* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1-JAN 18 PG
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
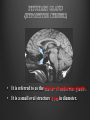
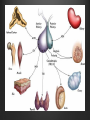
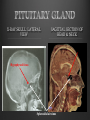
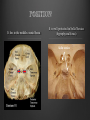
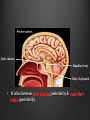
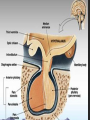
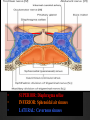
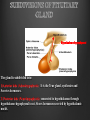
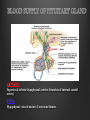
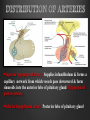
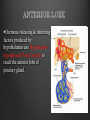
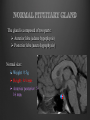
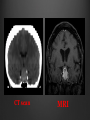
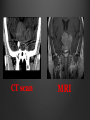
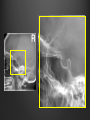
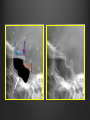
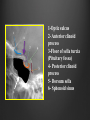
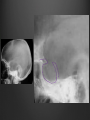
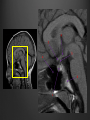
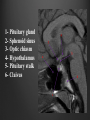
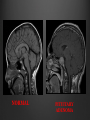
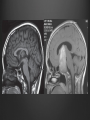
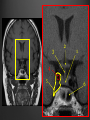
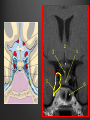
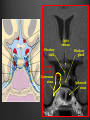
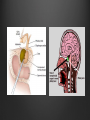
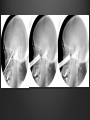
Dr. Sarah Al-Sultan • Describe the position of the pituitary gland. • List the structures related to the pituitary gland. • Differentiate between the lobes of the gland. • It is referred to as the master of endocrine glands. • It is a small oval structure 1 cm in diameter. X-RAY SKULL: LATERAL VIEW SAGITTAL SECTION OF HEAD & NECK Pituitary gland Hypophyseal fossa Sphenoidal air sinus It lies in the middle cranial fossa It is well protected in Sella Turcica (hypophyseal fossa) Sella turcica Optic chiasma Mamillary body Body of sphenoid • It is lies between optic chiasma (anteriorly) & mamillary bodies (posteriorly). A fold of dura mater (Diaphragma sellae) covers the pituitary gland & has an opening for passage of infundibulum (pituitary stalk) connecting the gland to hypothalamus. IMPORTANT RELATIONS • • • SUPERIOR: Diaphragma sellae INFERIOR: Sphenoidal air sinuses LATERAL: Cavernous sinuses Hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract The gland is subdivided into: 1)Anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis): It is the True gland, synthesize and Secretes hormones. 2) Posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis): connected to hypothalamus through hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract, Stores hormones secreted by hypothalamic nuclei. ARTERIES: Superior & inferior hypophyseal arteries (branches of internal carotid artery) VEINS: Hypophyseal veins drain into Cavernous Sinuses. a hypothalamohypophseal portal vessel Superior hypophyseal artery: Supplies infundibulum & forms a capillary network from which vessels pass downward & form sinusoids into the anterior lobe of pituitary gland (Hypophyseal portal system). Inferior hypophyseal artery: Posterior lobe of pituitary gland. Hormone-releasing & inhibiting factors produced by hypothalamus use Hypothalmohypophyseal Portal vessels to reach the anterior lobe of pituitary gland. It is consists mainly of neuronal projections extending from the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei. The gland is composed of two parts: Anterior lobe (adeno hypophysis) Posterior lobe (neuro hypophysis) Normal size: Weight: 0.5g. Height: 4-8 mm Anterior posterior: 516 mm. Hormonal dysfunction Cushing syndrome Growth abnormalities e.g. Growth hormone deficiency, acromegaly Visual abnormality. Headache. Question What is the best modality to image the pituitary gland ? A. X ray B. CT scan C. MRI D. US E. Nuclear medicine Question What is the best modality to image the pituitary gland ? A. X ray B. CT scan C. MRI D. US E. Nuclear medicine CT scan MRI CT scan MRI 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 1-Optic sulcus 2- Anterior clinoid process 3-Floor of sella turcia (Pituitary fossa) 4- Posterior clinoid process 5- Dorsum sella 6- Sphenoid sinus 4 3 5 2 6 1 1- Pituitary gland 2- Sphenoid sinus 3- Optic chiasm 4- Hypothalamus 5- Pituitary stalk 6- Claivus 4 3 5 2 6 1 NORMAL PITUITARY ADENOMA 3 2 1 4 5 6 3 2 1 4 5 6 Pituitary stalk Carotid artery Cavernous sinus Optic chiasm Pituitary gland Sphenoid sinus