* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spinal and Cranial Nerves
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
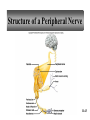
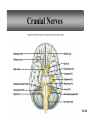
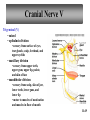
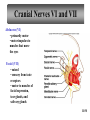
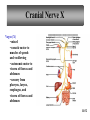
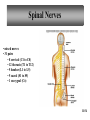
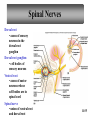
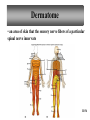
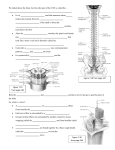
Peripheral Nervous System • Cranial nerves arising from the brain • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera • Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera 11-42 Structure of a Peripheral Nerve 11-43 Nerve Fiber Classification • Sensory Nerves – conduct impulses into CNS • Motor Nerves – conduct impulses to muscles or glands • Mixed Nerves – contain both sensory nerve fibers and motor nerve fibers; most nerves General somatic efferent fibers • carry motor impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles General somatic afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to CNS from skin and skeletal muscles General visceral efferent fibers • carry motor impulses away from CNS to smooth muscles and glands General visceral afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to CNS from blood vessels and internal organs 11-44 Nerve Fiber Classification Special somatic efferent fibers • carry motor impulses from brain to muscles used in chewing, swallowing, speaking, and forming facial expressions Special visceral afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to brain from olfactory and taste receptors Special somatic afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to brain from receptors of sight, hearing, and equilibrium 11-45 Cranial Nerves 11-46 Cranial Nerves I and II Olfactory (I) • sensory • fibers transmit impulses associated with smell Optic (II) • sensory • fibers transmit impulses associated with vision 11-47 Cranial Nerves III and IV Oculomotor (III) • primarily motor • motor impulses to muscles that • raise eyelids • move the eyes • focus lens •adjust light entering eye Trochlear (IV) • primarily motor • motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes 11-48 Cranial Nerve V Trigeminal (V) • mixed • opthalmic division • sensory from surface of eyes, tear glands, scalp, forehead, and upper eyelids • maxillary division • sensory from upper teeth, upper gum, upper lip, palate, and skin of face • mandibular division • sensory from scalp, skin of jaw, lower teeth, lower gum, and lower lip • motor to muscles of mastication and muscles in floor of mouth 11-49 Cranial Nerves VI and VII Abducens (VI) • primarily motor • motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes Facial (VII) • mixed • sensory from taste receptors • motor to muscles of facial expression, tear glands, and salivary glands 11-50 Cranial Nerves VIII and IX Vestibulocochlear (VIII) • sensory • sensory from equilibrium receptors of ear • sensory from hearing receptors Glossopharyngeal (IX) • mixed • sensory from pharynx, tonsils, tongue, and carotid arteries • motor to salivary glands and muscles of pharynx 11-51 Cranial Nerve X Vagus (X) • mixed • somatic motor to muscles of speech and swallowing • autonomic motor to viscera of thorax and abdomen • sensory from pharynx, larynx, esophagus, and viscera of thorax and abdomen 11-52 Cranial Nerves XI and XII Accessory (XI) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, neck, and back Hypoglossal (XII) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of the tongue 11-53 Spinal Nerves • mixed nerves • 31 pairs • 8 cervical (C1 to C8) • 12 thoracic (T1 to T12) • 5 lumbar (L1 to L5) • 5 sacral (S1 to S5) • 1 coccygeal (Co) 11-54 Spinal Nerves Dorsal root • axons of sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglion Dorsal root ganglion • cell bodies of sensory neurons Ventral root • axons of motor neurons whose cell bodies are in spinal cord Spinal nerve • union of ventral root and dorsal root 11-55 Dermatome • an area of skin that the sensory nerve fibers of a particular spinal nerve innervate 11-56