* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power point presentation
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Biblical and Quranic narratives wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Naskh (tafsir) wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
History of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
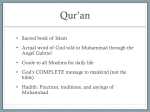
Prophet Muhammad Islam Brief History and Teachings Arabia in 600 AD Populated by various Arabic-speaking people – Bedouin - organized in tribes – Caravan meerchants and agriculturalists, living either in oases in the north, or in the more fertile and thickly settled areas to the south – Intense tribal loyalties & warfare Arab culture revered oral story telling Majority of Arabs followed polytheistic religions & worshipped idols – Few tribes followed Judaism, Christianity or Zoroastrianism City of Mecca was a religious & trade center – Rich mixtures of culture – Ka'aba - temple founded by Abraham – Yearly pilgrimage to site – Much social injustice & economic disparity Muhammad (570 – 632) Born at Mecca into the Quraysh tribe Orphaned at an early age & raised by uncle Illiterate but very articulate & well liked Became a successful merchant – traveled north Married older wealthy widow at 25 - Khadijah Saw a crisis in Arab society 610 AD….the divine call – Visited while meditating in cave by the Archangel Gabriel who commanded him to recite verses sent by God – Revelations continued for the next 22 years – Revelations collected in the Quran – Revelations directly related to the needs of the Arab people – First memorized the verses & passed them to his wife & close relatives – Small band of followers would memorize the recitations First converts – wife, cousin Ali, kinsman Abu Bakr Starts preaching in 612 New recruits mainly from slaves and lower classes Night journey to Jerusalem Muhammad 612-622 AD - in Mecca preaching and gaining followers – Seen as a trouble maker for attacking the establishment – Attempts to assasinate him AD 622… the Hejira to Medina – Request to resolve dispute between rival tribes – With followers moved to neighboring city of Medina – Year 622 as the start of the Muslim calendar 622-630 AD---in Medina – Becomes leader of city Develops concept of Ummah - community – Mecca and Medina in conflict – Unites the surrounding tribes 630 – Mecca captured without fight – Cleansed the Kaaba of idols 632 – first Hajj or pilgrimage By his death in 632, Muhammad had united the entire Arabian peninsula MECCAN PERIOD To establish Oneness of God Warner Giver of Glad Tidings Day of God MEDINAN PERIOD Social Order Law & Justice Equity Ummah Religion of Muhammad Islam is the religion of submission or surrender to Allah – Simple and uncompromising faith in oneness of God Muhammad did not believe he was preaching a new religion – Did not reject Judaism and Christianity – Sent by God in order to complete and perfect those teachings – Accepted Abraham, Moses and Jesus as prophets – Muhammad is the messenger of God – Last in a long line of prophets Chosen by God to preach repentance and submission to God Judgment Day – Allah rewards the faithful with a paradise filled with eternal pleasure – Warns of the inevitable apocalypse & end of the world – Humanity will be forced to atone for sins – Images of heaven (oasis) & hell (desert) Belief in Predestination – Whatever happens, good and evil, proceeds from divine will Quran - Koran Means “Recitation” – Recitation – Communicating directly with God Provides a guide for living as a Muslim Revelations from God delivered through the angel Gabriel to Mohammed over 22 years Revelations came from a heavenly book containing God’s wisdom – Mother of the Book Final uncorrupted revelation of God Contains 114 suras – verses – Arranged by the length of sura Contents: Theological dogma, ceremonial regulations, laws related to social, civil and criminal behavior Themes – Oneness of Allah, his attributes, the ethical duties of man, and coming retribution Quran must remain in Arabic – Translations not authentic Writing of the Quran None of Quran was written during Muhammad’s life – Still an oral scripture Words of the Prophet at first memorized & written on parchment or clay by followers Zayd ibn Thabit – one of Muhammed’s secretaries Began gathering the verses of the Quran soon after his death Interviewed closest associates Sorted into a type of order Uthman (644-656) Third Caliph – created an official and final version Committee charged with compiling Quran in 651 Wanted to avoid controversy Collect and authenticate verses Strict criteria for authenticity 2 eyewitnesses had to testify that each verses had been recorded in the presence of Muhammad Then verified with companions of Muhammad Approved verses amassed into single text Uthman then ordered all other texts destroyed Quran not altered since Legacy of Muhammad Concept of Ummah – Community of Allah – First attempt to create a social organization out of faith instead of tribal relationships Vision of social justice for all – Weak & vulnerable should be protected & treated with respect Prophet, lawgiver, religious leader, chief judge, commander of the army and civil head of state Inspiration as role model for living divinely inspired life – By studying details of his external life Muslims stove to acquire his interior attitude of perfect surrender to God Islam Islam is open to all who accept its tenets Prohibition against idolatry or graven images Islam has no organized hierarchy – No religious authority, clerical elite or priesthood to act as intermediary – Mullahs (teachers) occupy positions of authority because of their knowledge of the Quran Sunna or Hadith - written collection of Arab oral traditions concerning life of Muhammad – Address issues not specifically covered in the Quran Sharia – Islamic Law – Three sources – Quran, Sunna and Ijtihad – analytic reasoning to cover locally raised issues Quran prohibits alcohol and gambling Jihad – Call for Holy War against infidels???? Quran insists that there be no coercion in matters of faith The Five Pillars of Faith 1. Profession of Faith - Shahadah “There is no God but Allah (God), and Muhammad is His Prophet.” – First and last words heard – Most repeated words by Muslims – Person a Muslim once profession is repeated 2. Prayer – Salat – Direction toward Mecca – 5 times a day – Call of Muezzin – Dawn, midday, mid-afternoon, sunset & nightfall – Create sense of solidarity and social equality – Body posture essential – Must use Arabic – Friday noon prayer is only mandatory public prayer for all adult males 3. Charity – Zakat – purification Compassion for the poor 2.5 % of wealth expected The Five Pillars of Faith 4. Fasting - Sawm Ramadan – based on lunar calendar – different each year Daylight hours during month of Ramadan 5. Pilgrimage to Kaaba in Mecca – Hajj All those who can afford and physically fit Ideal of equality & unity among believers Unites cultures and ideas Women in Islam Under Arabian pre-Islamic law of status, women had virtually no rights – No limitations were set on men's rights to marry or to obtain a divorce. Islamic law provided women with new legal rights – Reforms affected marriage, divorce, and inheritance – Islamic law restricted the polygamy – Women could obtain a divorce – Women could inherit and keep their own property Marriage was no longer viewed as a "status" but rather as a "contract" Law doesn't require women to wear veils Islam After Muhammad Shiites – Only descendants of Fatima or her husband Ali should succeed Mohammed – Death of Imam Hussein (son of Ali) most celebrated event in Shiite calendar Sunnis – any follower of Islam should be eligible to lead – Division political & religious – Never settled to this day Series of Caliphs governed the Islamic State Struggle for Succession Number of conflicting parties sought to succeed Muhammad Companions – belonged to Muhammad’s tribe or had accepted mission early Legitimists – heir must belong to family of Muhammad – Aristocracy of Quraysh – Umayyads – Ali paternal cousin, husband of daughter Fatima & one of first believers Held reigns of power & wealth in pre-Islamic days Companions triumphed with selection of abu-Bakr Rashidun - Four “righteous” caliphs (632-661 AD) – All were close associates and relatives of Muhammad Abu Bakr (632-634) Father-in-law of Muhammad and one of first believers Umar (634-644) main military genius who carried Islam forward from the Arabian peninsula Uthman (644-656) - empire fell into a civil war called the Fitna – In 656 Uthman is assassinated by followers of Ali Ali (656-661) Muhammad's son-in-law and cousin – Many refused to accept Ali as a leader – Killed by assassin Umayyad dynasty claims the caliphate – Damascus capital Abbasid dynasty – 754 – seizes caliphate – al Mansur (754-775) builds new capital at Baghdad Conquest & Expansion Expansion of Islamic empire against Byzantine & Sassanid (Persian) empires Abu-Bakr –Orders jihad (holy struggle) against the "infidel" Christian or Byzantine Empire north of Arabia Damascus becomes capital Umar 637 – Defeated great Persian Sassanid army 639 – Conquers Alexandria – base of Byzantine navy 643 – Arabs to border of India Tariq ibn Zaid crossed from North Africa (Morocco) into Spain in 711 Expansion stopped in France in 732 – Charles Martel Military victories Justice not fanaticism No longer making war with other Arabs Use of cavalry and camels Remarkable mobility High morale from religious enthusiasm Conquered peoples more open to Islam Reduced heavy burden of taxation No persecution of Faiths The Spread of Islam Islamic Unity Arabic became language of business, government & literature Uniform enforcement of law contributed to growth of united culture Vast trade network extended from India to the Mediterranean Rich Cultural Achievements Many Islamic centers of culture and science – Baghdad – Cairo – Damascus – Cordoba – Alexandria Scholarship – Produced notable scientists, astronomers, mathematicians, doctors and philosophers – Importance of reading the Qur'an produced a comparatively high level of literacy in the general populace Heirs to Hellenistic Learning – Maintained Classical learning – Translation of Greek texts - Aristotle Medicine Architecture – Mosques, Palaces & Minarets Art – Geometric patterns, calligraphy, metal work Science & Medicine Muslim scientists Saw no contradiction between religion and laws governing natural world Scientific method born Utilized Classical Greek medical texts Alchemy – beginnings of chemistry Muslim medicine Advanced techniques & ideas Theory that disease born through air born organisms Study of anatomy Vascular & cancer surgery Study of light, lenses & physiology of eye – led to camera Use of anesthetics Pharmacies Hospitals – separate disease in different wards Pioneers of Medicine Razi (865 – 925) – Rhazes in the West Authored more than 100 books on medicine First to diagnose and treat smallpox Ibn Sina (980 – 1037) – Known as Avicenna Contributions in philosophy, music, mathematics, geography & literature Utilized experimentation & observation wrote Canon of Medicine – encyclopedia of medicine Study of infectious disease Main medical text for 6 centuries Printed extensively throughout the West Mathematics Introduced “Arabic” numerals – originally from India Replaced Roman numerals Included the zero – made for complex calculations Perfected use of decimals and fractions Invented Algebra Trade Seaborne Trade developed from Persian Gulf Began to sail to China to trade Traveled to Russia and Central Asia by land Able to travel from Europe to Asia - Silk, furs, gold and precious stones, spices, and slaves - Orange tree, sugar, and paper An Ever Advancing Civilization Abraham: Infancy/Family Moses: Jesus: Toddlerhood/Tribe Childhood/Love Muhammad: Adolescence/Nation Where are Muslims Today?