
45
Objective 19: identify at least one nursing
diagnosis that may be applicable for clients
receiving diuretic therapy under the guidance
of the instructor
46