* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download START Human Population and Life Expectancy THE FUTURE
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
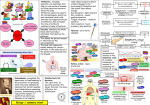
SYSTEMS CANCER BIOLOGY 2007 STRUCTURE SYSTEMS How-to 1 REC. DNA Population Growth 5 1975 CELL TYPE 1960 1930 CELL BIOL HUMAN DISEASE 1830 LIFE EXPECTANCY 4 3 Billion How-to 2 NERVOUS X 6 3D PROBLEMS SYSTEMS IMMUNE BIOLOGY FUTURE LIFE FORMATION SYSTEMS VIRUSES BIOLOGY Human Population and Life Expectancy STEM CELLS, CLONING 86 2 1 50 2000 1950 BIOCHEM GENETICS START MOL. BIO GENOMICS FOUNDATIONS Slide 2 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 THE FUTURE? Early Humans and Disease Hunter-gatherers: ? 132 LIFE EXPECTANCY • Life was short, death rates were high. • Main causes of death were accidents, food shortage, predation, infectious disease. 86 • Non-communicable diseases (cancer, obesity, diabetes,hypertension) were rare to non-existent. 50 1950 2000 YEAR Slide 3 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 2050 • Early nomads lived in small bands, infrequently contacting others. Numbers were not large enough -- and bands were not dense enough -- to maintain (spread) acutely infectious diseases, e.g. measles, smallpox, polio, enteric and respiratory infections. Slide 4 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 Early Humans and Disease Modern Humans and Disease Domestication of plants and animals (~6000 years ago): Highly Developed Countries • Creation of first !urban" areas with large populations in continuous close contact. Increase in food supply and expansion of populations. • Life expectancy has increased from ~50 yrs in 1950 to 86 yrs in 2000. For the first time in history a mother knows that the loss of one of her children before maturity is an unlikely event. • Main causes of death were accidents, food shortage, predation, infectious disease, with increases in communicable diseases. TB, Measles, Smallpox, Leprosy, Polio • Main causes of death are non-communicable diseases (cancer, obesity, diabetes, hypertension). • Diet was different from that of hunter-gatherer, but still based mainly on unrefined plant foods. • Acute infections decline because of improved public health information, vaccines, medical treatments, and increased resistance to infection due to nourishment. • Food plentiful, sedentary lifestyle. • Non-communicable diseases (cancer, obesity, diabetes, hypertension) were rare to non-existent. Slide 5 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 Slide 6 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 Causes of Death in US Slide 7 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 Cardiovascular Disease: Genetic and Environmental Contributions Slide 8 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 Source: Dr. Thomas C. Isaacson Common Diseases Can Have Multiple Genetic and Environmental Contributions Positional Cloning: Finding Associated Markers Colon Cancer Find Markers associated with disease - SNPs can be used: 1M SNPs already mapped - Microarray-based method Slide 9 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 Figure 11.10 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Positional Cloning: Finding the Affected Gene 1) Use Markers (M1 and M2) to identify chromosomal interval 2) Identify genes in known genome sequence 3) Sequence to identify mutation that may be responsible for phenotype Slide 11 - 7.013 - 4/25/07 Slide 10 - 7.013 - 4/25/07