* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
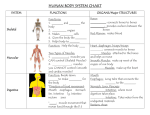
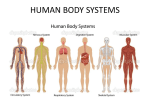
Cells basic building block that makes up all living things the smallest part of a living thing that can carry out all the process of life can carry out all the processes of life: o breathe o take in food and turn it into energy o grow and develop o get rid of waste o respond to their environment o reproduce o move unicellular organism an organism made up of only one cell simplest forms of life carry out the basic process of life – can move, find food, and grow can reproduce remove waste by moving them to the outside of their cells bacteria unicellular found everywhere 3 basic shapes – rod, round, spiral billions in your body some bacteria are helpful while others are harmful amoeba unicellular eats by surrounding a food particle and then bringing the food into the cell moves by changing its shape paramecium unicellular has many hair-like structures called cilia that help it move and take in food found mainly in lakes, ponds and puddles euglena unicellular has a whip-like part that moves it forward uses sunlight to take in food multicellular organism an organism made up of 2 or more cells each cell does a different job each cell has a shape and structure that helps it do its job example – nerve cells are long and thin; their shape helps to send signals to other cells groups of cells of the same type work together to perform certain functions take in food and water, reproduce, grow, move, get rid of waste, die Most have cells that are not able to exchange gases with the outside environment tissue similar cells that work together to perform a task organ a group of tissues that work together to do a certain job organ system a group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions cells tissue organ organ system organism Circulatory System Includes the heart and blood vessels Body’s transportation system Moves oxygen and nutrients to each cell Takes away cell’s waste Three types of blood vessels - arteries, veins and capillaries o Arteries carry blood away from the heart o Veins carry blood from cells to heart o Capillaries connect arteries and veins; smallest blood vessel with thin walls so gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) can pass through Heart has 4 chambers – right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle and left ventricle Oxygen-rich blood enters the heart from the lungs and goes out into the body Oxygen-poor blood enters the heart from the body and goes out to the lungs Respiratory System respiratory system takes in oxygen from the air that you breathe. you breathe air in through your nose or mouth air travels down throat and passes through your trachea (or windpipe). Trachea leads to two branches called bronchi that go into the lungs. bronchi (bronchus) let air in and out of your lungs so you can breathe bronchi branch into smaller tubes called bronchioles bronchioles end in clusters of tiny thin-walled alveoli, or air sacs, in the lungs - oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves the blood. when you breathe out, carbon dioxide leaves your body Your diaphragm is dome-shaped muscle below the lungs. It tightens and relaxes to make you breathe in and breathe out Digestive System Digestion is the process by which food and drink are broken down into their smallest parts so the body can use them to build and nourish cells and to provide energy Direction food goes: mouth – esophagus – stomach – small intestine – large intestine MOUTH - Digestion begins in your mouth when you chew. Saliva begins the breakdown of food. ESOPHAGUS - Muscles contract in waves to move the food down the esophagus. STOMACH - food is mixed with chemicals that help break it down. (An adult’s stomach can hold about 1.5 liters of material) SMALL INTESTINE - Next, food goes to the small intestine where more chemicals continue to break down food. Nutrients are then absorbed by the body. o three organs help the small intestine gather the nutrients: pancreas, liver, gall bladder LARGE INTESTINE - Water is removed from food and taken into the body. Any remaining food that has not been digested becomes waste. Food the body can’t use is stored in the large intestine. Nervous System made up of the brain, spinal cord and nerves controls all other body systems two main parts of the nervous system o Central Nervous System brain and spinal cord brain has three parts cerebrum cerebellum brain stem and medulla o Peripheral Nervous System delivers messages from the central nervous system to the rest of the body neurons transmit messages throughout the body Two types of nerves o central nerves – carry information to the central nervous system o motor nerves – carry information from the central nervous system to other parts of the body Muscular System voluntary muscles – muscles that can be controlled with the mind involuntary muscles – These don’t need the brain to send them messages. You can’t control them. Three types of muscles: Smooth Muscles – involuntary muscle that are in sheets or layers with one layer of muscle behind the other. o Examples - Your stomach muscles work to digest your food. The muscles in your eyes keep the eyes focused. The muscles at the bottom of the hairs on your arms will make your hairs stand up when you are cold. Cardiac Muscle – heart – works to pump blood throughout your body. Your heart is an involuntary muscle. Skeletal Muscles – voluntary muscles that help you kick a ball, lift a pencil, etc. Skeletal System Skeletal system is made up of bones, ligaments and tendons Adult has 206 bones. Babies are born with about 300 bones. Their bones fuse (grow together) as you get older. Jobs of the skeletal system o supports the body o helps you move o stores calcium and other minerals until the body needs them o protects internal organs skull protects brain ribs protect heart and lungs o produces blood cells – made by bone marrow which is found at the center of the bone Joints hold your bones together and allow them to move o ball and socket – allow for lots of movement in every direction (example – shoulder and hips) o hinge – allows forward or backward motion (example – elbows, knees) o gliding – one bone slides over enough (example is wrist or ankle) Tendon –tissue that connects muscles to bones so the bones can move. The tendons and muscles work together to control joint movement Ligament – connects bone to bone and helps to stabilize the joints they surround.