* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
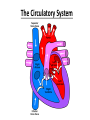
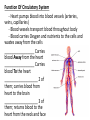
The Circulatory System • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AIcAF34 MPpU Function Of Circulatory System - Heart pumps blood into blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) - Blood vessels transport blood throughout body - Blood carries Oxygen and nutrients to the cells and wastes away from the cells _________________ Carries blood Away from the heart _________________ Carries blood To the heart ___________________ 2 of them; carries blood from heart to the brain ___________________ 3 of them; returns blood to the heart from the neck and face Heart: has a “septum” that divides it into 2 halves with 2 chambers each. ____________ Upper chambers through which blood enters the heart ____________ Lower chambers through which blood leaves the heart The Right Atrium is larger than the Left Atrium. Why? Blood comes to the Right Atrium from EVERYWHERE. It comes to the Left Atrium ONLY from lungs. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Circulation Of Blood Blood with CO2 is brought into the Rt Atrium by the Superior and Inferior Vena Cava (largest vessels in the body) To the Rt Ventricle and pumped into the Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Artery takes it to the lungs to exchange CO2 for O2 Blood with O2 returns to the heart through Pulmonary Vein Pulmonary Vein gives blood to Left Atrium Transferred to Left Ventricle and pumped to body through Aorta (Aortic Arch=“Big Arch”) Blood: Delivers hormones, O2, and nutrients to cells and takes wastes away; 55% of blood is___________ the fluid portion of blood, or lymph, in which RBCs, WBCs, and platelets are suspended (92% water) _________________ - Carry oxygen in blood _________________ - Protein rich in iron; binds with O2 in lungs, releases it to the body tissues; gives blood red color _________________- Prevent/fight infection; larger than RBCs but far fewer in number; during infection the number increases (RBCs decrease) _________________ - Smallest type of blood cell; causes clotting (scabs) Care/Problems: Most problems of the heart are under our control (smoking; weight management) 1.________________- pressure on the inner walls of the arteries; exerted by the blood 2.________________ - high blood pressure; smoking, obesity, poor diet 3.________________ - anything that occurs at birth; innate (ex. - congenital heart defect) 4._________________ - low levels of hemoglobin; cells don’t get enough O2 (Low # of RBCs); pale skin, weakness, breathlessness 5._________________ - cancer of the bone marrow; abnormal number of WBCs 6._________________ - genetic disorder, more common in males, in which the blood does not clot, lack of platelets